ANAT2241 Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas
| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241 |
General Objective
To know the histological structure and major functions of the liver, gall bladder and pancreas.
Specific Objectives
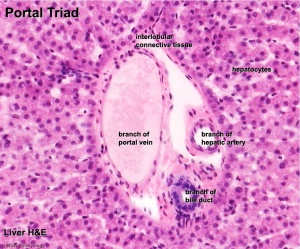
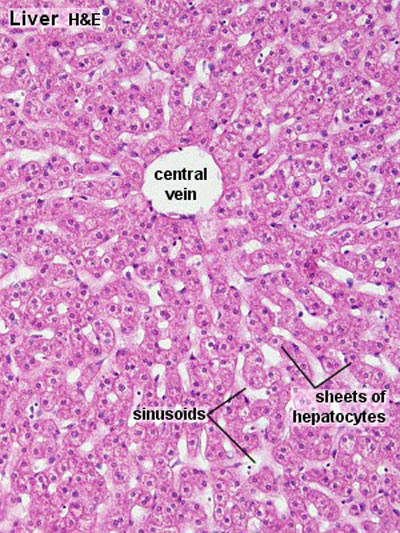
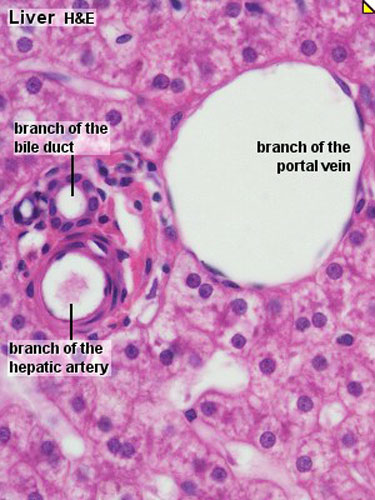
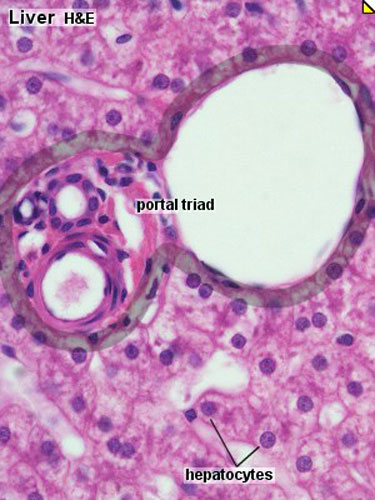
- To know the histology of the liver, including the hepatic lobule, hepatic acinus, hepatic parenchyma, portal area, and histological features of the vascular and biliary systems.
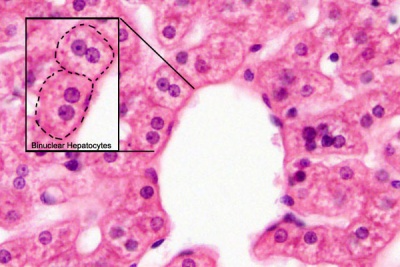
- To appreciate the 3-D arrangement of hepatocytes and know their major functions.
- To know the histological features of the wall of the gallbladder.
- To know the histological features of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas.
Learning Activities
Examine the following virtual slides, identify, draw and label the following features.
Discuss and make a note of their function(s).
Virtual Slides: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas
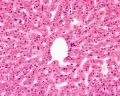
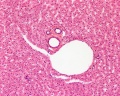
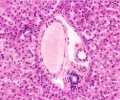
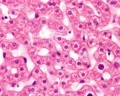
Liver
- Liver Histology: Central vein (label) | Central vein (unlabel) | Portal triad 1 (label) | Portal triad 2 (label) | Portal triad (unlabel) | Hepatocytes (unlabel) | Hepatocytes polyploid (label) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (LP) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver Development | GIT Histology
Liver Lobule
| This looped animation shows the different ways of interpreting the cellular structure of the liver lobule. | 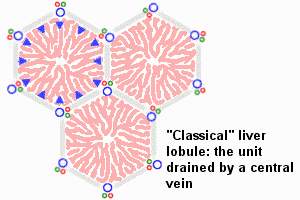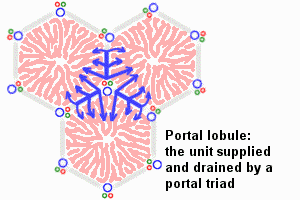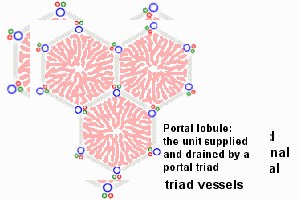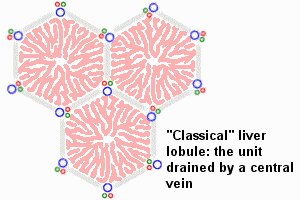
|
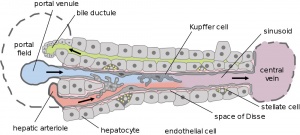
Liver Blood Flow
Dual blood supply of the liver merges upon entry into the liver lobule at the portal field.
|
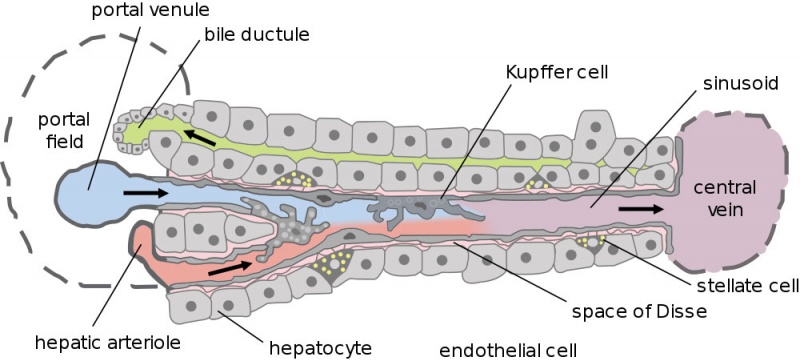
|
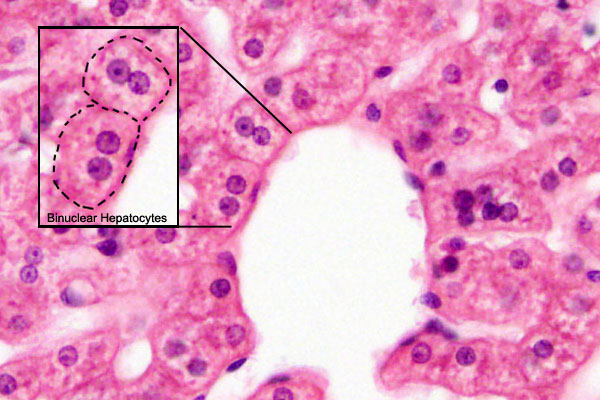
Hepatocytes
Liver Histology
- Liver Histology: Central vein (label) | Central vein (unlabel) | Portal triad 1 (label) | Portal triad 2 (label) | Portal triad (unlabel) | Hepatocytes (unlabel) | Hepatocytes polyploid (label) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (LP) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver Development | GIT Histology
|
|
|
|
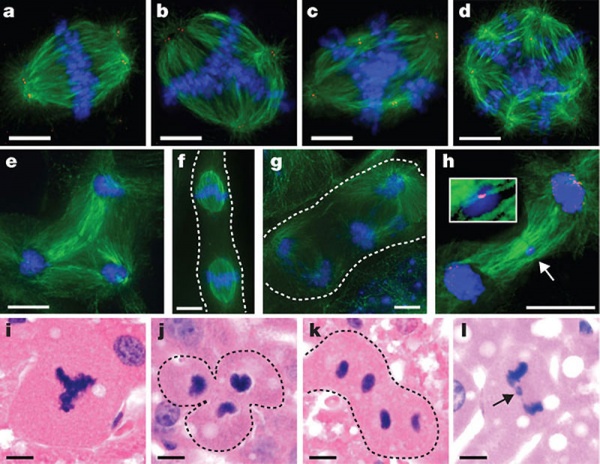
Hepatocyte Polyploidy
Human hepatocytes
Mouse hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo[1]
Electron Micrograph
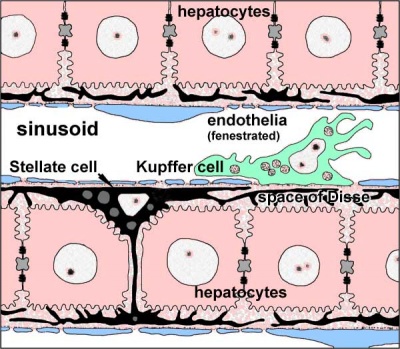
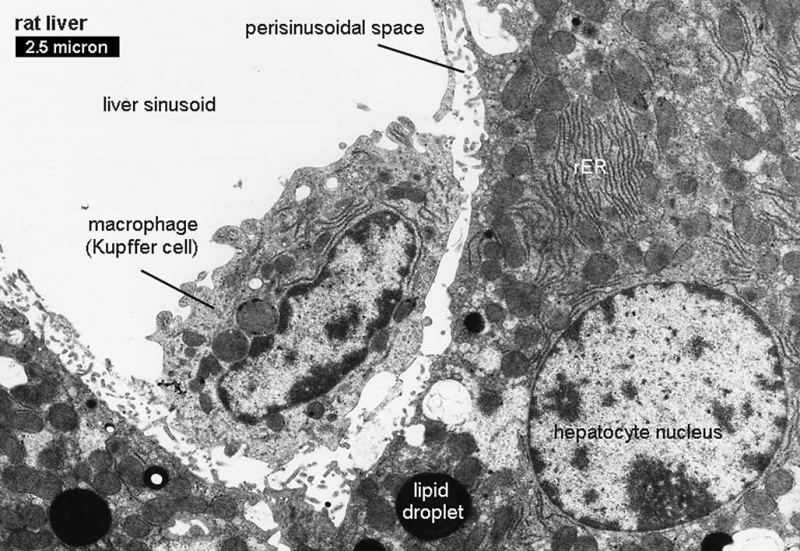
The electron micrographs below show the cellular, vascular and bilary organisation of the liver.
| Kupffer cell in liver sinusoid |
|---|
|
| Bile canaliculi |

|
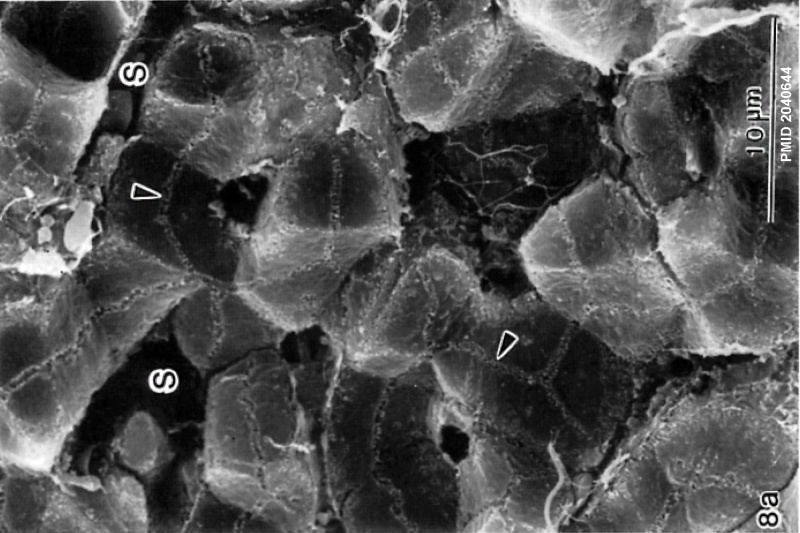

Bile Canaliculi and Sinusoids [2] |
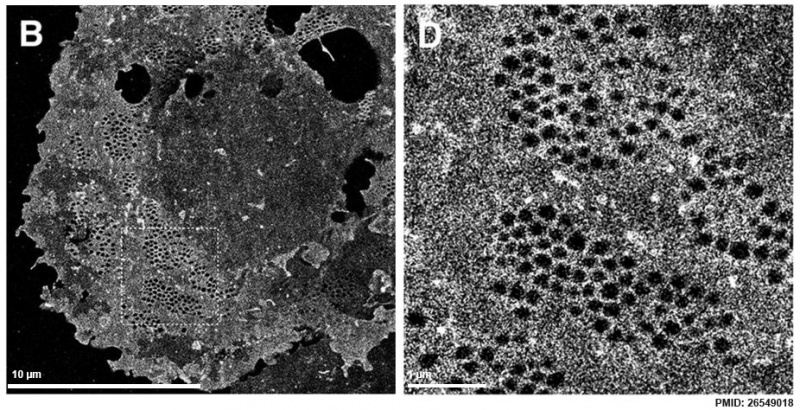
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrations[3] |
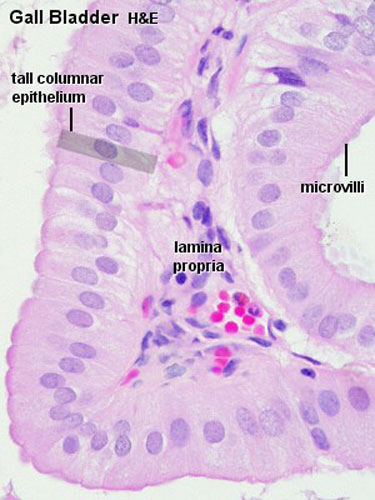
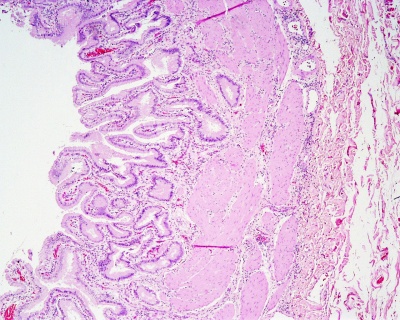
Gall Bladder
Anatomy
- Pear-shaped
- distensible sac (about 50ml volume)
- Attached to posterioinferior surface of liver
- Embryonic - foregut, forms from primitive bile duct
- leads to cystic duct
- Liver -> hepatic duct
- Gall bladder -> cystic duct
- Common Bile duct
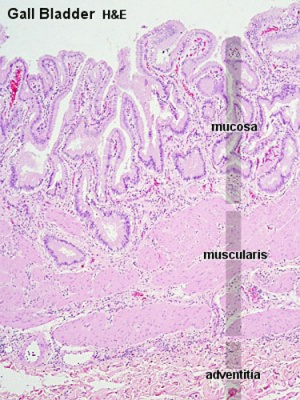
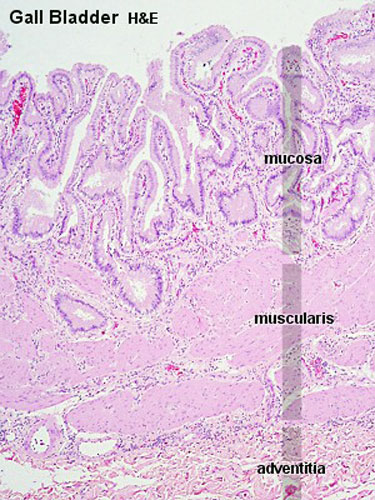
Macroscopic Mucosal features:
- Mucosa (epithelium + lamina propria)
- Mucosal folds
- Rokintansky-Aschoff sinuses
- Serosa/Adventitia (dense CT + visceral mesothelium)
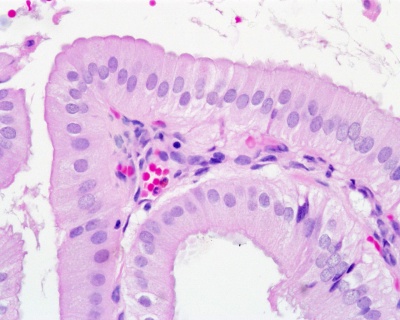
Epithelium
- Columnar epithelium with microvilli (absorptive epithelium)
- Epithelium lining the biliary system does not contain mucus-producing cells (few located in neck of gall bladder)
- Basement membrane (not basal lamina which forms part of basement membrane and only visible by EM)
Lamina Propria
- connective tissue
- collagen fibers and fibroblasts
- fenestrated capillaries and venules
- lymphocytes and plasma cells
Smooth Muscle Layer
- random orientation of smooth muscle cells (fibers)
- muscularis propria (or fibromuscular coat)[4]
- not like the rest of GIT smooth muscle organisation, which is divided into muscularis mucosa (inside submucosa), muscularis externa (circular and longitudinal)
- various terminology used for this layer in different sources
Serosa/Adventitia
- Dense connective tissue layer covered with visceral mesothelium epithelial layer
- Adventitia - where it is attached to the liver
- Serosa - where it is free in the peritoneum
- Large blood vessels (arteries, veins)
- Obvious lymphatic vessels
- Autonomic nerve bundles
- Adipose tissue
Histology
See also Animated labeled image
References
- ↑ <pubmed>20861837</pubmed>| PMC2967727 | Nature
- ↑ Watanabe N, Tsukada N, Smith CR & Phillips MJ. (1991). Motility of bile canaliculi in the living animal: implications for bile flow. J. Cell Biol. , 113, 1069-80. PMID: 2040644
- ↑ Mönkemöller V, Øie C, Hübner W, Huser T & McCourt P. (2015). Multimodal super-resolution optical microscopy visualizes the close connection between membrane and the cytoskeleton in liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrations. Sci Rep , 5, 16279. PMID: 26549018 DOI.
- ↑ <pubmed>21074688</pubmed>
Terms
- Glisson's capsule (Glisson's sheath) - a collagenous capsule covering the external surface of the liver the outer layer comprising a single layer of mesothelial cells. The capsule also extends into the liver as "sheaths" around the hepatic ducts, hepatic arteries and portal tributaries. Named after Francis Glisson (1599 – 1677) a British anatomist.
- Kupffer cells - liver macrophage located in sinusoidal space. Named after Karl Wilhelm von Kupffer (1829 - 1902 ) a German anatomist.
- sinusoids (vascular sinusoids, liver sinusoids) - the spaces between the hepatocytes that are distensible vascular channels lined with fenestrated endothelial cells forming a discontinuous simple squamous epithelium.
- stellate cells (Ito cells) - Named after Toshio Ito, a twentieth century Japanese physician PMID 11450594
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Blue Histology Liver
- UNSW Virtual Slides Medicine phase 1 Health Maintenance B Hepatobiliary System 1 Practical (requires login for access).
- UIOWA Virtual Slidebox of Histology Liver and biliary system
Course Links
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 1) Embryology ANAT2241 Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Liver,_Gallbladder,_and_Pancreas
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G