Zona pellucida: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 1== | ==Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 1== | ||
(ZP1) A glycoprotein located in the | (ZP1) A 638 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte. | ||
:'''Links:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/195000 OMIM - ZP1] | :'''Links:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/195000 OMIM - ZP1] | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 22 September 2010
Introduction
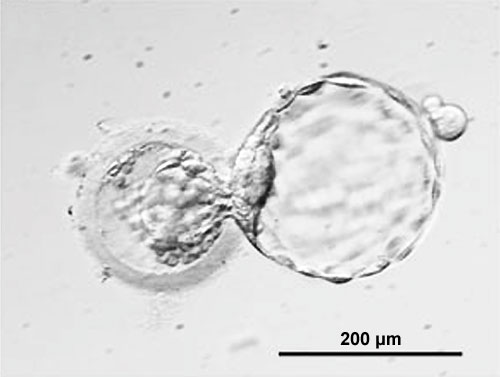
(Latin, zona pellucida = transparent zone) A specialized extracellular matrix surrounding the developing oocyte (egg, ovum) within each follicle within the ovary. This thick matrix is thought to be formed by secretions from the oocyte and the follicle granulosa cells and consists of three types of zona pellucida glycoproteins ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3 which have different roles in fertilization.
Following fertilization, the zona pellucida also surrounds the blastocyst during the first week of development, from which it "hatches".
The zona pellucida has a role in fertilization, sperm binding, preventing polyspermy, blastocyst development and preventing premature implantation (ectopic pregnancy).
Links: Carnegie stage 1 | Carnegie stage 3 | Science Lecture - Cell Division and Fertilization
Original page links: Week 1 - Fertilization | Week 1 - Oogenesis |
Some Recent Findings
- Zona pellucida glycoprotein-1 binds to spermatozoa and induces acrosomal exocytosis[1] "These studies revealed for the first time that in humans ZP1, in addition to ZP3 and ZP4, binds to capacitated spermatozoa and induces acrosomal exocytosis."
Zona Pellucida Glycoproteins
These glycoproteins share several common structural features:
- N-terminal hydrophobic signal peptide sequence.
- potential N- and O-linked glycosylation sites.
- a C-terminal hydrophobic transmembrane-like domain (TMD)
- a potential consensus proprotein convertase (furin) cleavage site (CFCS) upstream of transmembrane-like domain (TMD).
- "ZP domain" a signature domain comprised of approximately 260 amino acid (aa) residues.
Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 1
(ZP1) A 638 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte.
- Links: OMIM - ZP1
Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 2
(ZP2) A 745 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte. The protein acts as a secondary sperm receptor that binds sperm only after the induction of the sperm acrosome reaction. Before fertilization ZP2 binds spermatozoa. After fertilization ZP2 is proteolytically cleaved as an initial block to polyspermy.
- Links: OMIM - ZP2
Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 3
(ZP3) A 424 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte required for initial zona matrix formation and during fertilization for species-specific sperm binding. Now thought to exist in 2 isoforms ZP3A and ZP3B (a second polymorphic allele).
- Links: OMIM - ZP3
Zona Pellucida glycoprotein 4
(ZP4)A 540 amino acid glycoprotein located in the zona pellucida, synthesized by and surrounding the oocyte required for initial zona matrix formation and along with ZP3 during fertilization for inducing the acrosome reaction and inhibited the binding of spermatozoa to zona pellucida in a time- and dose-dependent reaction.
- Links: OMIM - ZP4
Zona Pellucida Binding Protein 1
(ZPBP1) A spermatozoa protein found located on the acrosome surface.
Terms
acrosome reaction
The chemical change within the spermatozoa following binding to the zona pellucida, that leads to the release of acrosomal enzymatic contents. These enzymes degrade the zona pellucida and allow a spermatozoa to penetrate an oocyte.
granulosa cell
A specific cell type that proliferates in association with the oocyte within the developing follicles of the ovary. These cells form the follicle stratum granulosa and are also given specific names based upon their position within the follicle. In the antral follicle, membrana granulosa sits on the follicular basal lamina and lines the antrum as a stratified epithelium. The cumulus oophorus is a column of granulosa cells that attaches the oocyte to the follicle wall. The corona radiata are the granulosa cells that directly surround the oocyte, and are released along with it at ovulation. Following ovulation the corona radiata provide physical protection to the oocyte and granulosa cells within the ovulating follicle contribute to corpus luteum.
References
- ↑ <pubmed>20504872</pubmed>
Search NCBI Bookshelf zona pellucida | acrosome reaction
Search Pubmed
July 2010 "zona pellucida" All (4801) Review (582) Free Full Text (1408)
Search Pubmed zona pellucida | acrosome reaction
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 7) Embryology Zona pellucida. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Zona_pellucida
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G