BGDA Practical 12 - Third Trimester: Difference between revisions
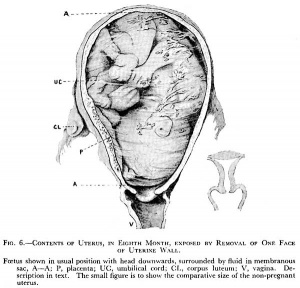
(Created page with "{{Template:BGDALab12}} ==Introduction== thumb|300px|Historic drawing of the fetus in the uterus at 8 months compared to non-pregnant uterus size. *...") |
|||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
=== Third Trimester === | === Third Trimester === | ||
(Clinical Week 28) | (Clinical Week 28) [[Third Trimester]] | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
| | | | ||
| Clinical third trimester | | Clinical third trimester | ||
| [[File:Fetal_size_change.jpg|90px|link=Fetal Development]] [ | | [[File:Fetal_size_change.jpg|90px|link=Fetal Development]] [[Sensory_-_Hearing_and_Balance_Development|Hearing]] 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus. | ||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
| <center>28</center> | | <center>28</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [ | | [[Respiratory_System_Development|Respire]] Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs | ||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
| | | | ||
[ | [[Genital_System_Development|Genital]] male gonad (testes) descending | ||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
| <center>32</center> | | <center>32</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | [[Integumentary_System_-_Nail_Development|Nail Development]] fingernails reach digit tip | ||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| <center>33</center> | | <center>33</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [ | | [[Neural System Development|Neural]] brain cortical sulcation - primary sulci present<ref name="PMID11158907"><pubmed>11158907</pubmed></ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>34</center> | | <center>34</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [ | | [[Neural System Development|Neural]] brain cortical sulcation - insular, cingular, and occipital secondary sulci present<ref name="PMID11158907" /> | ||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
| <center>36</center> | | <center>36</center> | ||
| | | | ||
| [[File:Frazer006_bw600.jpg|90px|link=Fetal Development]] | | [[File:Frazer006_bw600.jpg|90px|link=Fetal Development]] [[Integumentary_System_-_Nail_Development|Nail Development]] toenails reach digit tip | ||
[[Vision_-_Lens_Development|Lens Development]] - lens growth and interocular distance plateaus after 36 weeks of gestation<ref name ="PMID19541779"><pubmed>19541779</pubmed></ref> | |||
|-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | |-bgcolor="#AFEEEE" | ||
| Line 161: | Line 163: | ||
| [[File:Newborn.jpg|90px|link=Birth]] Clinical Week 40 | | [[File:Newborn.jpg|90px|link=Birth]] Clinical Week 40 | ||
[ | [[Cardiovascular System Development|Heart]] pressure difference closes foramen ovale leaving a fossa ovalis | ||
[ | [[Endocrine_-_Thyroid_Development|Thyroid]] TSH levels increase, thyroxine (T3) and T4 levels increase to 24 h, then 5-7 days postnatal decline to normal levels | ||
[ | [[Endocrine_-_Adrenal_Development|Adrenal]] - zona glomerulosa, zona fasiculata present | ||
| Line 171: | Line 173: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 22:59, 22 May 2011
| Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities |
Introduction
- Fetal Neural
- Fetal Respiratory
- Fetal Cardiovascular
- survival issues for early delivery
- fetal weight
- fetal origins hypothesis
Week 24+
- Earliest potential survival expected if born
- Respiratory Week 24 to 40 lung histology - terminal sac, end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant
- saccule - a large thin-walled airspace lined by flattened epithelium present from about 28 weeks gestation to 2 months after birth
- Gonad - male gonad (testes) descending (week 30) Development Animation - Testis Descent
- 10 to 23 weeks - (9.45%) had migrated from the abdomen and were situated in the inguinal canal
- 24 to 26 weeks - (57.9%) had migrated from the abdomen
- 27 to 29 weeks - (16.7%) had not descended to the scrotum
| Testis Descent Failure of descent (cryptorchidism) either unilateral or bilateral testicular descent, occurring in up to 30% premature and 3-4% term males. |
References: Sampaio FJ, Favorito LA. Analysis of testicular migration during the fetal period in humans. J Urol. 1998 Feb;159(2):540-2. | Malas MA, Sulak O, Ozturk A. The growth of the testes during the fetal period. BJU Int. 1999 Oct;84(6):689-92.
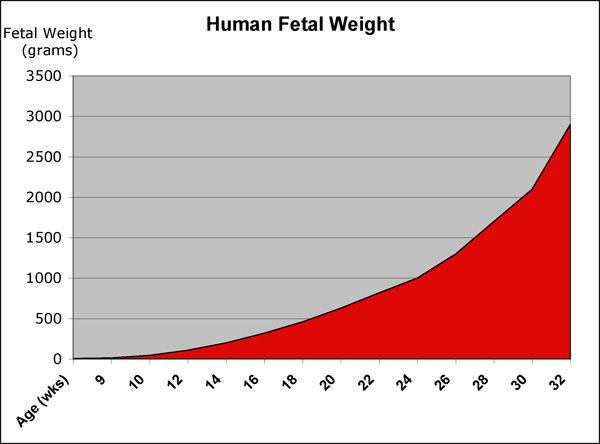
Fetal Weight
Fetal Birth
Most of the serious illness and mortality is concentrated in the 1 to 2 percent of infants who are born at less than 32 weeks of gestation (week 30) and who weigh less than 1500 g.
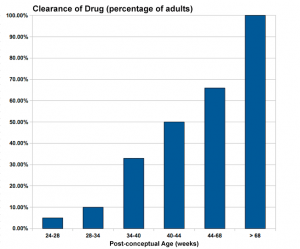
Teratogens - Infant Drug Clearance
Teratogen (Greek, teraton = monster) Any agent that causes a structural abnormality following exposure during pregnancy. The overall effect depends on dosage and time of exposure.
The drug clearance data below are only approximate calculated rates for the fetus and infant from NZ Drug Safety in Lactation
| Post-conceptual Age (weeks) | Clearance of Drug (percentage of adults) |
| 24-28 | 5% |
| 28-34 | 10% |
| 34-40 | 33% |
| 40-44 | 50% |
| 44-68 | 66% |
| > 68 | 100% |
Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities
Additional Information
The following information is a detailed timeline of third trimester development and content does not form part of the current practical class.
Third Trimester
(Clinical Week 28) Third Trimester
| Event | ||
| Clinical third trimester |  Hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus. Hearing 3rd Trimester - vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle respone in fetus.
| |
| Respire Month 7 - respiratory bronchioles proliferate and end in alveolar ducts and sacs | ||
|
Genital male gonad (testes) descending | ||
| Nail Development fingernails reach digit tip | ||
| Neural brain cortical sulcation - primary sulci present[1] | ||
| Neural brain cortical sulcation - insular, cingular, and occipital secondary sulci present[1] | ||
 Nail Development toenails reach digit tip Nail Development toenails reach digit tip
Lens Development - lens growth and interocular distance plateaus after 36 weeks of gestation[2] | ||
| Birth |  Clinical Week 40 Clinical Week 40
Heart pressure difference closes foramen ovale leaving a fossa ovalis Thyroid TSH levels increase, thyroxine (T3) and T4 levels increase to 24 h, then 5-7 days postnatal decline to normal levels Adrenal - zona glomerulosa, zona fasiculata present
|
BGDA: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12 | Lecture Neural | Practical 14 | Histology Support - Female | Male | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 8) Embryology BGDA Practical 12 - Third Trimester. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDA_Practical_12_-_Third_Trimester
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G