File:Extravillous trophoblast cartoon.jpg
Original file (1,028 × 829 pixels, file size: 249 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
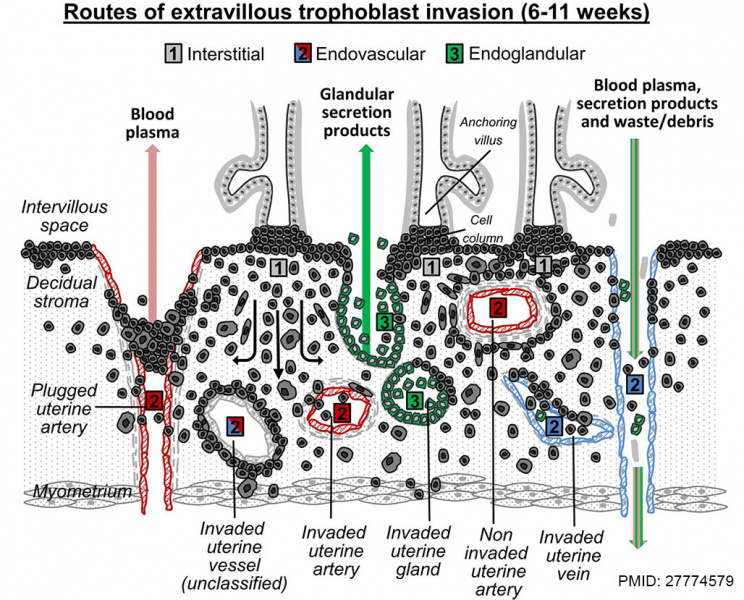
Extravillous Trophoblast (EVT)
Invasion in first trimester human placenta. EVTs originate from cell columns of anchoring villi. During the first trimester of pregnancy, EVTs invade into the decidual interstitium (1) reaching the inner third of the myometrium, thereby anchoring the placenta to the uterus. They also follow the (2) endovascular route of invasion, plug, line and remodel spiral arteries (2, red), thus being responsible for the establishment of the maternal–fetal blood flow starting with the beginning of the second trimester.
Prior to the opening of spiral arteries toward the intervillous space, maternal blood plasma is seeping through the trophoblastic plugs. Endovascular trophoblasts also reach and invade uterine veins and replace the venous endothelium (2, blue). Via the opened and dilated veins, maternal blood plasma and glandular secretion products are drained from the intervillous space into the maternal circulation. Endovascular trophoblasts invade and replace the tunica media of vessels, which in some cases leads to the fact that classification into artery or vein is no longer possible (2, red and blue). Endoglandular trophoblasts (3) are situated nearby uterine glands, replace the glandular epithelium and open the lumen of uterine glands toward the intervillous space.
Reference
<pubmed>27774579</pubmed>
Copyright
© The Author(s) 2016 Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. Fig. 8 adjusted in size and labelled with PMID. Figure Scheme adapted from (Moser et al. 2015 PMID 26493408).
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Extravillous trophoblast cartoon.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Extravillous_trophoblast_cartoon.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:25, 5 June 2017 |  | 1,028 × 829 (249 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 14:24, 5 June 2017 |  | 2,092 × 1,805 (736 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | Extravillous trophoblast (EVT)== Invasion in first trimester human placenta. EVTs originate from cell columns of anchoring villi. During the first trimester of pregnancy, EVTs invade into the decidual interstitium (1) reaching the inner third of the m... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.