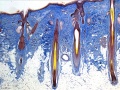
| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241
|
General Objective
To know the structure and function of skin and its appendages (derivatives).
Specific Objectives
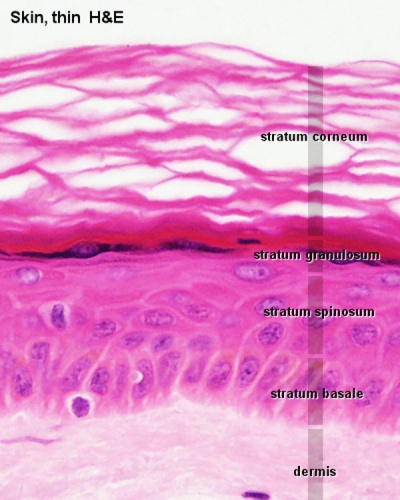
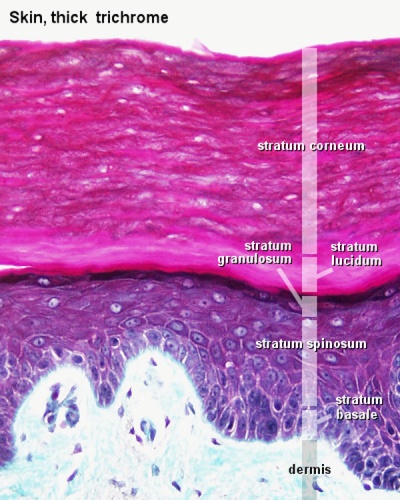
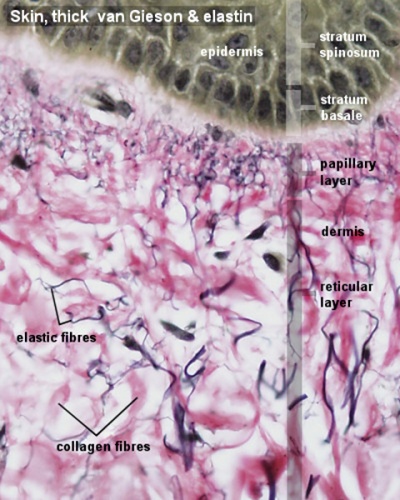
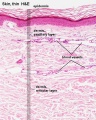
- To know the microscopic structure of the epidermis and dermis.
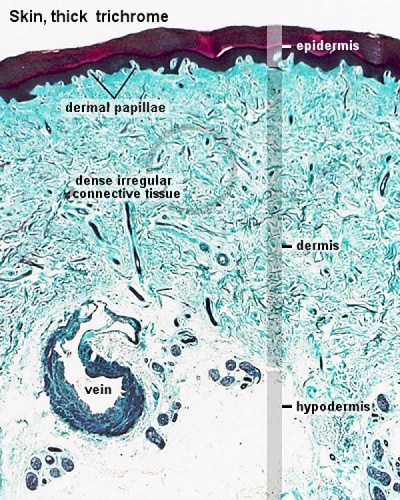
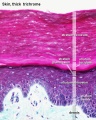
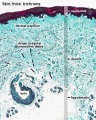
- To know the histological differences between hairy (thin) and glabrous (thick) skin.
- To know the formation and histology of skin appendages: eccrine and apocrine sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hairs, nails and specialised glands as listed below.
- To know the histological features of Pacinian and Meissner corpuscles and free nerve endings.
Learning activities
Examine the following virtual slides, and in course manual identify draw and label the following structures and note their function.
Virtual Slides: Integumentary System (skin)
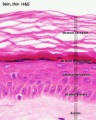
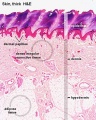
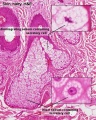
Histology
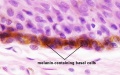
Pigmentation
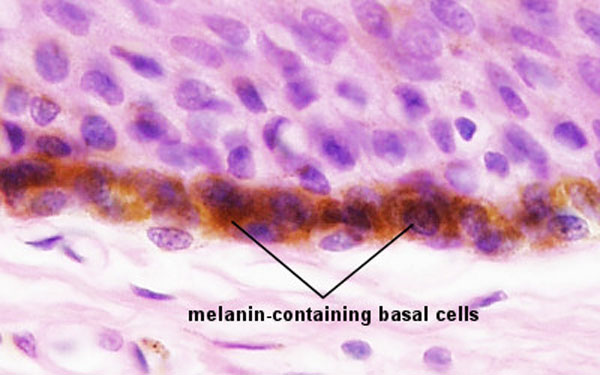
Melanin in Basal Cell Layer
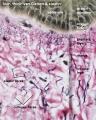
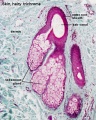
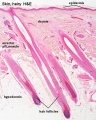
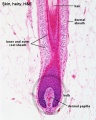
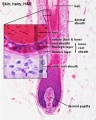
Glands and Hair
|

|

|
| Merocrine secretion (sweat gland)
|
Apocrine secretion (axilla)
|
Holocrine secretion (hair follicle)
|
Sebaceous gland histology
Sebaceous gland histology
Sensory
| Touch
|
Pressure
|
|
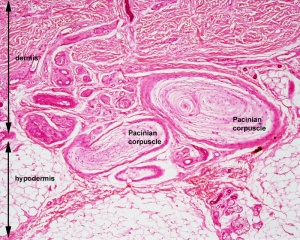
|
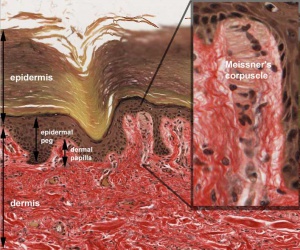
| Meissner corpuscle a sensory touch cellular structure located in the dermis superficial region.
|
Pacinian corpuscle a sensory pressure cellular structure located in the dermis deep region.
|
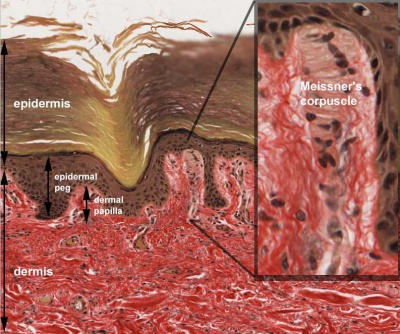
Meissner Corpuscle
- coiled, spring-like structures composed of stacked, disk-like lamellar cells.
- lamellae orientation is usually parallel to the skin surface.
- lamellar cells - Schwann cell-derived with peripherally displaced nuclei in a fibroblastic capsule incomplete at the apex.
- sensory neurites - course through the lamellae, not visible by (Stain - Haematoxylin Eosin).
|
|
- Links: touch
Lip
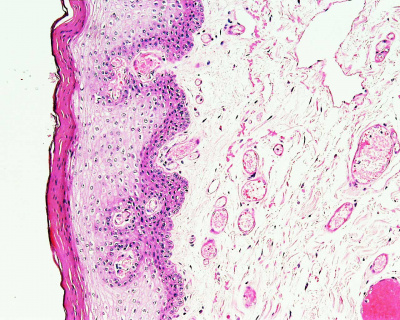
vermilion border
|
- anatomical lips - comprise the entire fleshy fold surrounding the oral orifice.
- vermilion - red part of the lips.
- vermilion border (prolabium) - only a small part, area of transition from skin to oral mucosa.
- outside - covered by thin skin, stratified squamous keratinised epithelium
- skin side - hairs, swear and sebaceous glands.
- inside - lined by oral mucosa, stratified squamous non-keratinised epithelium
- mucosa side - labial salivary glands (mucoserous).
- orbicularis oris muscle - skeletal (striated) muscle that shapes the lips.
|
Nail
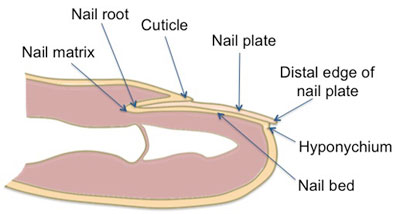
|
- convex on its outer surface, concave within
- in a groove in the skin, implanted by a portion called the root
- exposed portion is called the body
- distal extremity the free edge
|
- Integument Histology Links: Adult Skin | Epidermis and Dermis | Thin Skin Epidermis | Thick Skin Epidermis | Elastic Fibres | Basal Cell Melanin | Foundations Practical Support | Integumentary System Development | Histology Stains
Course Links
Moodle - ANAT2241 - 2019
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains
|
| Histology Stains - Common Stains and Their Reactions
|
| Stain
|
Nucleus
|
Cytoplasm
|
Collagen
|
RBCs
|
Other
|
| Haematoxylin
|
blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins - light blue
|
| Eosin
|
-
|
pink
|
pale pink
|
bright red
|
colloid - pinkmuscle - red
|
| Iron Haematoxylin
|
blue/black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
| Van Gieson
|
-
|
brown/yellow
|
red
|
yellow
|
muscle: yellow/browncartilage - pink
|
| Verhoeff's Elastin
|
black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres - black
|
| Tartrazine
|
-
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
|
| Silver Impregnation
|
-
|
-
|
grey/brown
|
-
|
reticular fibres - black
|
| Methyl Green
|
dark green
|
light green
|
light green
|
green
|
|
| Nuclear Fast Red
|
red
|
pink
|
pink
|
pink
|
|
| Gomori's Trichrome
|
purple/red
|
purple
|
green
|
red
|
keratin - redmuscle - purple/red
|
| Heidenhain's Azan
|
red
|
purple/red
|
deep blue
|
red
|
muscle - red
|
| Osmium Tetroxide
|
-
|
-
|
brown
|
brown
|
myelin, lipids - black
|
| Alcian Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins, - blue
|
| Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
|
-
|
-
|
pink
|
-
|
mucins, glycogen, glycocalyx - magenta
|
| Phosphotungstic Acid-Hematoxylin (PTAH)
|
blue
|
-
|
red
|
blue
|
muscle bands - blue
|
| Masson's Trichrome
|
blue/black
|
red
|
green/blue
|
red
|
cartilage, mucins - blue or green; muscle - red
|
| Luxol Fast Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
variable
|
myelin - blue
|
| Aldehyde Fuchsin
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres, mast cells - deep purple
|
| Light Green
|
-
|
-
|
light green
|
-
|
|
| Gallocyanin
|
dark blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
nucleic acids, Nissl granules - dark blue
|
| Romanowsky (e.g. Leishman's)
|
blue
|
pink
|
|
|
acidophils - red, basophils - blue, azurophilic - purple
|
| Aldehyde Pararosanilin
|
|
|
|
|
elastic fibres - purple
|
|
| Haematoxylin and Eosin
|
| One of the most common staining techniques in pathology and histology. Acronym "H and E" stain. (H&E, HE).
|
Haematoxylin
- Stains nuclei blue to dark-blue.
- Stains the matrix of hyaline cartilage, myxomatous, and mucoid material pale blue.
- Stains myelin weakly but is not noticeable if combined with eosin stain.
- combined with Orange G (H & Or. G.) instead of eosin, specifically stains the granules of acidophilic cells of the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary).
|
Eosin
- Stains cytoplasm pink to red; red blood cells are also bright red.
- Common counterstain to hematoxylin.
- Stain intensity varies with the formula as well as the fixative.
|
|
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology ANAT2241 Integumentary System. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Integumentary_System
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G