Musculoskeletal System - Abnormalities: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* '''Essentials of Human Embryology''' Larson Chapter 11 p207-228 | * '''Essentials of Human Embryology''' Larson Chapter 11 p207-228 | ||
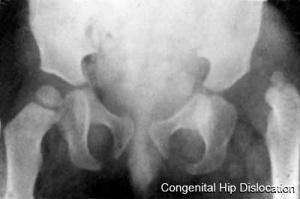
== | ==Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip== | ||
[[File:Congenital dislocation hip.jpg|thumb|File:Congenital dislocation hip]] | |||
===Barlow test=== | |||
(Barlow maneuver) A clinical term to describe a physical examination of the newborn for [[D#developmental dysplasia of the hip|developmental dysplasia of the hip]] (DDH). The examiner adducts the hip (bringing the thigh towards the midline) while applying light pressure on the knee, directing the force posteriorly. A positive sign is the hip being dislocatable, if the hip can be popped out of socket with this test. This test is then combined with the [[O#Ortolani test|Ortolani test]] (maneuver). The test is named after Thomas Barlow (1845 – 1945) a British royal physician. | |||
==Computer Activities== | ==Computer Activities== | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 3 June 2010
Introduction
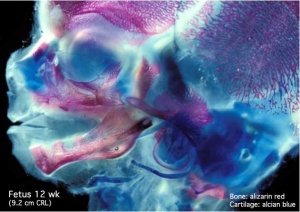
There are a large number of different musculoskeletal abnormalities affecting one or a combination of bone and muscle development in the skull, trunk and limbs. This page therefore can only broadly introduce the topic.
Musculoskeletal and limb disorders together form the largest group of congenital defects that occur in Australia. Some defects appear as obvious malformations, such as syndactyly and limb reductions. Other muscular defects only become obvious postnatally when the muscles are required to be used, those in highest use are respiratory (diaphragm, intercostals) and anti-gravity (those that hold you upright) muscles.
| System Links: Introduction | Cardiovascular | Coelomic Cavity | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal Tract | Genital | Head | Immune | Integumentary | Musculoskeletal | Neural | Neural Crest | Placenta | Renal | Respiratory | Sensory | Birth |
--Mark Hill 09:25, 14 April 2010 (EST) Page Template only - content from original UNSW Embryology site currently being edited and updated.
Some Recent Findings
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 15 the skeletal system
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 11 Limb Dev (bone not well covered in this textbook)
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 16,17: p379-397, 399-405
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Chapter 11 p207-228
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
Barlow test
(Barlow maneuver) A clinical term to describe a physical examination of the newborn for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). The examiner adducts the hip (bringing the thigh towards the midline) while applying light pressure on the knee, directing the force posteriorly. A positive sign is the hip being dislocatable, if the hip can be popped out of socket with this test. This test is then combined with the Ortolani test (maneuver). The test is named after Thomas Barlow (1845 – 1945) a British royal physician.
Computer Activities
Development Overview
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search April 2010
- Musculoskeletal System Development - All (44637) Review (5065) Free Full Text (6601)
- Musculoskeletal Development - All (44637) Review (5065) Free Full Text (6601)
Search Pubmed: musculoskeletal system abnormalities
Additional Images
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology Musculoskeletal System - Abnormalities. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Musculoskeletal_System_-_Abnormalities
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G