Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis
Introduction
These resources give a general introduction to some of the many new prenatal genetic diagnostic techniques available at different stages of pregnancy. These diagnostic techniques now include Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) in association with the many Assisted Reproductive Technologies, more commonly known as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Some Recent Findings
|
Preimplantation Genetic Screening
A range of techniques including fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-based testing, PCR amplification-based testing and both polar body and embryo biopsy for PGD/preimplantation genetic screening (PGS).
- Links: In Vitro Fertilization
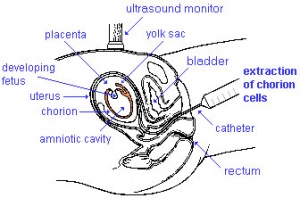
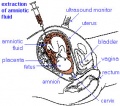
Biological Collection Techniques
Cordocentesis
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS, fetal blood sampling, umbilical vein sampling) This chromosome analysis test is done at in the 18th week or later of high-risk pregnancies. The technique may be used when either alternative tests (amniocentesis, CVS, ultrasound) are either inconclusive or not achievable (severe oligohydramnios).
The risk of a miscarriage related to the test is about 3 per cent (occurring in 3 in 100 pregnancies).
Coelocentesis
Is a technique of sampling of extracoelomic fluid usually for an early prenatal diagnostic technique.
Fetal Fibronectin
As a prenatal diagnostic test, a positive fetal fibronectin test result can indicate a higher risk of preterm delivery, but may also has false positive results. The negative result is more reliable as an indicator of reduced risk of preterm birth.
(fFN) is an extracellular matrix glycoprotein produced by fetal cells. Fetal fibronectin appears to act as an adhesive between the interface of the chorion and the decidua (fetal membrane and uterine lining).
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
This technique has several diagnostic and screening applications including:
- embryo sexing for X-linked diseases
- embryo sexing for social reasons (gender selection/family balancing)
- inherited chromosome rearrangements
- aneuploidy screening (PGS)
The following information for probe selection is based upon the European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) PGD Consortium set of Guidelines for Best Practice PGD. The guidelines were first published in 2005 and recently updated in 2010.
Embryo Sexing
A probe set containing at least probes specific for the centromere regions of the X and Y chromosomes, and one autosome.
Chromosome Rearrangements
A probe set should at least contain sufficient probes to detect all expected unbalanced forms of the chromosomal rearrangement.
Comparative Genomic Hybridization
This new test under development is based upon microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH).
All fetal cells should have complete copies of maternal and paternal genomes. The test compares regions of fetal DNA that deviate from this "pattern" due to either too much or too little DNA, alterations reflect regions of the genome that are either copied or deleted. These genetic changes may therefore cause disease. (More? Prenatal Diagnosis - Comparative Genomic Hybridization)
Gene Tests
A new site developed by NIH "GeneTests" provides medical genetics information resources available at no cost to all interested persons. It contains educational information, a directory of genetic testing laboratories and links to other databases such as OMIM.
Links: GeneTests
Ethics of Testing
Major developmental abnormalities detected early enough can be resolved far more easily than those discovered late in a pregnancy.
What are the ethical questions that are raised by prenatal testing? Future individual rights or parents rights? But what about diseases, like Huntington's, where a diagnostic test can be made but there are no current treatments for the postnatal (95% of cases adult onset) disease?
Huntington's disease
Guidelines for the molecular genetics predictive test
- Recommendation 2.1 "the test is available only to individuals who have reached the age of majority."
- Recommendation 7.2 "the couple requesting antenatal testing must be clearly informed that if they intend to complete the pregnancy if the fetus is a carrier of the gene defect, there is no valid reason for performing the test."
- ART - Assisted Reproductive Technology a general term to describe all the clinical techniques used to aid fertility.
- blastomere biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at cleavage stage (day 3), excluding poor quality embryos, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin. May not detect cellular mosaicism in the embryo.
- blastocyst biopsy - An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique carried out at blastocyst stage (day 4-5), removes several trophoblast (trophoderm) cells, detects chromosomal abnormalities of both maternal and paternal origin and may detect cellular mosaicism.
- cell-free fetal deoxyribonucleic acid - (cfDNA) refers to fetal DNA circulating and isolated from the plasma portion of maternal blood. Can be performed from GA 10 weeks as a first-tier test or as a second-tier test, with women with increased probability on combined first trimester screening offered cfDNA or diagnostic testing.
- false negative rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test negative given that the congenital anomaly is present.
- false positive rate - The proportion of pregnancies that will test positive given that the congenital anomaly is absent.
- free β human chorionic gonadotrophin - beta-hCG subunit of hCG used as a diagnostic marker for: early detection of pregnancy, Trisomy 21, spontaneous abortion, ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma.
- multiples of the median - (MoM) A multiple of the median is a measure of how far an individual test result deviates from the median and is used to report the results of medical screening tests, particularly where the results of the individual tests are highly variable.
- negative predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is absent given that the prenatal screening test is negative.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing - (NIPT) could refer to ultrasound or other imaging techniques, but more frequently used to describe analysis of cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood.
- polar body biopsy - (PB biopsy) An ART preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique that removes either the first or second polar body from the zygote. As these are generated by oocyte meiosis they detects chromosomal abnormalities only on the female genetics.
- positive predictive value - The probability that a congenital anomaly is present given that the prenatal screening test is positive.
- pre-implantation genetic diagnosis - (PGD, pre-implantation genetic screening) a diagnostic procedure for embryos produced through Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART, in vitro fertilisation, IVF) for genetic diseases that would generate developmental abnormalities or serious postnatal diseases.
- prenatal screening sensitivity - (detection rate) The probability of testing positive on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is present.
- prenatal screening specificity - The probability of testing negative on a prenatal screening test if the congenital anomaly is absent.
- quadruple test (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
- single nucleotide polymorphisms - (SNPs) the variation in a single DNA nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome.
- triple test - (maternal serum testing of a-fetoprotein Template:AFP, free B-hCG or total hCG, and unconjugated estriol) is a fetal chromosomal anomaly test usually carried out later in pregnancy (GA 14 to 20 weeks).
| Other Terms Lists |
|---|
| Terms Lists: ART | Birth | Bone | Cardiovascular | Cell Division | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal | Genital | Genetic | Head | Hearing | Heart | Immune | Integumentary | Neonatal | Neural | Oocyte | Palate | Placenta | Radiation | Renal | Respiratory | Spermatozoa | Statistics | Tooth | Ultrasound | Vision | Historic | Drugs | Glossary |
References
Journals
Reviews
<pubmed>20494259</pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>19795450</pubmed> <pubmed>15127362</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search PubMed: Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis | Prenatal Genetic Screening
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Prenatal_Genetic_Diagnosis
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G