Z
| Embryology - 28 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Z
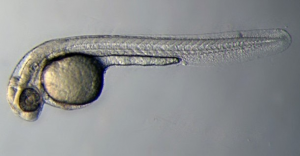
zebrafish
- A fish model of vertebrate embryological development. Embryos are translucent and there are a large number of known, and manufactured mutants.
- (More? zebrafish)
zeugopod
- Limb development term describing the mid-section of the limb in the proximo-distal sequence: stylopod, zeugopod and autopod. The skeletal components of the upper limb (forelimb) are the radius and ulna, and for the lower limb (hindlimb) are the tibia and fibula.
ZIFT
- Acronym for Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer, a in vitro fertilization procedure in which eggs are collected from a woman's ovaries and fertilized outside her body. A laparoscope is then used to assist in placing the resulting zygote (fertilized egg) into the woman's uterine (fallopian) tube through small incisions in her abdomen.
- (More? Assisted Reproductive Technology | ART)
zinc finger
- Protein structure term refers to a small, irregular domain stabilized by binding of a zinc ion. Found in transcription factors, DNA-binding proteins. A signature metal-ion binding sequence motif with one or more zinc ions to stabilize its structure through cysteine and/or histidine residues.
- (More? Molecular Development)
ZP1
- Acronym for Zona Pellucida Protein 1, a glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte.
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida | OMIM - ZP1)
ZP2
- Acronym for Zona Pellucida Protein 2, a glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte. The protein acts as a secondary sperm receptor that binds sperm only after the induction of the sperm acrosome reaction. Before fertilization ZP2 binds spermatozoa. After fertilization ZP2 is proteolytically cleaved as an initial block to polyspermy.
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida | OMIM - ZP2)
ZP3
- Acronym for Zona Pellucida Protein 3, a glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte required for initial zona matrix formation and during fertilization for species-specific sperm binding. Now thought to exist in 2 isoforms ZP3A and ZP3B (a second polymorphic allele).
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida | OMIM - ZP3)
ZP4
- Acronym for Zona Pellucida Protein 4, a 540 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte required for initial zona matrix formation and along with ZP3 during fertilization for inducing the acrosome reaction and inhibited the binding of spermatozoa to zona pellucida in a time- and dose-dependent reaction.
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida | OMIM - ZP4)
ZPBP1
- Acronym for Zona Pellucida Binding Protein 1 A spermatozoa protein found located on the acrosome surface.
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida)
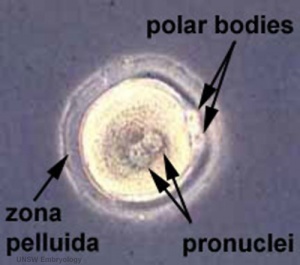
zona pellucida
- (egg coat, oolemma, vitelline membrane, Latin, zona pellucida = transparent zone) A specialized extracellular matrix surrounds the developing oocyte (egg, ovum) within the ovary and following ovulation. The oocyte synthesizes and secretes each zona pellucida glycoprotein ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3 where it is assembled into the insoluble zona pellucida matrix. The proteins have different roles in fertilization. Following fertilization, the zona pellucida also surrounds the blastocyst during the first week of development, from which it "hatches". The zona pellucida has a role in fertilization, sperm binding, preventing polyspermy, blastocyst development and preventing premature implantation (ectopic pregnancy).
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida | Category:Zona Pellucida)
zona pellucida binding protein 1
- (ZPBP1) A spermatozoa protein found located on the acrosome surface which has a role during spermiogenesis (acrosome compaction, Sertoli-spermatid junctions) and also binds the zona pellucida during fertilization.
- (More? ovary | fertilization | zona pellucida)
zona pellucida birefringence
- (ZPB) Optical property of the zona pellucida using polarization imaging when viewed microscopically. Used to qualitatively predict the developmental potential of a in vitro matured metaphase-II (MII) oocytes. High birefringence has been associated with oocytes contributing to conception cycles when compared with those of nonconception cycles and higher implantation, pregnancy, and live birth rates from transferred oocytes.
- (More? fertilization | zona pellucida | Assisted Reproductive Technology | Oocyte Development | Ovary Development | PMID 18284880 | PMID 20079896)
zone of polarizing activity
- (ZPA) Region within the early developing limb bud involved in patterning the organization of tissues/structures within the limb as it grows and develops. The region is mesodermal in origin and the cells have a mesenchymal organization.
- (More? limb | sonic hedgehog | musculoskeletal | Molecular Development)
zoonotic disease
- (zoonosis) An animal disease that can be transmitted to humans. This can be through contact with animals (pets, farm animals, wildlife) or their products (milk, meat, waste).
zygote
- The first diploid cell that forms following fertilization by fusion of haploid oocyte (egg or ovum) and spermatozoa (sperm), resulting in the combination of their separate genomes. This single cell will divide by mitosis to form all cells of the embryo, fetal membranes and the embryonic component of the placenta. The term conceptus is used to describe all these cells derived from the fertilization event forming the zygote.
- (More? zygote | fertilization | Week 1)
zygote arrest
- Term used mainly in assisted reproductive technology (ART) for blockage at the first cleavage stage that can be due to molecular and chromosomal anomalies, some of which are apparent as morphological abnormalities. Morphological differences observed by light microscopy include: the absence of a light halo, the absence of a dark halo, and non-aligned nucleolar precursor bodies (NPB).
- (More? zygote | fertilization | Week 1)
zygote intrafallopian transfer
- (ZIFT) A procedure in which eggs are collected from a woman's ovaries and fertilized outside her body. A laparoscope is then used to assist in placing the resulting zygote (fertilized egg) into the woman's uterine tube (fallopian) through small incisions in her abdomen.
- (More? zygote | fertilization | Week 1)
zygotene stage
- (zygotene phase, zygonema, Greek, zygotene = "paired threads") A meiotic cell division stage seen during prophase I. Prophase I is further divided into 5 stages based upon changes associated with the synaptonemal complex structure that forms between two pairs of homologous chromosomes. In zygotene, the synaptonemal complex begins to form between the two sets of sister chromatids in each bivalent (the duplicated chromosome paired with its homologous duplicated chromosome).
- Prophase I stages: leptotene - zygotene - pachytene - diplotene - diakinesis
- (More? meiosis | oocyte | spermatozoa | Week 1 | MBoC)
zymogen
- Term used to describe the precursor inactive form of any protein enzyme. These precurors can be seen as zymogen granules in some secretory cells.
Glossary Comments
Use this page to access brief definitions of specific embryology terms. Additional information can be accessed from links listed at the end of each definition. Glossary from the UNSW Embryology program compiled and written by Dr Mark Hill. Reference material used in preparing this glossary list includes: texts listed on page 1 "Reading" of each notes section, Department of Anatomy Publications, WWW resources from NCBI, NIH, OMIM, NHMRC (Australia), AMA (USA), Office of Rare Diseases (USA), PubMed Medline Dictionaries, MSDS, Merck Manual home edn. and WHO ART terminology (2009).
These notes are for Educational Purposes Only Please email Dr Mark Hill if you wish to make a comment about this current project.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology Z. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Z
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G