Gastrointestinal Tract - Pancreas Histology
| Embryology - 28 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
This section of notes provides an overview mainly of adult pancreas histology, see also Pancreas Development notes.
Page also provides further histology background information for Medicine phase 1 Health Maintenance B Practical Virtual Slides. This page content is not part of the HMB practical class.
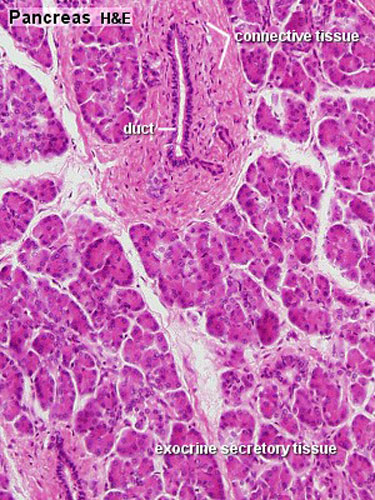
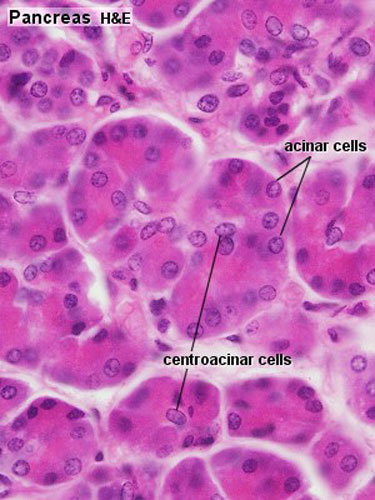
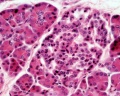
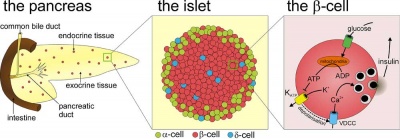
- exocrine pancreas consists of tubuloacinar glands.
- single layer of pyramidal shaped cells forms the secretory acini (cells contain zymogen granules).
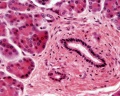
- Secretory duct pathway:
- Intercalated Duct
- Intralobular Duct (low columnar or cuboidal epithelium, non-striated)
- Interlobular Duct (columnar epithelium + goblet cells)
- Main Pancreatic Duct
Histology Images
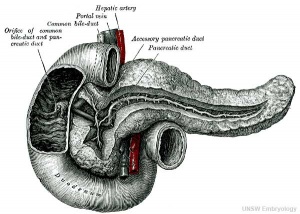
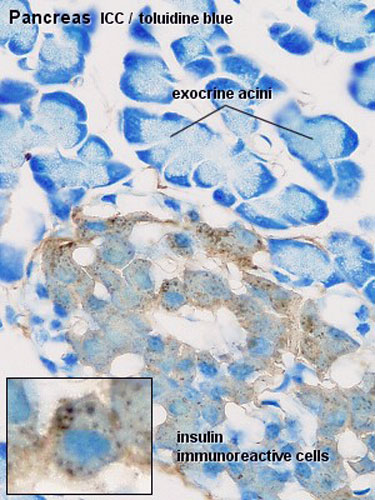
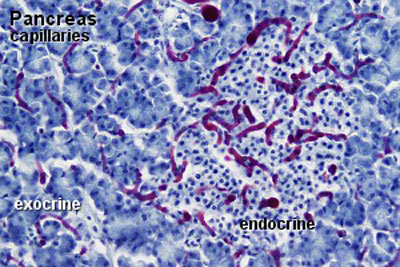
- Pancreas Histology Links: overview (label) | exocrine (label) | endocrine (label) | blood vessels (label) | insulin (label) | overview | exocrine | endocrine | blood vessels | insulin | Islet labeled for insulin and Glucagon | Insulin (Fl) | Glucagon (Fl) | GIT Histology
Development Histology
Adult Histology
Unlabeled Large Images
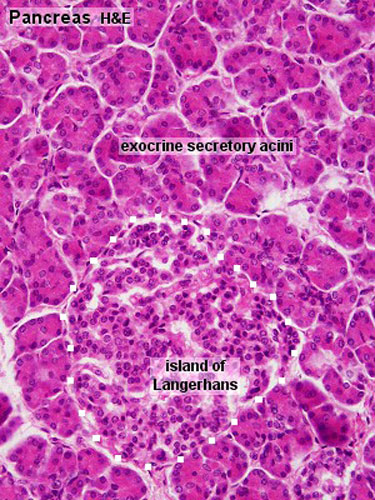
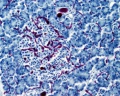
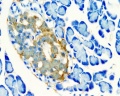
Pancreatic Islets
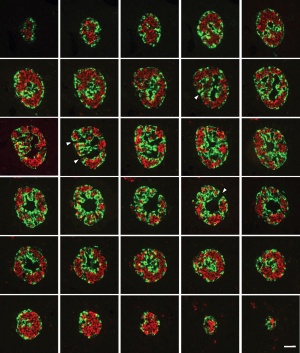
The pancreatic islets (Islets of Langerhans) contain four distinct endocrine cell types.
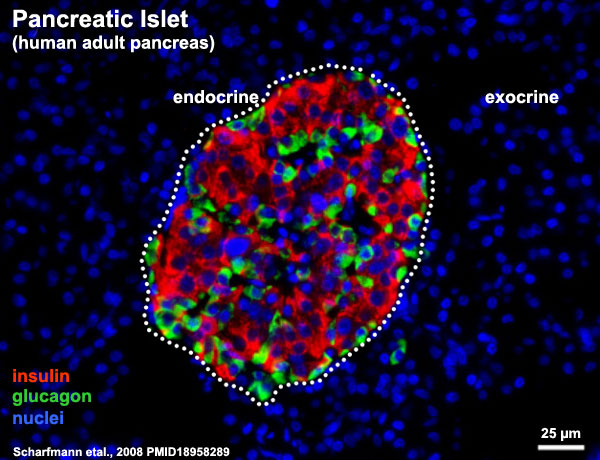
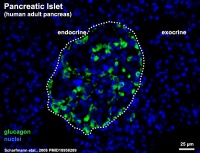
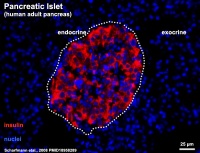
Cytoarchitecture of Islets from adult human Pancreas[1] See also a recent paper on the organisation of these cells in human islets of Langerhans.[2] Image - Three-dimensional analysis of human pancreatic islets |
Section of an adult human pancreas stained for glucagon (green) and insulin (red).
Scale bars: 25 µm. |
Alpha Cells
|
Beta Cells
|
Delta Cells
|
F-cells
|
References
- ↑ Scharfmann R, Xiao X, Heimberg H, Mallet J & Ravassard P. (2008). Beta cells within single human islets originate from multiple progenitors. PLoS ONE , 3, e3559. PMID: 18958289 DOI.
- ↑ Bosco D, Armanet M, Morel P, Niclauss N, Sgroi A, Muller YD, Giovannoni L, Parnaud G & Berney T. (2010). Unique arrangement of alpha- and beta-cells in human islets of Langerhans. Diabetes , 59, 1202-10. PMID: 20185817 DOI.
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Blue Histology Pancreas
- UNSW Virtual Slides Medicine phase 1 Health Maintenance B Pancreas Practical (requires login for access).
- UIOWA Virtual Slidebox of Histology Pancreas
- Who named it? Paul Langerhans (1847 - 1888)
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 28) Embryology Gastrointestinal Tract - Pancreas Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Gastrointestinal_Tract_-_Pancreas_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G