File:Human placenta vascular MRI 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Human Placenta Vascular Bed - Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)== | |||
Placenta is viewed from the fetal side of the placenta using MRI imaging. Chorionic artery and its branches have been colour coded. | |||
{{Placenta vascular bed links}} | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Methodology technical information | |||
|- | |||
| 3D reconstruction made using Osirix software viewed from the fetal side of the placenta. | |||
:"A placenta was harvested immediately after elective caesarean section and placed in a water bath at 37°C. The umbilical cord was cut off approximately 5 cm proximal to the insertion to the placenta. The amnion was cut off as well. The blood vessels of the umbilical cord were catheterized using three venous catheters (size 17). The venous catheters were fixed to the blood vessels using polyester sutures (2-0 Ethicon) and the umbilical cord was clamped using a suture to prevent reflux of the injected solutions. The placenta was then perfused using saline with 5000 IU/L heparin [11]. The solution was heated to 37°C and 500 mL was injected into the two umbilical arteries with a pressure-controlled pump using the sphygmanometric principle. Contrast mix 1 was then injected using the pump with a pressure ≤ 60 mmHg [12]. During injection, the placenta was placed in a water bath at a temperature of 35-40°C to ensure that the contrast solution remained liquid. It was then positioned in the MR scanner and the 3D MRA protocol was followed by subsequent fixation with 4% formalin or 2.8% FineFix (Milestone Medical Technologies, USA). MRA showed vessels from a number of different generations starting with the cotelydonary arteries branching off into primary, secondary and tertiary stem vessels: even 6th generation blood vessels were visible. Subsequently, the placenta was subjected to CTA (Figure 4), which also showed branching of the vessels down to the 6th generation of stem vessels. In general, MRA was capable of showing considerably more very small vessels than CTA, giving the overall impression that the quality of MRA was as good or better than the results of conventional CTA." | |||
(text from original reference) | |||
|} | |||
{{Placenta Links}} | |||
===Reference=== | |||
{{#pmid:20226038}} | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
© 2010 Rasmussen et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | |||
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | |||
Original file name: Figure 4. 1472-6793-10-3-4-l.jpg (original figure has been cropped, resized and relabeled) | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Human]] [[Category:Placenta]] [[Category:Magnetic Resonance Imaging]] [[Category:Cardiovascular]] [[Category:Magnetic Resonance Imaging]] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:15, 21 March 2018
Human Placenta Vascular Bed - Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Placenta is viewed from the fetal side of the placenta using MRI imaging. Chorionic artery and its branches have been colour coded.
- Vascular Bed Links: Image - MRA and CTA | Image - magnetic resonance | Image - magnetic resonance labeled | Image - computed tomography | Placenta - Vascular Beds | Placenta Development
| Methodology technical information |
|---|
3D reconstruction made using Osirix software viewed from the fetal side of the placenta.
(text from original reference) |
Reference
Rasmussen AS, Lauridsen H, Laustsen C, Jensen BG, Pedersen SF, Uhrenholt L, Boel LW, Uldbjerg N, Wang T & Pedersen M. (2010). High-resolution ex vivo magnetic resonance angiography: a feasibility study on biological and medical tissues. BMC Physiol. , 10, 3. PMID: 20226038 DOI.
Copyright
© 2010 Rasmussen et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Original file name: Figure 4. 1472-6793-10-3-4-l.jpg (original figure has been cropped, resized and relabeled)
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 26) Embryology Human placenta vascular MRI 02.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Human_placenta_vascular_MRI_02.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:07, 18 May 2013 | 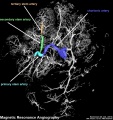 | 938 × 1,000 (156 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: