Digital Embryology Consortium - Information
| Embryology - 1 May 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
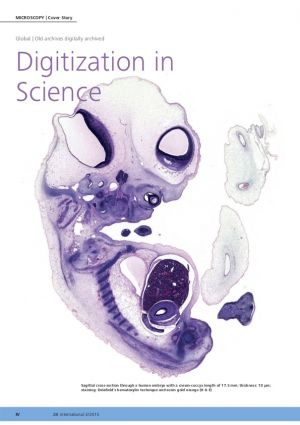
The Digital Embryology Consortium was first established in 2014. The objective of this international partnership is to digitise, preserve, and make available for researchers the major embryology histological collections. There currently exists worldwide only a few large collections of human embryological material. These collections are held in universities and associated research institutions as either whole fixed embryos or more commonly sectioned and histological stained. Many of these collections are historic between 30 to 100 years old. There have been previous attempts to partially document some of these collections, but the equipment and technology was not sufficiently developed to allow the process to be completed and in some cases the data was restricted in availability.
The collection curators will hold a complete digital copy of their collection and control all online copyright, citation and further reuse. The research project is not intended to change any existing controls that are held over these invaluable collections. An internet address (human-embryology.org) has been specifically allocated to remove any rebranding or re-association of the existing collections and would be seen as a collaborative research website between contributing institutions and researchers.
Consortium Embryo Collections
- Blechschmidt Collection – University of Goettingen, Germany Prof. Christoph Viebahn (Head of Embryology Department).
- Hinrichsen Collection – Ruhr-University Bochum, Prof. Beate Brand-Saberi (Head of Embryology Department).
- Embryological Collection – Museum für Naturkunde, Leibniz Institute for Research on Evolution and Biodiversity. Dr Peter Giere (curator of the embryological collection).
- Madrid Collection – Complutense University of Madrid, Institute of Embryology. Prof. José-Vicente Sanz-Casado (Head, Embryology Institute of Complutense University of Madrid).
- Carnegie Collection – National Museum of Health and Medicine Elizabeth Lockett (curator NMHM).
- Kyoto Collection – Kyoto University, Prof. Shigehito Yamada.
- Perry-Arey-Milligan Collection – University of British Columbia, Prof. Virginia Diewert.
- HDBR and HuDSeN Collection – Newcastle University, Prof. Susan Lindsay.
- Domenech-Mateu Collection – Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Prof Rosa Mirapiex.
Presentations
| Kyoto (Nov 2015) | Washington (Dec 2015) |
|---|---|

|

|
Image Server
There is currently a pilot server being tested using the OMERO platform. OMERO - DEC
| DEC OMERO Server |
- DEC - OMERO (pilot) - can be access by web browser or through OMERO.insight program.
- OMERO.insight (tutorial) - How to install and use the OMERO.insight program.
Reference
Hill MA. (2019). Two Web Resources Linking Major Human Embryology Collections Worldwide. Cells Tissues Organs (Print) , , 1-10. PMID: 30673660 DOI.
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Digital Embryology Consortium http://human-embryology.org
- Zeiss Axio Scan.Z1
- The Open Microscopy Environment OMERO
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 1) Embryology Digital Embryology Consortium - Information. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Digital_Embryology_Consortium_-_Information
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G