Book - Liver development
| Embryology - 14 Mar 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Zorn AM. (2008). Liver development. , , . PMID: 20614624 DOI. | online extract | PDF
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
Liver Development
Aaron M. Zorn
Division of Developmental Biology, Cincinnati Children’s Research Foundation, Cincinnati, Ohio 45229-3039, USA
Abstract
The liver is the largest internal organ and it provides many essential metabolic, exocrine and endocrine functions. Hepatocytes are the principal cell type in the liver and these along with biliary epithelial cells are derived from the embryonic endoderm. Embryological experiments in animal models have demonstrated that liver development occurs through a progressive series of reciprocal tissue interactions between the embryonic endoderm and nearby mesoderm. In the last ten years many of the genes and molecular pathways that regulate hepatogenesis have been identified. Recently application of this knowledge has enabled researchers to produce “hepatic-like” tissue from embryonic stem (ES) cells in vitro, which may ultimately lead to therapeutically useful tissue for transplantation. This review summarizes the current understanding of the molecular pathways controlling liver and biliary system development focusing on studies in the mouse embryo where this process is best understood.
Full chapter - Liver Development (2008) PDF
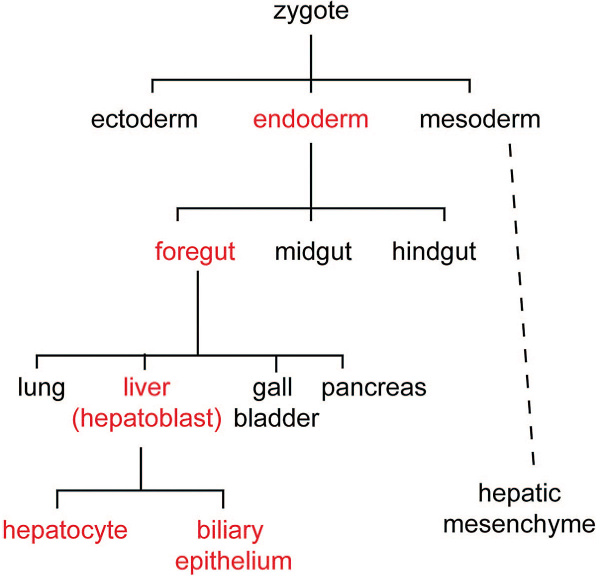
Fig.1. Liver cell lineage. The cell lineage steps during hepatic development (red) from uncommitted endoderm to functional adult hepatocytes and biliary epithelium.
Reference
Zorn AM. (2008). Liver development. , , . PMID: 20614624 DOI. | online extract | PDF
Copyright
2008 Aaron M. Zorn. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 14) Embryology Book - Liver development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Book_-_Liver_development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G