ANAT2241 Cardiovascular System: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{ANAT2241 header}} ==Introduction== thumb|300px|Adult human cardiovascular system Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of ...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
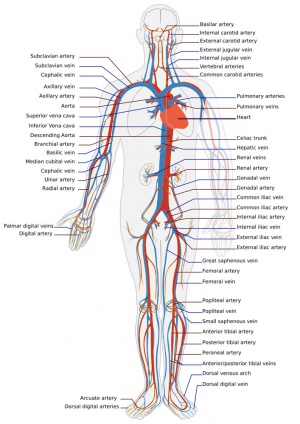
[[File:Adult human cardiovascular system.jpg|thumb|300px|Adult human cardiovascular system]] | [[File:Adult human cardiovascular system.jpg|thumb|300px|Adult human cardiovascular system]] | ||
--[[User:Z8600021|Mark Hill]] 17:32, 6 February 2013 (EST) Pat do you cover heart here or in muscle class? | |||
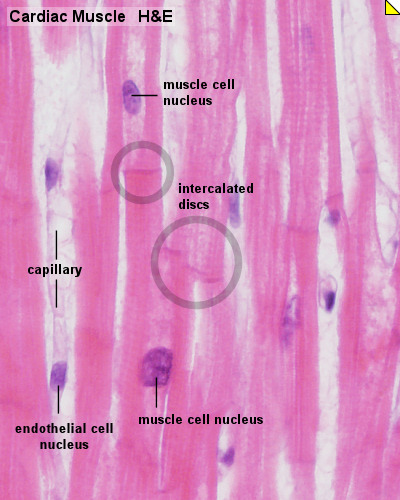
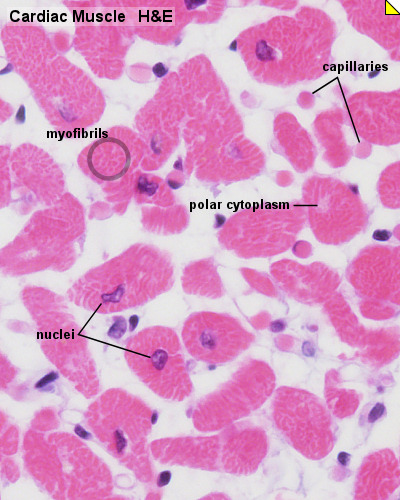
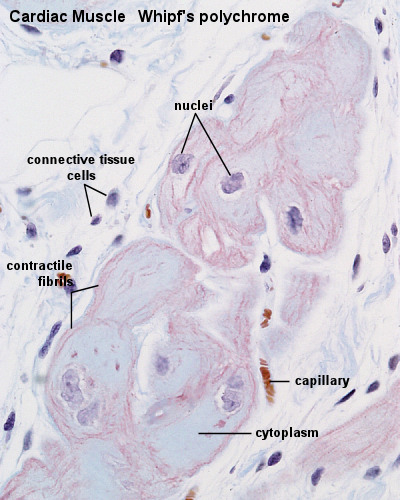
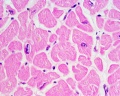
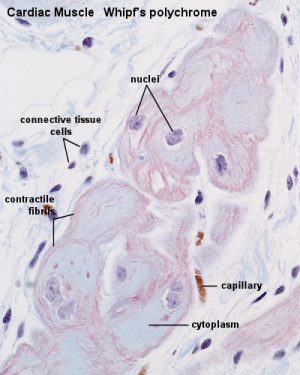
Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus. | Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus. | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 6 February 2013
| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241 |
Introduction
--Mark Hill 17:32, 6 February 2013 (EST) Pat do you cover heart here or in muscle class?
Cardiac muscle, the myocardium, consists of cross-striated muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, with one centrally placed nucleus.
- Nuclei are oval, rather pale and located centrally in the muscle cell which is 10 - 15 µm wide.
- Cardiac muscle cells excitation is mediated by rythmically active modified cardiac muscle cells.
- Cardiac muscle is innervated by the autonomic nervous system (involuntary), which adjusts the force generated by the muscle cells and the frequency of the heart beat.
- Cardiac muscle cells often branch at acute angles and are connected to each other by specialisations of the cell membrane in the region of the intercalated discs.
- Intercalated discs invariably occur at the ends of cardiac muscle cells in a region corresponding to the Z-line of the myofibrils.
- Cardiac muscle does not contain cells equivalent to the satellite cells of skeletal muscle.
Histology
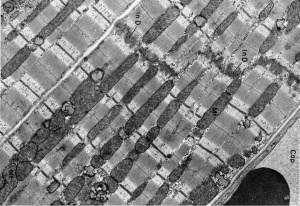
Unlabeled Images
Cardiac Layers
Endocardium
- Inner layer of the heart, contains blood vessels. Has 3 sublayers
- Endothelium - innermost portion a simple squamous epithelium.
- Smooth Muscle and Connective Tissue - middle layer of the endocardium is mix of connective tissue and smooth muscle.
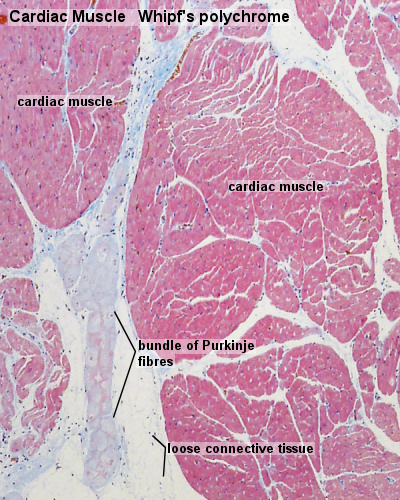
- Subendocardial Layer - outer layer of the endocardium is loose connective tissue joining the endocardium and myocardium.
Myocardium
- Middle layer of the heart, thickest contains cardiomyocytes, blood vessels.
- Muscular layer.
Epicardium
- Outer layer of the heart, contains blood vessels and lymphatics.
- Visceral layer of pericardium rather thin.
Cardiac Features
Intercalated Discs
- seen in longitudinal sections.
- connect the individual muscle cells.
- permit the conduction of electrical impulses between the cells.
Histology "step-like" appearance due to:
- transverse part - crossing fibres at right angle to myofibrils.
- lateral part - runs in parallel to myofibrils.
Junctional Components
- Fascia adherens – major portion of transverse component. Anchoring sites for actin, and connect to the closest sarcomere.
- Macula adherens – (desmosomes) transverse and lateral components. Bind individual myocytes to one another. stop separation during contraction by binding intermediate filaments, joining the cells together. Macula adherens junctions are also called desmosomes.
- Gap junctions - lateral component. Allow action potentials to spread between cardiac cells by passage of ions between cells, producing depolarization of the heart muscle. Allows muscle to act as syncytium.
- Links: EM image - intercalated disc
Purkinje Fibres
- modified cardiac muscle cells. Compared to ordinary cardiac muscle cells:
- contain large amounts of glycogen.
- fewer myofibrils.
- thicker cells.
- extend from the atrioventricular node, pierces the fibrous body, divides into left and right bundles, and travels, beneath the endocardium, towards the apex of the heart.
- bundle branches contact cardiac muscle cells through specialisations similar to intercalated discs.
- conduct stimuli faster than ordinary cardiac muscle cells (2-3 m/s vs. 0.6 m/s).
- discovered in 1839 by Jan Evangelista Purkyně).
- Links: Heart Histology | Cardiac AZB Labeled | Cardiac AZB | Cardiac label LS | Cardiac LS | Cardiac label TS | Cardiac TS | Purkinje fibres | Purkinje fibres detail | Histology
Terms
- cardiomyocyte -
- chordae tendineae - tricuspid and mitral valves connective tissue bands attached on the other end to the papillary muscles.
- intercalated disc -
- nodule - (of semilunar valve) small fibrous nodules located in the middle of the flaps, the nodules of the semilunar valve come closely together to fill the triangular opening.
- Purkinje fibres -
Course Links
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 8) Embryology ANAT2241 Cardiovascular System. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Cardiovascular_System
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G