Endocrine - Parathyroid Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:Parathyroid adult.jpg|thumb|Parathyroid adult]] | [[File:Parathyroid adult.jpg|thumb|Parathyroid adult]] | ||
[[2009_Lecture_11|Lecture - Head Development]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine17.htm | {{Template:Endocrine Links}} | [[2009_Lecture_11|Lecture - Head Development]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine17.htm original page] | ||
* Parathyroid Hormone - Increase calcium ions [Ca2+], stimulates osteoclasts, increase Ca GIT absorption (opposite effect to calcitonin) | * Parathyroid Hormone - Increase calcium ions [Ca2+], stimulates osteoclasts, increase Ca GIT absorption (opposite effect to calcitonin) | ||
Revision as of 14:01, 25 April 2010
Introduction
| Lecture - Head Development | original page
- Parathyroid Hormone - Increase calcium ions [Ca2+], stimulates osteoclasts, increase Ca GIT absorption (opposite effect to calcitonin)
- Adult Calcium and Phosphate - Daily turnover in human with dietary intake of 1000 mg/day
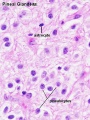
- secreted by chief cells
Principal cells cords of cells
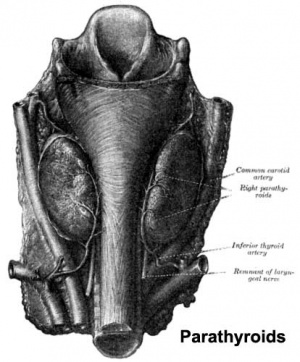
Parathyroid Development
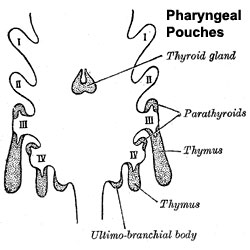
- Endoderm - third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, could also have ectoderm and neural crest
- 3rd Pharyngeal Pouch - inferior parathyroid, initially descends with thymus
- 4th Pharyngeal Pouch - superior parathyroid
- Week 6 - diverticulum elongate, hollow then solid, dorsal cell proliferation
- Fetal parathyroids - respond to calcium levels, fetal calcium levels higher than maternal
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search April 2010
- Endocrine Development - All (14277) Review (4620) Free Full Text (3140)
Search Pubmed: parathyroid development
Additional Images
Adult Histology
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Endocrine - Parathyroid Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Endocrine_-_Parathyroid_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G