ANAT2341 Lab 5 - Abnormalities
| Lab 5: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Atresia and Stenosis
The gastrointestinal tract can be considered as a simple tube or pipe, anything which blocks the tube (at different levels) can have different effects.
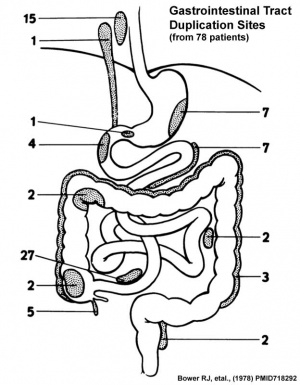
There are two types of abnormalities that impact upon the continuity of the gastrointestinal tract lumen.
Atresia - interuption of the lumen (esophageal atresia, duodenal atresia, extrahepatic biliary atresia, anorectal atresia)
Stenosis - narrowing of the lumen (duodenal stenosis, pyloric stenosis)
Duplication - incomplete recanalization resulting in parallel lumens, this is really a specialized form of stenosis.
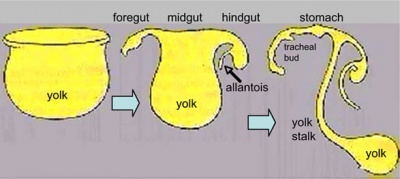
Persistent Vitelline Duct
Meckel's Diverticulum
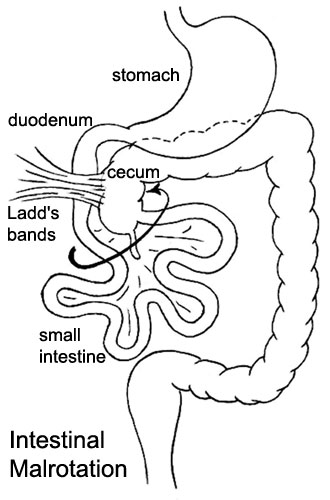
Abnormal Gut Rotation
Midgut Volvulus, Situs Inversus
Organ Abnormalities
Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia, Accessory Pancreatic Tissue, Anular Pancreas, Accessory Spleen
Motility Disorders
Aganglionic colon (Hirschprung's disease) - abnormalities of neural crest migration.
Related Abnormalities
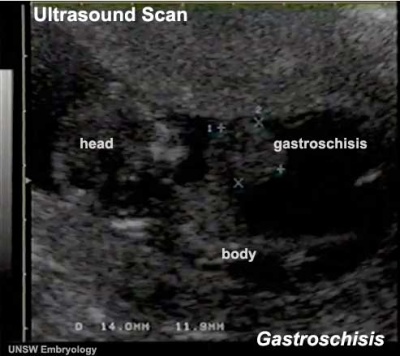
Abdominal Wall Defects
| Gastroschisis is a developmental abnormality occurs due to an abdominal wall defect, that allows the evisceration of the intestine.
|
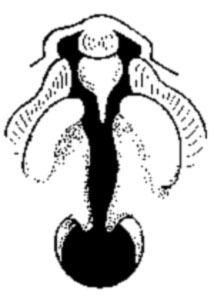
Clefting
Cleft lip and palate can affect postnatal nutrition, due to the inability of the infant to form a liquid seal on the breast during feeding.
Cleft Lip
An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the upper lip. Due to failure during the embryonic period of maxillary process fusion with the frontonasal prominence. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. Depending on many factors, this cleft may extend further into the oral cavity leading to a cleft palate. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery.
Cleft Palate
An abnormality of face development leading to an opening in the palate, the roof of the oral cavity between the mouth and the nose. If it occurs alone, due to failure during the early fetal period of palatal shelves. Clefting of the lip and or palate occurs with 300+ different abnormalities. In most cases clefting of the lip and palate can be repaired by surgery.
Galactosemia
A genetic enzyme deficiency disorder, the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase metabolizes galactose in milk sugar. The incidence is approximately 1 in 60,000 births among Caucasians and the rate is different for other groups.
Meconium Peritonitis
A condition caused by intra-uterine intestinal perforation leading to a sterile inflammatory reaction of the peritoneum.
Abnormalities and Development
- How these abnormalities may be generated in development.
- When they first occur.
- How can we detect these abnormalites.
- Do the abnormalites have a direct or indirect effect on the GIT.
- How serious to the embryo, fetus, newborn, child and adult are these conditions.
- What therapeutics are available for these conditions.
| Lab 5: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 2) Embryology ANAT2341 Lab 5 - Abnormalities. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2341_Lab_5_-_Abnormalities
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ <pubmed>718292</pubmed>