| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241
|
General Objective
To recognise exocrine and endocrine glandular epithelium.
Specific Objectives
- To know the morphological characteristics of mucous and serous secretory cells.
- To identify the following types of exocrine glands: unicellular (Goblet cell), secretory sheet, simple tubular (straight and coiled), simple and branched alveolar (acinar) glands, compound tubular and tubulo-alveolar (tubulo-acinar) glands.
- To recognise the different arrangement of endocrine glands when compared to exocrine glands.
Learning Activities
- The arrangement of the gland cells and the presence or absence of branched ducts.
- Examine the following virtual slides, identify draw and label the following types of glands.
Glandular Epithelia | Histology Drawings
Histology Stains
| Common Histology Stains
|
| Histology Stains - Common Stains and Their Reactions
|
| Stain
|
Nucleus
|
Cytoplasm
|
Collagen
|
RBCs
|
Other
|
| Haematoxylin
|
blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins - light blue
|
| Eosin
|
-
|
pink
|
pale pink
|
bright red
|
colloid - pinkmuscle - red
|
| Iron Haematoxylin
|
blue/black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
| Van Gieson
|
-
|
brown/yellow
|
red
|
yellow
|
muscle: yellow/browncartilage - pink
|
| Verhoeff's Elastin
|
black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres - black
|
| Tartrazine
|
-
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
|
| Silver Impregnation
|
-
|
-
|
grey/brown
|
-
|
reticular fibres - black
|
| Methyl Green
|
dark green
|
light green
|
light green
|
green
|
|
| Nuclear Fast Red
|
red
|
pink
|
pink
|
pink
|
|
| Gomori's Trichrome
|
purple/red
|
purple
|
green
|
red
|
keratin - redmuscle - purple/red
|
| Heidenhain's Azan
|
red
|
purple/red
|
deep blue
|
red
|
muscle - red
|
| Osmium Tetroxide
|
-
|
-
|
brown
|
brown
|
myelin, lipids - black
|
| Alcian Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins, - blue
|
| Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
|
-
|
-
|
pink
|
-
|
mucins, glycogen, glycocalyx - magenta
|
| Phosphotungstic Acid-Hematoxylin (PTAH)
|
blue
|
-
|
red
|
blue
|
muscle bands - blue
|
| Masson's Trichrome
|
blue/black
|
red
|
green/blue
|
red
|
cartilage, mucins - blue or green; muscle - red
|
| Luxol Fast Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
variable
|
myelin - blue
|
| Aldehyde Fuchsin
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres, mast cells - deep purple
|
| Light Green
|
-
|
-
|
light green
|
-
|
|
| Gallocyanin
|
dark blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
nucleic acids, Nissl granules - dark blue
|
| Romanowsky (e.g. Leishman's)
|
blue
|
pink
|
|
|
acidophils - red, basophils - blue, azurophilic - purple
|
| Aldehyde Pararosanilin
|
|
|
|
|
elastic fibres - purple
|
|
| Haematoxylin and Eosin
|
| One of the most common staining techniques in pathology and histology. Acronym "H and E" stain. (H&E, HE).
|
Haematoxylin
- Stains nuclei blue to dark-blue.
- Stains the matrix of hyaline cartilage, myxomatous, and mucoid material pale blue.
- Stains myelin weakly but is not noticeable if combined with eosin stain.
- combined with Orange G (H & Or. G.) instead of eosin, specifically stains the granules of acidophilic cells of the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary).
|
Eosin
- Stains cytoplasm pink to red; red blood cells are also bright red.
- Common counterstain to hematoxylin.
- Stain intensity varies with the formula as well as the fixative.
|
|
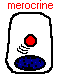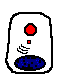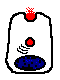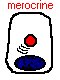
Gland Secretion Mechanisms
|

|

|
| Merocrine (eccrine) secretion
|
Apocrine secretion
|
Holocrine secretion
|
Respiratory Epithelium
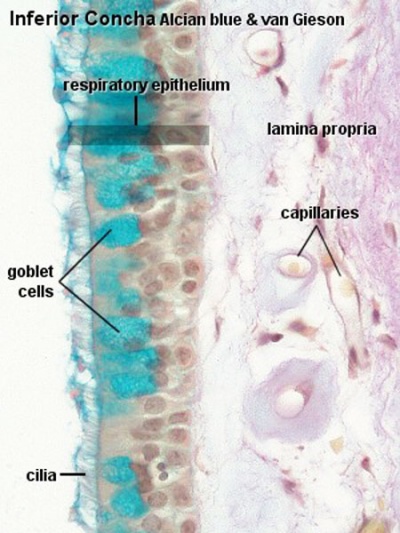
Pseudostratified columnar and ciliated. This type of epithelium is characteristic for all conductive passages dedicated to the respiratory system and therefore also called respiratory epithelium.
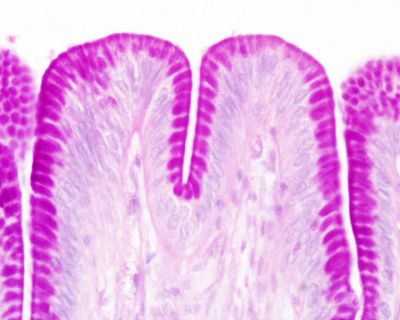
Stomach
Secretory sheath (sheet)

Salivary Glands
Large salivary glands form 3 paired groups:
- sublingual glands (beneath the tongue and embedded in oral cavity connective tissue)
- submandibular glands
- parotid glands (lie outside the oral cavity)
Tubuloacinar Glands
- have secretory acini
- also the first part of the duct system from the acini participates in secretory process
- salivary glands are divided by connective tissue septa into lobes
- further subdivided into lobules
Ducts
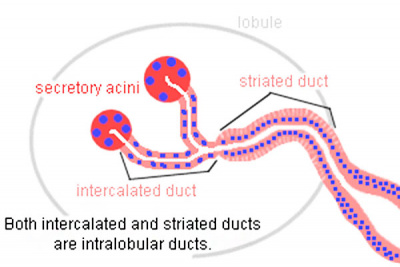
|
- Interlobular and interlobar ducts - embedded in the connective tissue surrounding the lobes and lobules of the glands
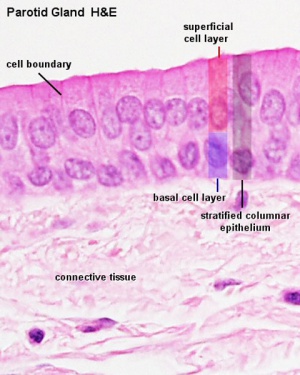
- stratified cuboidal or stratified columnar epithelium
- stratified squamous epithelium at the oral cavity opening
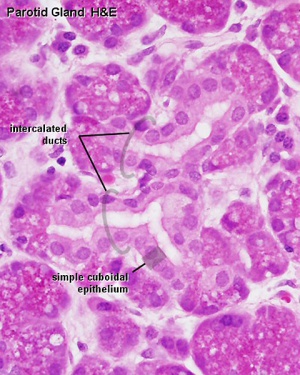
- Intralobular ducts - in between the secretory acini within the lobules
- Intercalated ducts - difficult to identify in mucous glands
- Striated ducts - absent in purely mucous glands
|
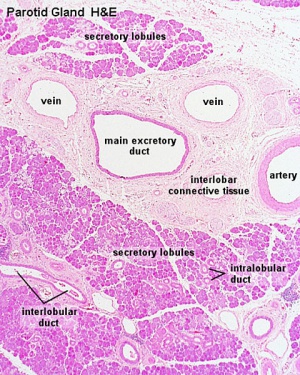
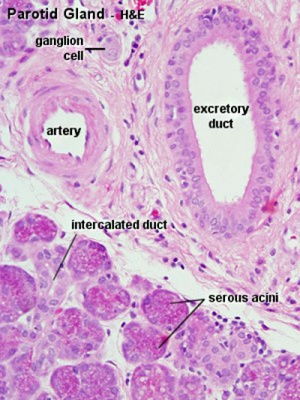
| Parotid Ducts
|
|
|
|
| Interlobar duct
|
Interlobar duct epithelium
|
Intercalated duct
|
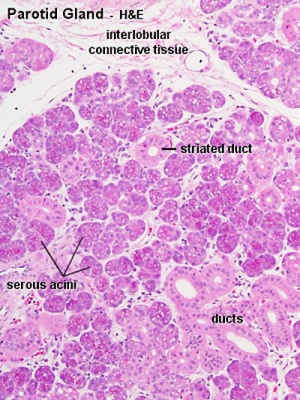
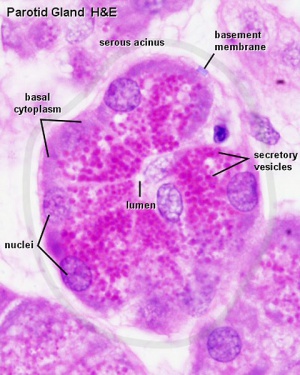
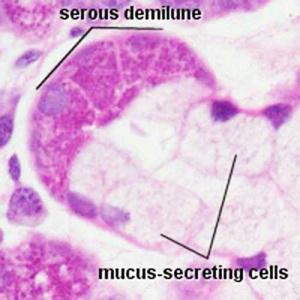
Serous and Mucous
| Serous acini
|
Mucous acini
|
- round or slightly ovoid nucleus placed basally
- (Stain - Haematoxylin Eosin) - apical cytoplasm appears pinkish/red containing reddish granules
|
- flattened nuclei "pressed" against basal surface
- secretory vesicles fill the apical cytoplasm
- apical cytoplasm appears "spongy"
- secretory product dissolved during staining process or remains unstained
|
|
|
|
| Serous acini and interlobular ducts
|
Serous acini secretory granules (zymogen granules)
|
Serous demilune
|
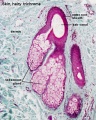
Integumentary Glands
Skin merocrine sweat gland
Skin merocrine sweat gland
Skin merocrine sweat gland
Skin merocrine sweat gland (detail)
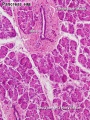
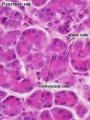
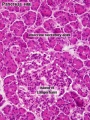
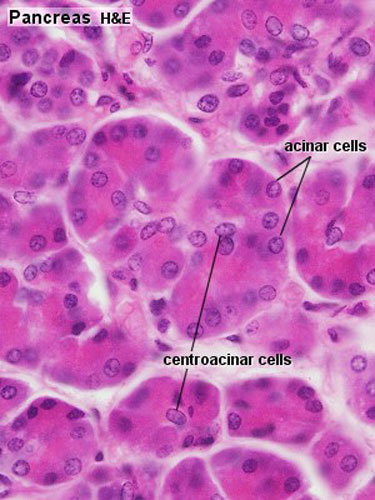
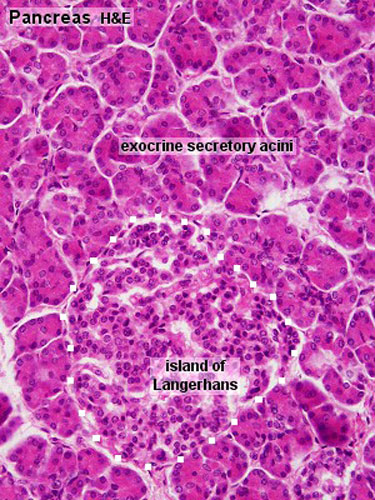
Pancreas - Exocrine and Endocrine
| Exocrine
|
Endocrine
|
|
|
|
|
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans)
|
Course Links
Moodle - ANAT2241 - 2019
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains
|
| Histology Stains - Common Stains and Their Reactions
|
| Stain
|
Nucleus
|
Cytoplasm
|
Collagen
|
RBCs
|
Other
|
| Haematoxylin
|
blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins - light blue
|
| Eosin
|
-
|
pink
|
pale pink
|
bright red
|
colloid - pinkmuscle - red
|
| Iron Haematoxylin
|
blue/black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
| Van Gieson
|
-
|
brown/yellow
|
red
|
yellow
|
muscle: yellow/browncartilage - pink
|
| Verhoeff's Elastin
|
black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres - black
|
| Tartrazine
|
-
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
|
| Silver Impregnation
|
-
|
-
|
grey/brown
|
-
|
reticular fibres - black
|
| Methyl Green
|
dark green
|
light green
|
light green
|
green
|
|
| Nuclear Fast Red
|
red
|
pink
|
pink
|
pink
|
|
| Gomori's Trichrome
|
purple/red
|
purple
|
green
|
red
|
keratin - redmuscle - purple/red
|
| Heidenhain's Azan
|
red
|
purple/red
|
deep blue
|
red
|
muscle - red
|
| Osmium Tetroxide
|
-
|
-
|
brown
|
brown
|
myelin, lipids - black
|
| Alcian Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins, - blue
|
| Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
|
-
|
-
|
pink
|
-
|
mucins, glycogen, glycocalyx - magenta
|
| Phosphotungstic Acid-Hematoxylin (PTAH)
|
blue
|
-
|
red
|
blue
|
muscle bands - blue
|
| Masson's Trichrome
|
blue/black
|
red
|
green/blue
|
red
|
cartilage, mucins - blue or green; muscle - red
|
| Luxol Fast Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
variable
|
myelin - blue
|
| Aldehyde Fuchsin
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres, mast cells - deep purple
|
| Light Green
|
-
|
-
|
light green
|
-
|
|
| Gallocyanin
|
dark blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
nucleic acids, Nissl granules - dark blue
|
| Romanowsky (e.g. Leishman's)
|
blue
|
pink
|
|
|
acidophils - red, basophils - blue, azurophilic - purple
|
| Aldehyde Pararosanilin
|
|
|
|
|
elastic fibres - purple
|
|
| Haematoxylin and Eosin
|
| One of the most common staining techniques in pathology and histology. Acronym "H and E" stain. (H&E, HE).
|
Haematoxylin
- Stains nuclei blue to dark-blue.
- Stains the matrix of hyaline cartilage, myxomatous, and mucoid material pale blue.
- Stains myelin weakly but is not noticeable if combined with eosin stain.
- combined with Orange G (H & Or. G.) instead of eosin, specifically stains the granules of acidophilic cells of the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary).
|
Eosin
- Stains cytoplasm pink to red; red blood cells are also bright red.
- Common counterstain to hematoxylin.
- Stain intensity varies with the formula as well as the fixative.
|
|
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology ANAT2241 Glandular Epithelia. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Glandular_Epithelia
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G