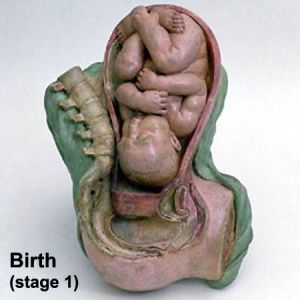
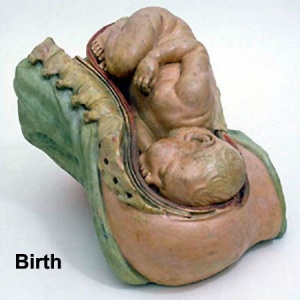
BGDA Practical 12 - Birth
| Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities |
Introduction
Birth or parturition is a critical stage in development, representing in mammals a transition from direct maternal support of fetal development, physical expulsion and establishment of the newborns own respiratory, circulatory and digestive systems. These notes only cover the biological processes surrounding birth including fetal signaling changes and maternal signaling changes. Note that there is a growing worldwide trend in developed countries toward caesarean section delivery. There are a great number of comprehensive, scientific and general, books and articles that cover birth, childbirth or parturition. The time surrounding birth is known as the perinatal period.
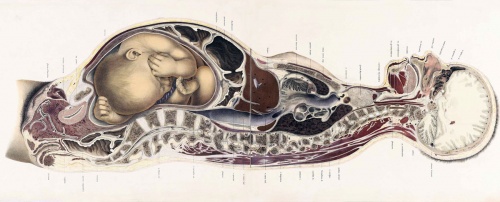
Position of the Uterus and Fetus at Term (Braune, 1877)
Childbirth
- Parturition (Latin, parturitio = "childbirth") describes expelling the fetus, placenta and fetal membranes and is probably initiated by fetus not mother.
- Preterm birth - Risks of preterm birth in abnormal low birth weight (intrauterine growth restriction) and high (large for gestational age) categories are 2- to 3-fold greater than the risk among appropriate-for-gestational-age infants.
- Maternal labor - uterine contractions and dilation of cervix, process under endocrine regulation
- Placenta and fetal membranes - (Latin, secundina = "following") expelled after neonate birth
Uterine Myometrial Changes
- Smooth muscle fibers - hypertrophy not proliferation
- Stretching of myometrium - stimulates spontaneous muscular contraction, during pregnancy progesterone inhibits contraction
- Stimulating contraction - increased estrogen levels (placental secretion sensitizes smooth muscle), increased oxytocin levels (fetal oxytocin release- force and frequency of contraction), fetal pituitary prostaglandin production (estrogen and oxytocin stimulate endometrial production of prostaglandin)
| Hormones | Roles |
|---|---|
| Progesterone |
|
| Estrogens |
|
| Oxytocin |
|
| Prostaglandins |
|
| Endocrine | Birth |
External Environment
- mainly shown in other species parturition occurs in peaceful undisturbed surroundings, stress may have an inhibitory effect on oxytocin release
- Most human births occur at night (peak at 3 am) diurnal rhythm influence
Labour Stages
| Labour Stages | Changes | Time | Roles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Dilatation | 7 to 12 hours longer for first child |
Uterine contractions 10 minutes apart, function to dilate cervix fetal membranes rupture releasing amnion. |
| Stage 2 | Expulsion | 20 to 50 minutes | Uterine contractions 2 to 3 minutes apart, function to push fetus through cervix and vagina. |
| Stage 3 | Placental | 15 minutes | Uterine contractions following child delivery expel placenta. Haematoma separates placenta from uterine wall, separation occurs at spongy layer of decidua basalis. |
| Stage 4 | Recovery | 2+ hours | Uterine contractions continue and myometrial contraction closes spiral arteries, also begins to reduce uterine volume. |
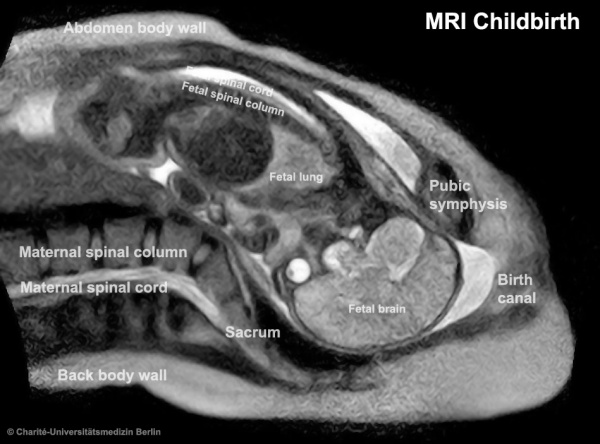
|
The birth of a child in an “open” MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scanner that allows a mother-to-be to fit fully into the machine.
|
Birth Method
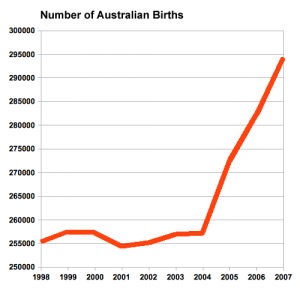
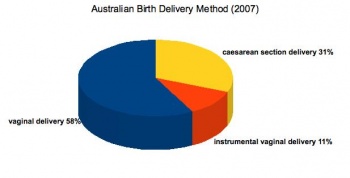
Method of Birth (Australia, 2007)
|
|
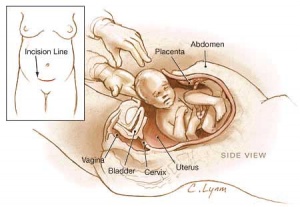
Birth - CaesareanThe rate of caesarean delivery (c-section or C/S) compared to normal vaginal birth is variable between countries (12-25%) and increasing, particularly in older women. There are a number of different explanations as to why this is occuring, including maternal or fetal complications of either development or delivery. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommended rate (10 - 15%). |
|
Links: caesarean
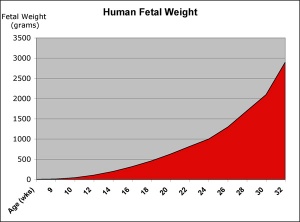
Birth Weights
| no colour | |||||||||||
| Birth weight (grams) | less 500 | 500 – 999 | 1,000 – 1,499 | 1,500 – 1,999 | 2,000 – 2,499 | 2,500 – 2,999 | 3,000 – 3,499 | 3,500 – 3,999 | 4,000 – 4,499 | 4,500 – 4,999 | 5,000 or more |
| Classification | |||||||||||
The primary causes of VLBW are premature birth (born <37 weeks gestation, and often <30 weeks) and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), usually due to problems with placenta, maternal health, or to birth defects. Many VLBW babies with IUGR are preterm and thus are both physically small and physiologically immature.
Birthweight (Australia, 2007)
- 92.1% of liveborn babies had a birthweight in the range 2,500–4,499 grams
- average birthweight was 3,374 grams
- 17,976 (6.2%) low birthweight (weighing less than 2,500 grams)
- 2,956 (1.0%) very low birthweight (weighing less than 1,500 grams)
- 1,288 (0.4%) extremely low birthweight (weighing less than 1,000 grams)
Data: Australia’s mothers and babies 2007 AIHW Perinatal statistics series no. 23
Birth Interactive Component
| Attempt the Quiz - Birth | ||
|---|---|---|

Here are a few simple Quiz questions that relate to Birth from the practical.
|
| Practical 12: Embryo to Fetus | Second Trimester | Third Trimester | Birth | Neonatal | Abnormalities |
Birth Terms
| Birth Terms | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
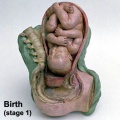
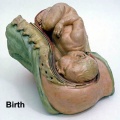
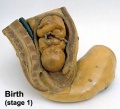
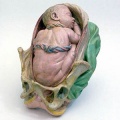
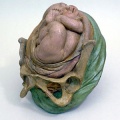
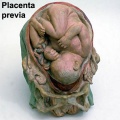
Historic Birth Models
About The Models - a series of models commissioned by Giuseppe Galletti (? - 1819) currently held in the Institute and Museum of the History of Science (Italy) Istituto e Museo di Storia della Scienza (IMSS). Giuseppe Galletti and others used terracotta and wax models that he had commissioned in Florence between 1770 and 1775 to train surgeons and midwives.
Premature Birth
| Year | < 34 weeks % | 34-36 weeks % | total preterm % |
| 1990 | 3.3 | 7.3 | 10.6 |
| 1995 | 3.3 | 7.7 | 11 |
| 2000 | 3.4 | 8.2 | 11.6 |
| 2005 | 3.6 | 9.1 | 12.7 |
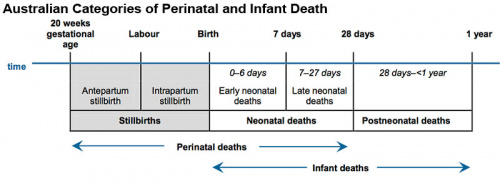
Stillbirths
|
Definition of stillbirth in Australia
|
Reducing the world's stillbirths[1]
- "One of the major success stories of modern obstetrics in high-income countries in the last 5 decades is the reduction of stillbirths from rates as high as 50 per 1000 births to about 5 per 1000 births today. Fetal mortality associated with obstructed labour, asphyxia, hypertension, diabetes, Rh disease, placental abruption, post-term pregnancies and infections such as syphilis all have declined. Much of this success has occurred in term births in the intrapartum period so that most stillbirths in high-income countries now occur in the antepartum period and are pre-term."
References
BGDA: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12 | Lecture Neural | Practical 14 | Histology Support - Female | Male | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 27) Embryology BGDA Practical 12 - Birth. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDA_Practical_12_-_Birth
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G