| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241
|
General Objective
cribriform
|
|
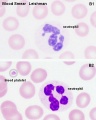
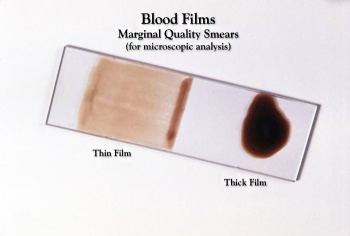
| Blood Smear Slide (unstained)
|
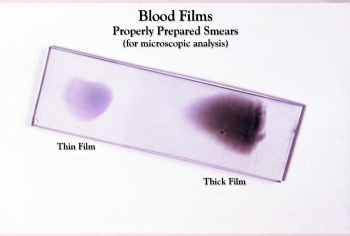
Blood Smear Slide (stained)
|
To know the formed elements of human blood and to appreciate that blood could be regarded as a “tissue” in which plasma constitutes the intercelluar substance.
Specific Objectives
- To differentiate blood cells on the basis of morphology and staining properties.
- To understand the principles of blood formation and the tissues and cells involved.
Learning Activities
Virtual Slides: Blood | Histology Drawings
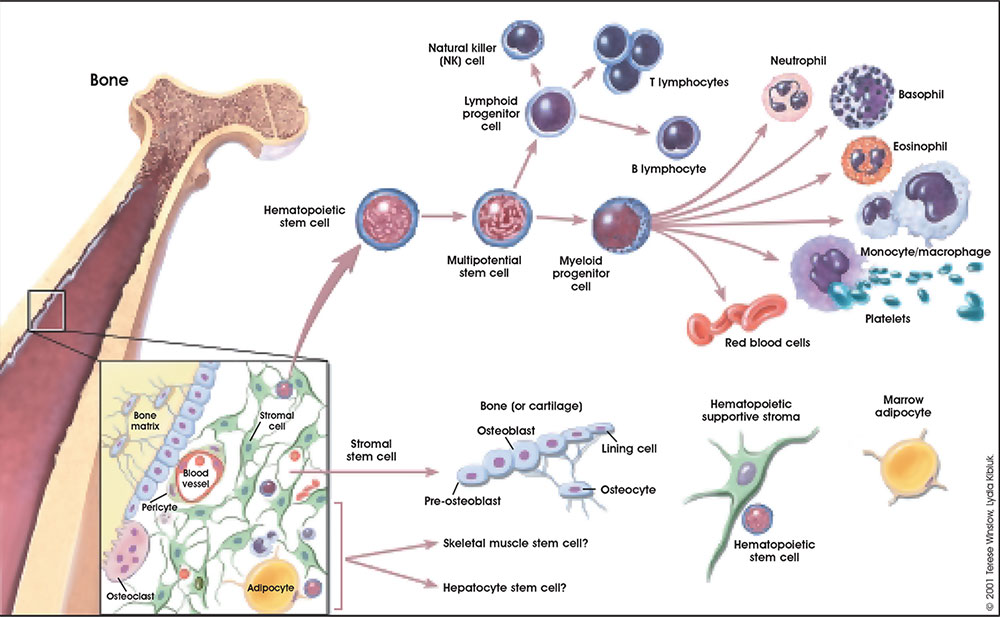
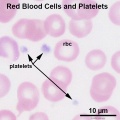
The circulating blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells (red and white blood cells), fragments of cells (platelets) and liquid (plasma). The different cell types are all derived from haemopoietic stem cells located in the bone marrow. Red blood cells (RBCs) have a metabolic role, in carrying oxygen to tissues and carbon dioxide to the lungs. White blood cells (WBCs or leukocytes) have a role in the body’s defence, and are an important clinical indicator of disease.
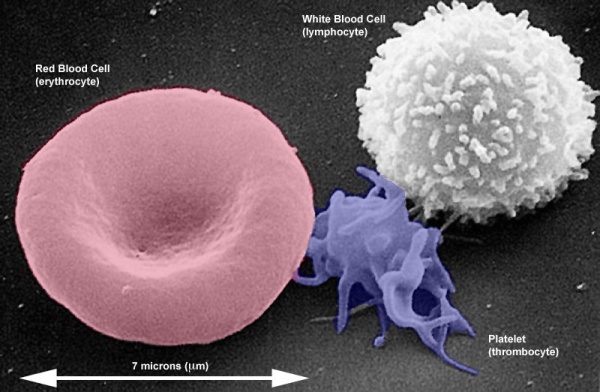
Scanning EM (coloured) of adult erythrocyte, thrombocyte and lymphocyte.
Showing relative sizes and morphologies. Remember a thrombocyte is not a cell, but circulating part or a fragment of a cell.
Virtual Slide - RBC
Virtual Slide Box: 1. Human Blood Smear Slide
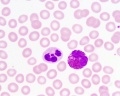
Find an area in the smear where the red blood cells are spread out and individual cells can be identified.
Identify:
- Red blood cells (7-8 um diameter anucleate biconcave disc)
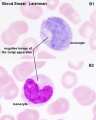
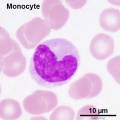
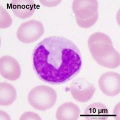
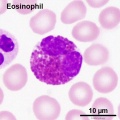
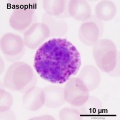
- White blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes (basophils are normally rare).
Note the presence or absence of granules, shape of the nucleus and relative cell sizes. Also identify platelets.
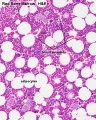
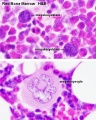
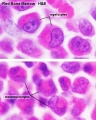
Virtual Slide Box: 2. Bone Marrow Smear Slide
- Do not attempt to identify all the cells in the bone marrow smear, but compare its appearance with that of the blood smear.
- Haematopoiesis (hematopoiesis) is the process of blood cell differentiation and occurs mainly in the bone marrow.
- This bone marrow smear will contain a large number of differentiating blood cells: band cells and normoblasts.
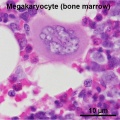
- The largest cells visible are megakaryocytes, which are responsible for platelet production.
Lymphocyte differentiation begins in the bone marrow and continues in central lymphoid organs (bone marrow - B cells and thymus - T cells), then in the peripheral lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen).
Blood Smear

|

|
| Blood Smear Slide (unstained)
|
Blood Smear Slide (stained)
|
Histology Stains
| Common Histology Stains
|
| Histology Stains - Common Stains and Their Reactions
|
| Stain
|
Nucleus
|
Cytoplasm
|
Collagen
|
RBCs
|
Other
|
| Haematoxylin
|
blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins - light blue
|
| Eosin
|
-
|
pink
|
pale pink
|
bright red
|
colloid - pinkmuscle - red
|
| Iron Haematoxylin
|
blue/black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
| Van Gieson
|
-
|
brown/yellow
|
red
|
yellow
|
muscle: yellow/browncartilage - pink
|
| Verhoeff's Elastin
|
black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres - black
|
| Tartrazine
|
-
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
|
| Silver Impregnation
|
-
|
-
|
grey/brown
|
-
|
reticular fibres - black
|
| Methyl Green
|
dark green
|
light green
|
light green
|
green
|
|
| Nuclear Fast Red
|
red
|
pink
|
pink
|
pink
|
|
| Gomori's Trichrome
|
purple/red
|
purple
|
green
|
red
|
keratin - redmuscle - purple/red
|
| Heidenhain's Azan
|
red
|
purple/red
|
deep blue
|
red
|
muscle - red
|
| Osmium Tetroxide
|
-
|
-
|
brown
|
brown
|
myelin, lipids - black
|
| Alcian Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins, - blue
|
| Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
|
-
|
-
|
pink
|
-
|
mucins, glycogen, glycocalyx - magenta
|
| Phosphotungstic Acid-Hematoxylin (PTAH)
|
blue
|
-
|
red
|
blue
|
muscle bands - blue
|
| Masson's Trichrome
|
blue/black
|
red
|
green/blue
|
red
|
cartilage, mucins - blue or green; muscle - red
|
| Luxol Fast Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
variable
|
myelin - blue
|
| Aldehyde Fuchsin
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres, mast cells - deep purple
|
| Light Green
|
-
|
-
|
light green
|
-
|
|
| Gallocyanin
|
dark blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
nucleic acids, Nissl granules - dark blue
|
| Romanowsky (e.g. Leishman's)
|
blue
|
pink
|
|
|
acidophils - red, basophils - blue, azurophilic - purple
|
| Aldehyde Pararosanilin
|
|
|
|
|
elastic fibres - purple
|
|
| Haematoxylin and Eosin
|
| One of the most common staining techniques in pathology and histology. Acronym "H and E" stain. (H&E, HE).
|
Haematoxylin
- Stains nuclei blue to dark-blue.
- Stains the matrix of hyaline cartilage, myxomatous, and mucoid material pale blue.
- Stains myelin weakly but is not noticeable if combined with eosin stain.
- combined with Orange G (H & Or. G.) instead of eosin, specifically stains the granules of acidophilic cells of the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary).
|
Eosin
- Stains cytoplasm pink to red; red blood cells are also bright red.
- Common counterstain to hematoxylin.
- Stain intensity varies with the formula as well as the fixative.
|
|
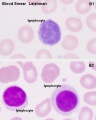
(Stain - Leishman) - Used to identify leucocytes and named after William Boog Leishman (1865 – 1926) was a Scottish pathologist.
- Methanol mixture of "polychromed" methylene blue (demethylated into various azures) and eosin.
- Methanol also acts as fixative.
- variations include Wright's stain (America) and Giemsa and May-Grünwald stains in Germany and Europe.
Blood Histology
- Circulating Blood
Red Blood Cells and Platelets
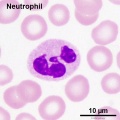
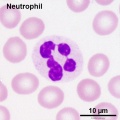
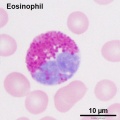
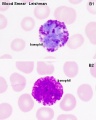
Neutrophil and Eosinophil
- Bone Marrow
Myelocyte and Metamyelocytes
Cell Histology Animation
|
|
Simple animation with cells labeled to help identify HE stain appearance and relative sizes.
Use the RBCs as a ruler.
|
Blood Cell Numbers
The adult ranges of cells / 1 litre (l), total blood volume is about 4.7 to 5 litres. Blood Development | Blood Histology
Red Blood Cells
- Male: 4.32 - 5.66 x 1012/l
- Female: 3.88 - 4.99 x 1012/l
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
- Male: 3.7 - 9.5 x 109/l
- Female: 3.9 - 11.1 x 109/l
Granulocytes
- 1.8 - 8.9 x 109/l
- Neutrophils: 1.5 - 7.4 x 109/l
- Eosinophils: 0.02 - 0.67 x 109/l
- Basophils: 0 - 0.13 x 109/l
Non-Granulocytes
- Monocytes 0.21 - 0.92 x 109/l
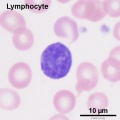
Lymphocytes
- 1.1 - 3.5 x 109/l
- B-cells: 0.06 - 0.66 x 109/l
- T-cells: 0.77 - 2.68 x 109/l
- CD4+: 0.53 - 1.76 x 109/l
- CD8+: 0.30 - 1.03 x 109/l
- NK cells: 0.20 - 0.40 x 109/l
Platelets
- 140 - 440 x 109/l
- not a cell, a cell fragment.
Terms
| Blood Terms
|
Cardiovascular System Development See also Heart terms, Immune terms and Blood terms.
- basophil - (basophil granulocyte) rare blood cell have 2 or 3 lobed nucleus and the nucleus may appear S-shaped. Cytoplasmic granules are stained deeply bluish or reddish-violetand fewer than those in eosinophils. Cells release vasoactive substances heparin and histamine that dilate blood vessels.
- blood islands - earliest sites of blood vessel and blood cell formation, seen mainly on yolk sac chorion.
- erythrocyte - (red blood cell) most abundant blood cell with no nucleus and cytoplasm contains haemoglobin.Cells are about 7 µm in diameter, "donut-shaped" and function to transport of oxygen.
- eosinophil (eosinophil granulocyte) blood cell nucleus has two lobes and cytoplasm filled with granules that stain red or pink when eosin. Cells involved with phagocytosis of antibody-antigen complexes, granules also contain histaminase and arylsufatase to degrade histamine and leukotrienes.
- extraembryonic mesoderm - mesoderm lying outside the trilaminar embryonic disc covering the yolk sac, lining the chorionic sac and forming the connecting stalk. Contributes to placental villi development.
- haemocytoblasts - stem cells for embryonic blood cell formation.
- growth factor - usually a protein or peptide that will bind a cell membrane receptor and then activates an intracellular signaling pathway. The function of the pathway will be to alter the cell directly or indirectly by changing gene expression. (eg VEGF, shh)
- leukocytes - subdivided into granular leukocytes (neutrophils, basophils and eosiniphils) and non-granular leukocytes (monocytes and lymphocytes).
- mesoderm - the middle layer of the 3 germ cell layers of the embryo. Mesoderm outside the embryo and covering the amnion, yolk and chorion sacs is extraembryonic mesoderm.
- monocyte - blood cell nucleus is C-shaped and cytoplasm slightly larger and stronger staining than granulocytes. Monocytes contain fine granules (lysosomes) and when leave the circulation and locate in tissues, differentiate into macrophages.
- neutrophil (neutrophil granulocytes) - most common granulocyte blood cell nucleus divided into 3-5 lobes connected by thin strands of chromatin. Cytoplasm contains two types of granules: primary granules (A granules, lysosomal enzymes) and Secondary granules (B granules, bactericidal enzymes).
- pericytes - (Rouget cells) cells located at the abluminal surface of microvessels close to endothelial cells, mainly found associated with CNS vessels and involved in vessel formation, remodeling and stabilization.
- platelets fragments of the cytoplasm from the bone marrow megakaryocyte (thrombocyte precursor cell).
- vascular endothelial growth factor - (VEGF) A secreted protein growth factor family, which stimulates the proliferation of vasular endotheial cells and therefore blood vessel growth. VEGF's have several roles in embryonic development. The VEGF family has 7 members (VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGF-E, VEGF-F, and PlGF) that have a common VEGF homology domain. PIGF is the placental growth factor. They act through 3 VEGF tyrosine kinase membrane receptors (VEGFR-1 to 3) with seven immunoglobulin-like domains in the extracellular domain, a single transmembrane region, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase sequence.
|
Course Links
Moodle - ANAT2241 - 2019
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains
|
| Histology Stains - Common Stains and Their Reactions
|
| Stain
|
Nucleus
|
Cytoplasm
|
Collagen
|
RBCs
|
Other
|
| Haematoxylin
|
blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins - light blue
|
| Eosin
|
-
|
pink
|
pale pink
|
bright red
|
colloid - pinkmuscle - red
|
| Iron Haematoxylin
|
blue/black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
| Van Gieson
|
-
|
brown/yellow
|
red
|
yellow
|
muscle: yellow/browncartilage - pink
|
| Verhoeff's Elastin
|
black
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres - black
|
| Tartrazine
|
-
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
yellow
|
|
| Silver Impregnation
|
-
|
-
|
grey/brown
|
-
|
reticular fibres - black
|
| Methyl Green
|
dark green
|
light green
|
light green
|
green
|
|
| Nuclear Fast Red
|
red
|
pink
|
pink
|
pink
|
|
| Gomori's Trichrome
|
purple/red
|
purple
|
green
|
red
|
keratin - redmuscle - purple/red
|
| Heidenhain's Azan
|
red
|
purple/red
|
deep blue
|
red
|
muscle - red
|
| Osmium Tetroxide
|
-
|
-
|
brown
|
brown
|
myelin, lipids - black
|
| Alcian Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
mucins, - blue
|
| Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
|
-
|
-
|
pink
|
-
|
mucins, glycogen, glycocalyx - magenta
|
| Phosphotungstic Acid-Hematoxylin (PTAH)
|
blue
|
-
|
red
|
blue
|
muscle bands - blue
|
| Masson's Trichrome
|
blue/black
|
red
|
green/blue
|
red
|
cartilage, mucins - blue or green; muscle - red
|
| Luxol Fast Blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
variable
|
myelin - blue
|
| Aldehyde Fuchsin
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
elastic fibres, mast cells - deep purple
|
| Light Green
|
-
|
-
|
light green
|
-
|
|
| Gallocyanin
|
dark blue
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
nucleic acids, Nissl granules - dark blue
|
| Romanowsky (e.g. Leishman's)
|
blue
|
pink
|
|
|
acidophils - red, basophils - blue, azurophilic - purple
|
| Aldehyde Pararosanilin
|
|
|
|
|
elastic fibres - purple
|
|
| Haematoxylin and Eosin
|
| One of the most common staining techniques in pathology and histology. Acronym "H and E" stain. (H&E, HE).
|
Haematoxylin
- Stains nuclei blue to dark-blue.
- Stains the matrix of hyaline cartilage, myxomatous, and mucoid material pale blue.
- Stains myelin weakly but is not noticeable if combined with eosin stain.
- combined with Orange G (H & Or. G.) instead of eosin, specifically stains the granules of acidophilic cells of the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary).
|
Eosin
- Stains cytoplasm pink to red; red blood cells are also bright red.
- Common counterstain to hematoxylin.
- Stain intensity varies with the formula as well as the fixative.
|
|
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 13) Embryology ANAT2241 Blood. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Blood
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G