User:Z3419587: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==Lab 7 Assessment== | |||
1. Identify and write a brief description of the findings of a recent research paper on development of one of the endocrine organs covered in today's practical. | |||
2. Identify the embryonic layers and tissues that contribute to the developing teeth. | |||
Tooth germ: aggregation of cells derived from the ectomesenchymal cells from neural crest and ectoderm of first arch. It is then organized into 3 components of the tooth germ, which are the enamel organ, dental papilla and dental follicle for the teeth development. | |||
Revision as of 01:10, 24 September 2014
Welcome to the 2014 Embryology Course!
- Links: Timetable | How to work online | One page Wiki Reference Card | Moodle
- Each week the individual assessment questions will be displayed in the practical class pages and also added here.
- Copy the assessment items to your own page and provide your answer.
- Note - Some guest assessments may require completion of a worksheet that will be handed in in class with your student name and ID.
| Individual Lab Assessment |
|---|
|
| Lab 12 - Stem Cell Presentation Assessment | More Info | |
|---|---|---|
| Group | Comment | Mark (10) |
| 1/8 |
|
7 |
| 2 |
|
7.5 |
| 3 |
|
7.5 |
| 4 |
|
8.5 |
| 5 |
|
8.5 |
| 6 |
|
8.5 |
| 7 |
|
7.5 |
Lab Attendance
Lab 1 --Z3419587 (talk) 12:45, 6 August 2014 (EST)
Lab 2 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:11, 13 August 2014 (EST)
Lab 3 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:12, 20 August 2014 (EST)
Lab 4 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:45, 27 August 2014 (EST)
Lab 5 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:02, 3 September 2014 (EST)
Lab 6 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:04, 10 September 2014 (EST)
Lab 7 --Z3419587 (talk) 11:05, 17 September 2014 (EST)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed
<pubmed>25084016</pubmed>
Lab 1 Assessment
<pubmed>25071849</pubmed> summary: This study was done to compare the clinical outcomes between fresh embryo transfers and frozen-thawed embryo transfers.
A total of 1891 cycle contains 1150 fresh embryo transfers and 741 frozen-thawed embryo transfers were studied. All data were transferred directly to SPSS 18 and analyzed.
A long gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist protocol was used in all cycles. Clinical pregnancy was defined by the observation of a gestational sac with or without a fetal heartbeat on ultrasound evaluation on the 30th day after embryo transfer. The number of sacs was taken as the number of implantations.
The results showed that there was a higher clinical pregnancy rate in fresh cleavage-stage embryo transfers than frozen-thawed cleavage-stage transfers but the clinical pregnancy rates were not different significantly.
<pubmed>25077107</pubmed>
summary:
The study was done to investigate the effect of vitamin D levels on implantation and clinical pregnancy rates in infertile women following in vitro fertilization (IVF).
173 women underwent IVF were included in the study under 3 criteria, including aged 18-41 years, follicle stimulating hormone level 12 IU/L or lower and able to provide informed consent. Vitamin D was determined by serum 25(OH)D levels and samples were collected before oocyte retrieval, while implantation was determined by the presence of a gestational sac, visible by ultrasonography.
χ2 and Student t tests or Mann-Whitney U tests were used to analyze categorical and continuous variables respectively. Multi-variable logistic regression was used to evaluate the relation between serum 25(OH)D level and implantation and clinical pregnancy after adjustment fpr parameters known to influence the IVF sucesss.
The results showed that women with sufficient levels of 25(OH)D had significantly higher rates of clinical pregnancy per IVF cycle started than that with insufficient levels. It also found that implantation rates were higher, but not statistically significant, in the sufficient 25(OH)D group. Therefore, the findings suggested that women with sufficient vitamin D levels are significantly more likely to achieve clinical pregnancy following IVF.
Lab 2 Assessment
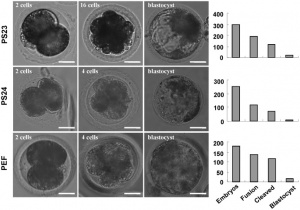
--Mark Hill (talk) 15:27, 22 August 2014 (EST) I have uploaded a smaller version of this image, but you still need to adjust the size as it appears on your page to 300px and include the reference. Please use jpg format images if possible. You need to reformat the reference as shown in the class tutorial.
Lab 3 Assessment
Neural development during fetal period
<pubmed>21042938</pubmed> <pubmed>12060827</pubmed> <pubmed>23727529</pubmed> <pubmed>16905335</pubmed> <pubmed>17848161</pubmed> <pubmed>18760424</pubmed> <pubmed>16971596</pubmed> <pubmed>17032846</pubmed>
Lab 4 Assessment
1. Identify a paper that uses cord stem cells therapeutically and write a brief (2-3 paragraph) description of the paper's findings. <pubmed>16099997</pubmed> summary: The paper presented the possibility of the therapeutic use of cord stem cells in Parkinson’s disease.
Human mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord were isolated and induced to transform into dopaminergic neurons in vitro. 12.7% of the cells were successfully transformed and generated through a stepwise culturing in neuron-conditioned medium, sonic hedgehog and FGF8. The cells were transplanted into the striatum of rats previously made Parkinsonian by unilateral striatal lesioning with the dopaminergic neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine HCl (6-OHDA). The effects of the transplantation were examined by quantification of rotations in response to amphetamine at 1, 2, 3 and 4 months after transplantation.
It was found that the transplantation of the stem cells corrected the lesion-induces amphetamine-evoked rotation and the cells in the striatum were still viable 4 months after transplantation. These results give the possibility to human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in treating Parkinson’s disease. However, it is suggested that the examination of the toxicity of growth factor and medium used is important, and the observation of the effects and side-effects for more than 1 year after transplantation is required before human studies
2. There are a number of developmental vascular "shunts" present in the embryo, that are closed postnatally. Identify these shunts and their anatomical location.
Ductus arteriosus: connection between the most cranial part of the pulmonary trunk and dorsal aorta
Ductus venosus: connection between the intra-abdominal umbilical vein and the inferior vena cava
Foramen ovale: located in interatrial septum, connecting left and right atria
Umbilical arteries: branch from the internal iliac arteries in the pelvis and connect to the placenta
Umbilical vein: connection between placenta and portal vein, or ductus venous
Lab 5 Assessment
Congenital Laryngeal Webs
Congenial laryngeal webs are caused by failure of recanalization of the laryngotracheal tube during the third month of gestation. Findings suggested that congenital laryngeal webs can be explained by abnormal development of the epithelial lamina, the laryngeal cecum, or the vestibulotracheal duct [1]. It has also been reported that there is an association between anterior webs, the most common laryngeal webs, with deletions of chromosome 22q11[2].
In human embryo, congenial laryngeal webs are formed during embryogenesis of the laryngotracheal groove [3]. The developing laryngeal is temporarily obliterated by actively proliferating epithelium, however, the lumen is normally re-established as the vocal cords. This abnormality is resulted from incomplete resorption of the epithelial layer during the 7th and 8th week of intrauterine development.
references:
Lab 7 Assessment
1. Identify and write a brief description of the findings of a recent research paper on development of one of the endocrine organs covered in today's practical.
2. Identify the embryonic layers and tissues that contribute to the developing teeth.
Tooth germ: aggregation of cells derived from the ectomesenchymal cells from neural crest and ectoderm of first arch. It is then organized into 3 components of the tooth germ, which are the enamel organ, dental papilla and dental follicle for the teeth development.