2010 Lecture 11
Head Development
Introduction
The face is the anatomical feature which is truly unique to each human, though the basis of its general development is identical for all humans and similar to that seem for other species. The face has a complex origin arising from a number of head structures and sensitive to a number of teratogens during critical periods of its development. The related structures of upper lip and palate significantly contribute to the majority of face abnormalities.
The head and neck structures are more than just the face, and are derived from pharyngeal arches 1 - 6 with the face forming from arch 1 and 2 and the frontonasal prominence. Each arch contains similar Arch components derived from endoderm, mesoderm, neural crest and ectoderm. These components though will form different structures depending on their arch origin. Because the head contains many different structures also review notes on Special Senses (Sensory System Development), Respiratation ([[Respiratory System Development]), Integumentary (Teeth), Endocrine (Endocrine System Development thyroid, pituitary) and Ultrasound - Cleft lip/palate.
Lecture Objectives
- List the main structures derived from the pharyngeal arches, pouches and clefts.
- Know the stages and structures involved in the development of the face.
- Predict the results of abnormal development of the face and palate.
- Briefly summarise the development of the tongue.
Textbook References
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240.
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418.
Animation of Face Development
| <Flowplayer width="420" height="500" autoplay="true">Face_001.flv</Flowplayer> |
Development of the Face
The separate embryonic components that contribute to the face have been colour coded.
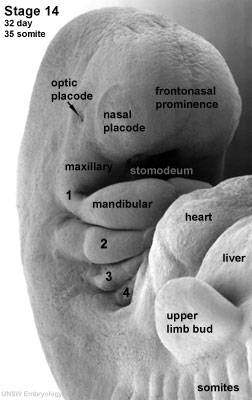
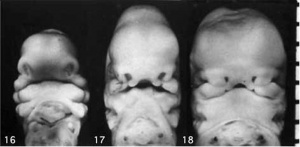
The stomodeum is the primordial mouth region and a surface central depression lying between the forebrain bulge and the heart bulge. At the floor of the stomodeum indentation is the buccopharyngeal membrane (oral membrane). Note the complex origin of the maxillary region (upper jaw) requiring the fusion of several embryonic elements, abnormalities of this process lead to cleft lip and cleft palate. See also the movie (Quicktime | Flash) showing a similar view of human embryo faces between Carnegie stage 16 to 18.
|
Terms
palate
- The roof of the mouth (oral cavity) a structure which separates the oral from the nasal cavity. Develops as two lateral palatal shelves which grow and fuse in the midline. Initally a primary palate forms with fusion of the maxillary processes with the nasal processes in early face formation. Later the secondary palate forms the anterior hard palate which will ossify and separate the oral and nasal cavities. The posterior part of the palate is called the soft palate (velum, muscular palate) and contains no bone. Abnormalities of palatal shelf fusion can lead to cleft palate. (More? Head | Head Abnormalities | Medline Plus - Cleft Lip and Palate)
palatogenesis
- The process of palate formation, divided into primary and secondary palate development. (More? Head | Head Abnormalities | Medline Plus - Cleft Lip and Palate)
pharyngeal arch
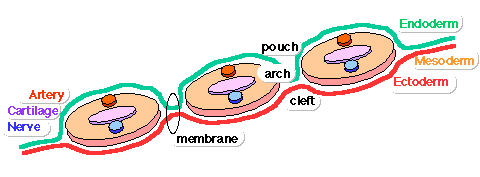
- (branchial arch, Greek, branchial = gill) These are a series of externally visible anterior tissue bands lying under the early brain that give rise to the structures of the head and neck. In humans, five arches form (1,2,3,4 and 6) but only four are externally visible on the embryo. Each arch has initially identical structures: an internal endodermal pouch, a mesenchymal (mesoderm and neural crest) core, a membrane (endoderm and ectoderm) and external cleft (ectoderm). Each arch mesenchymal core also contains similar components: blood vessel, nerve, muscular, cartilage. Each arch though initially formed from similar components will differentiate to form different head and neck structures. (More? | Head Development | Endocrine | Neural Crest)
pharyngeal arch artery
- Each early developing pharyngeal arch contains a lateral pair of arteries arising from the aortic sac, above the heart, and running into the dorsal aorta. later in development these arch arteries are extensively remodelled to form specific components of the vascular system. Pharyngeal Arch 1 arteries are mainly lost and forms part of maxillary artery. Pharyngeal Arch 2 arteries remains to form the stapedial arteries. Pharyngeal Arch 3 arteries forms the common carotid arteries, internal carotid arteries in the neck. Pharyngeal Arch 4 arteries will form part of aortic arch (left arch artery) and part right subclavian artery (right arch artery) Pharyngeal Arch 6 arteries form part of left pulmonary artery (left arch artery) and part of right pulmonary artery (right arch artery). (More? | Head Development | Cardiovascular)
pharyngeal arch cartilage
- Each early developing pharyngeal arch contains a horseshoe shaped band of cartilage that acts as a template and contributes to the development of head and neck bony and cartilagenous features, including the middle ear bones. Pharyngeal Arch 1 cartilage (Meckel’s cartilage) dorsal ends form malleus and incus midpart forms ligaments (ant. malleus, sphenomandibular) ventral part forms mandible template. Pharyngeal Arch 2 cartilage (Reichert’s cartilage) dorsal ends form stapes and Temporal bone styloid process, ventral part ossifies to form hyoid bone components, lesser cornu and superior body. Pharyngeal Arch 3 cartilage forms hyoid components, greater cornu and inferior part of hyoid. Pharyngeal Arch 4 and 6 cartilage forms laryngeal cartilages except epiglottis (from hypobranchial eminence). (More? | Head Development | Middle Ear)
pharyngeal arch nerve
- Each early developing pharyngeal arch contains the developing cranial nerves, as a pair, within the arch mesenchyme. Each cranial nerve is numbered (roman numeral) in rostrocaudal sequence and also has a specific name. The cranial nerve within each arch often relates to the other structures formed from taht arch. Pharyngeal Arch 1 contains the trigeminal nerve (CN V, cranial nerve 5). Pharyngeal Arch 2 contains the facial nerve (CN VII, cranial nerve 7). Pharyngeal Arch 3 contains the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX, cranial nerve 9) Pharyngeal Arch 4 and 6 contains the Vagus (CN X cranial nerve 10), forming the adult superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches. (More? | Head Development | Neural | Neural Crest)
pharyngeal arch pouch
- An out-pocketing of the endoderm lined pharynx occurring between each developing pharyngeal arch. Each of the pharyngeal arch pouches contributes different components of the head and neck, either cavities or endocrine tissues. Pharyngeal Arch 1 pouch elongates to form tubotympanic recess tympanic cavity, mastoid antrum and auditory tube (Eustachian tube). Pharyngeal Arch 2 pouch forms the tonsillar sinus and is later mostly oblierated by palatine tonsil. Pharyngeal Arch 3 pouch forms the inferior parathyroid and thymus. Pharyngeal Arch 4 pouch forms the superior parathyroid, parafollicular cells of Thyroid. (More? Middle Ear | Thyroid | Parathyroid | Thymus | Endocrine | Head Development
pharyngotympanic tube
- (auditory tube, eustachian tube, otopharyngeal tube) A narrow canal connecting the middle ear space to the back of the oral cavity. The tube allows ventilation, protection and clearance for the middle ear cavity. Ventilation is the pressure equalization in the middle ear. Clearance is to allow fluid drainage from the middle ear. Embryonic origin is from the first pharyngeal pouch. In development, the canal is initially both horizontal, short and very narrow leading to poor drainage and easy blockage. (More? Middle Ear | Hearing | Hearing Abnormalities)
pharynx
- (throat) Forms the initial segment of the upper respiratory tract divided anatomically into three regions: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). Anatomically extends from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. (More? Respiratory System Development)
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2010
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Lab 1 | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Integumentary | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology 2010 Lecture 11. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Lecture_11
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G