2011 Lab 3 - Abnormalities
| 2011 Lab 3: Introduction | Week 3 | Week 4 | Abnormalities | Online Assessment | Group Project |
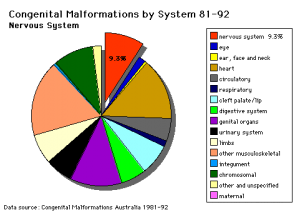
Neural Abnormalities
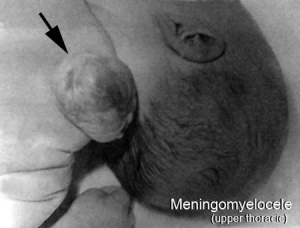
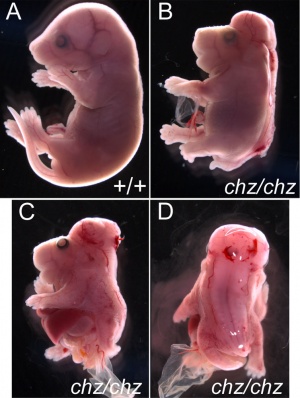
Neural Tube Defects (NTD)
- Failure of neural tube closure either incorrectly or incomplete.
- Dysraphism is the term often used to describe the defective fusion of the neural folds. The position and degree of failure of fusion will result in either embryonic death or a range of different neural defects. The way (mode) in which the human neural tube fuses has been a source of contention. In humans, fusion appears to initiate at multiple sites but the mode is different from that found in many animal models used in developmental studies. Severity dependent upon level within the tube and degree of failure (caudal - spina bifida; cranial - anancephaly)
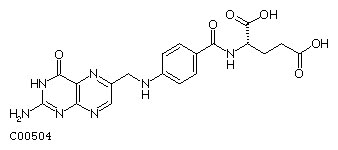
Maternal Diet - Folate
Research demonstrated that that supplementation of maternal diet with folate reduces incidence of NTDs (More? Abnormal Development - Folic Acid and Neural Tube Defects)
UK
A randomised controlled trial conducted by the Medical Research Council of the United Kingdom demonstrated a 72% reduction in risk of recurrence by periconceptional (ie before and after conception) folic acid supplementation (4mg daily).
USA
Women who have one infant with a neural tube defect have a significantly increased risk of recurrence (40-50 per thousand compared with 2 per thousand for all births)
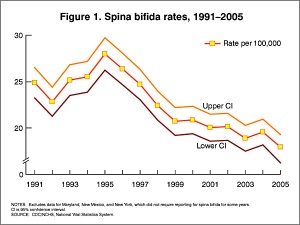
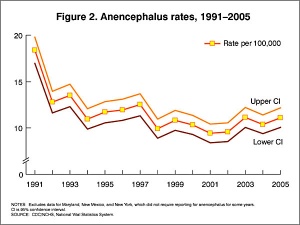
- Food and Drug Administration (USA) in 1996 authorized that all enriched cereal grain products be fortified with folic acid, with optional fortification beginning in March 1996 and mandatory fortification in January 1998. The data in the above graphs show the subsequent changes in anencephaly and spina bifida rate over that period.
Australia
- NHMRC policy statement (1993) emphasises the need for women who are capable of getting pregnant, or who are planning a pregnancy to be advised about folate and the importance of increasing folate intake to 0.4 - 0.5mg daily.
- Food Standards (FSANZ) had allowed industry two years to prepare to add folic acid to wheat flour used in making bread. Wheat flour will contain folic acid by 13 September 2009.
Links: Victoria - Folate information for health professionals | NHMRC - Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Including Recommended Dietary Intakes | NHMRC - Iodine supplementation for Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Embryo Stages and Events
| Day | Stage | Event |
| Stage 10 |  
Respiratory System Development
| |
| Heart begins to beat in humans by day 22-23, first functioning embryonic organ formed. | ||
| Stage 11 | 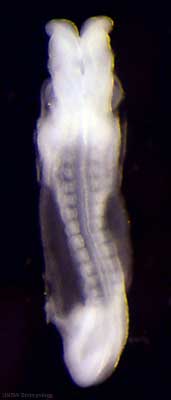
Thyroid thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx Neural System Development rostral (or cephalic) neuropore closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in two areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently. Optic ventricle appears | |
| Stage 12 | 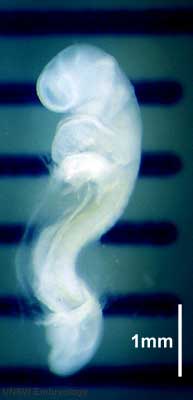
Pituitary Week 4 hypophysial pouch, Rathke’s pouch, diverticulum from roof GIT - Liver septum transversum forming liver stroma and hepatic diverticulum forming hepatic trabeculae PMID: 9407542 Neural System Development caudal neuropore takes a day to close (closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31/sacral vertebra 2) Neural System Development secondary neurulation begins Neural Crest Development cardiac crest, neural crest from rhombomeres 6 and 7 that migrates to pharyngeal arch 3 and from there the truncus arteriosus PMID: 17848161 Neural Crest Development vagal neural crest enter the foregut (20-25 somite stage) | |
| Stage 13 | 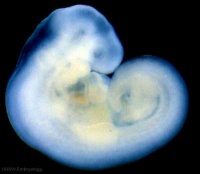 Neural System Development the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop. PMID: 3354839 Neural System Development the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop. PMID: 3354839
telencephalon cavity appears GIT - Liver epithelial cord proliferation enmeshing stromal capillaries PMID: 9407542 Sense - Smell Crest comes from the nasal platesPMID: 15604533 Skin 4 weeks - simple ectoderm epithelium over mesenchyme Skin 1-3 months ectoderm- germinative (basal) cell repeated division of generates stratified epithelium; mesoderm- differentiates into connective tissue and blood vessels |
| 2011 Lab 3: Introduction | Week 3 | Week 4 | Abnormalities | Online Assessment | Group Project |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 2) Embryology 2011 Lab 3 - Abnormalities. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2011_Lab_3_-_Abnormalities
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G