Mitochondria: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:Swapping mitochondrial DNA mammalian oocytes.jpg|400px]] | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Molecular_Development_-_Genetics|Genetics]] | Swapping mitochondrial DNA mammalian oocytes<ref><pubmed>19759608</pubmed></ref> | ||
:'''Links:''' [[Molecular_Development_-_Genetics|Genetics]] | [[Assisted Reproductive Technology]] | |||
== History Mitochodria== | == History Mitochodria== | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 11 October 2013
Introduction
Swapping mitochondrial DNA mammalian oocytes[1]
- Links: Genetics | Assisted Reproductive Technology
History Mitochodria
1857 Kölliker discovers mitochondria in muscle
1929 Karl Lohmann discovered ATP
1940s and 1950s ATP is formed in cell respiration in mitochondria and photosynthesis in chloroplasts of plants
1960 Efraim Racker and co-workers isolated, from mitochondria, the enzyme "F o F 1 ATPase" now call ATP synthase
1963 There’s DNA in those organelles DNA is directly visualized in first chloroplasts and then mitochondria, from the JCB Archive.
1992 Wallace identified degenerative disease caused by mtDNA mutations
1997 Nobel Prize in Chemistry - The three laureates have performed pioneering work on enzymes that participate in the conversion of the "high-energy" compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Paul D. Boyer and John E. Walker "for their elucidation of the enzymatic mechanism underlying the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)"
- Jens C. Skou "for the first discovery of an ion-transporting enzyme, Na+, K+ -ATPase
Evolution Mitochondria
- primitive Eubacterium
- symbiotic relationship with eukaryotic cell
- circular DNA
- see antibiotic-induced deafness due to similarity of mitochondrial and bacterial ribosomes
- genes transferred to nucleus
- mitochondrial genome bp
- 366,924 Arabidopsis
- 16,569 Human
- 5966 Plasmodium
Mitochondrial Genome
- In humans this genome is maternally inherited.
- Exists as multiple copies within the matrix of each mitochondrion within the cytoplasm of cells.
- In 1981 the human mitochondrial genome was sequenced.
- The genome is a small circular DNA molecule 16,568 bp in length containing 37 genes.
- 24 genes specify RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis (22 transfer RNAs (tRNA) and 2 ribosomal RNAs (rRNA))
- 13 genes encode proteins required for the biochemical reactions that make up respiration.
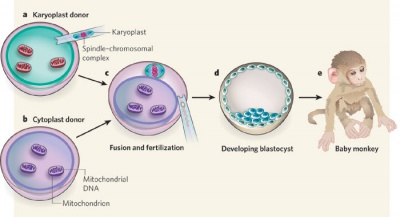
Spindle Transfer
(ST) An Assisted Reproductive Technology term referring to the transfer of the metaphase II-arrested (MII) spindle-chromosomal complex isolated as a karyoplast from a donor oocyte to the cytoplasm of a second recipient oocyte. The term cytoplast refers to the enucleated recipient oocyte. This technique has been suggested as a clinical solution to mitochondrial inherited disorders.
- Links: Assisted Reproductive Technology | Mitochondrial DNA Deletion Syndromes | PMID 20539289
References
- ↑ <pubmed>19759608</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Mitochondria
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 5) Embryology Mitochondria. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Mitochondria
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G