Virginia Diewert
Introduction
Prof. Virginia Divert, Professor of Orthodontics, University of British Columbia.
Researcher in human face and palate development. A contributor to the Digital Embryology Consortium of the Collection. Prof Diewert has also visited both the Kyoto Collection and Carnegie Collection annotating palate and face development in these embryos.
- Embryology Links: Virginia Diewert | contributors | Palate Development | Human Embryo Collections | Embryology Consortium - Perry-Arey-Milligan Collection
- Research Links: UBC Dentistry | Researchgate
Sample Images
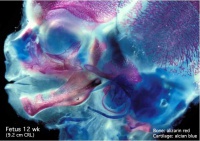
Fetal head (12 weeks, lateral) |
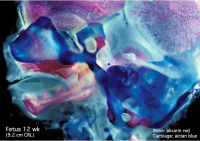
Fetal head (12 weeks, medial) |
Sample DEC Image: Fetus CRL 97mm (88 days, 14151, Slide 120-2) (requires DEC log-in)
Selected Publications
Analysis of human soft palate morphogenesis supports regional regulation of palatal fusion
Danescu A, Mattson M, Dool C, Diewert VM & Richman JM. (2015). Analysis of human soft palate morphogenesis supports regional regulation of palatal fusion. J. Anat. , 227, 474-86. PMID: 26299693 DOI. Online Paper Link
Danescu A, Mattson M, Dool C, Diewert VM, Richman JM.
Faculty of Dentistry, Life Sciences Institute, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Abstract
It is essential to complete palate closure at the correct time during fetal development, otherwise a serious malformation, cleft palate, will ensue. The steps in palate formation in humans take place between the 7th and 12th week and consist of outgrowth of palatal shelves from the paired maxillary prominences, reorientation of the shelves from vertical to horizontal, apposition of the medial surfaces, formation of a bilayered seam, degradation of the seam and bridging of mesenchyme. However, in the soft palate, the mechanism of closure is unclear. In previous studies it is possible to find support for both fusion and the alternative mechanism of merging. Here we densely sample the late embryonic-early fetal period between 54 and 74 days post-conception to determine the timing and mechanism of soft palate closure. We found the epithelial seam extends throughout the soft palates of 57-day specimens. Cytokeratin antibody staining detected the medial edge epithelium and distinguished clearly that cells in the midline retained their epithelial character. Compared with the hard palate, the epithelium is more rapidly degraded in the soft palate and only persists in the most posterior regions at 64 days. Our results are consistent with the soft palate following a developmentally more rapid program of fusion than the hard palate. Importantly, the two regions of the palate appear to be independently regulated and have their own internal clocks regulating the timing of seam removal. Considering data from human genetic and mouse studies, distinct anterior-posterior signaling mechanisms are likely to be at play in the human fetal palate. © 2015 Anatomical Society.
KEYWORDS: aponeurosis; craniofacial; hard palate; medial edge epithelium; palatal shelf; submucous cleft; tensor veli palatini; velopharyngeal
A morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth and changes in spatial relations during secondary palatal development in human embryos and fetuses
Diewert VM. (1983). A morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth and changes in spatial relations during secondary palatal development in human embryos and fetuses. Am. J. Anat. , 167, 495-522. PMID: 6624691 DOI.
Staged human embryos and fetuses in the Carnegie Embryological Collection were morphometrically analyzed to show craniofacial dimensions and changes in spatial relations, and to identify patterns that would reflect normal developmental events during palatal formation. Normal embryos aged 7-8 weeks postconception (Streeter-O'Rahilly stages 19 - 23) and fetuses aged 9 -10 weeks postconception, in eight groups with mean crown-rump (CR) lengths of 18-49 mm, were studied with cephalometric methods developed for histologic sections. In the 4-week period studied, facial dimensions increased predominantly in the sagittal plane with extensive changes in length (depth) and height, but limited changes in width. Growth of the mandible was more rapid than the nasomaxillary complex, and the length of Meckel's cartilage exceeded the length of the oronasal cavity at the time of horizontal movement of the shelves during stage 23. Simultaneously with shelf elevation, the upper craniofacial complex lifted, and the tongue and Meckel's cartilage extended forward beneath the primary palate. Analysis of spatial relations in the oronasal cavity showed that the palatomaxillary processes became separated from the tongue--mandibular complex as the head extended, and the tongue became positioned forward with growth of Meckel's cartilage. As the head position extended by 35 degrees, the cranial base angulation was unchanged and the primary palate maintained a 90 degrees position to the posterior cranial base. However, the sagittal position of the maxilla relative to the anterior cranial base increased by 20 degrees between stages 19 and 23. In the late embryonic and early fetal periods, the mean cranial base angulation of approximately 128 degrees and the mean maxillary position angulation of approximately 84 degrees were similar to the angulations previously shown to be present later prenatally and post-natally. The results suggest that human patterns of cranial base angulation and maxillary position to the cranial base develop during the late embryonic period when the chondrocranium and Meckel's cartilage form the primary skeleton.
References
Search PubMed: Diewert VM (Author)
Danescu A, Mattson M, Dool C, Diewert VM & Richman JM. (2015). Analysis of human soft palate morphogenesis supports regional regulation of palatal fusion. J. Anat. , 227, 474-86. PMID: 26299693 DOI.
Boughner JC, Wat S, Diewert VM, Young NM, Browder LW & Hallgrímsson B. (2008). Short-faced mice and developmental interactions between the brain and the face. J. Anat. , 213, 646-62. PMID: 19094181 DOI.
Buchtová M, Handrigan GR, Tucker AS, Lozanoff S, Town L, Fu K, Diewert VM, Wicking C & Richman JM. (2008). Initiation and patterning of the snake dentition are dependent on Sonic hedgehog signaling. Dev. Biol. , 319, 132-45. PMID: 18456251 DOI.
Parsons TE, Kristensen E, Hornung L, Diewert VM, Boyd SK, German RZ & Hallgrímsson B. (2008). Phenotypic variability and craniofacial dysmorphology: increased shape variance in a mouse model for cleft lip. J. Anat. , 212, 135-43. PMID: 18093101 DOI.
Buchtová M, Boughner JC, Fu K, Diewert VM & Richman JM. (2007). Embryonic development of Python sebae - II: Craniofacial microscopic anatomy, cell proliferation and apoptosis. Zoology (Jena) , 110, 231-51. PMID: 17499982 DOI.
Young NM, Wat S, Diewert VM, Browder LW & Hallgrímsson B. (2007). Comparative morphometrics of embryonic facial morphogenesis: implications for cleft-lip etiology. Anat Rec (Hoboken) , 290, 123-39. PMID: 17441205 DOI.
Iamaroon A, Wallon UM, Overall CM & Diewert VM. (1996). Expression of 72-kDa gelatinase (matrix metalloproteinase-2) in the developing mouse craniofacial complex. Arch. Oral Biol. , 41, 1109-19. PMID: 9134100
Iamaroon A, Tait B & Diewert VM. (1996). Cell proliferation and expression of EGF, TGF-alpha, and EGF receptor in the developing primary palate. J. Dent. Res. , 75, 1534-9. PMID: 8906120 DOI.
Iamaroon A & Diewert VM. (1996). Distribution of basement membrane components in the mouse primary palate. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 16, 48-51. PMID: 8675614
Wang KY, Juriloff DM & Diewert VM. (1995). Deficient and delayed primary palatal fusion and mesenchymal bridge formation in cleft lip-liable strains of mice. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 15, 99-116. PMID: 8642057
Nasir J, Floresco SB, O'Kusky JR, Diewert VM, Richman JM, Zeisler J, Borowski A, Marth JD, Phillips AG & Hayden MR. (1995). Targeted disruption of the Huntington's disease gene results in embryonic lethality and behavioral and morphological changes in heterozygotes. Cell , 81, 811-23. PMID: 7774020
Diewert VM, Wang KY & Tait B. (1993). A morphometric analysis of cell densities in facial prominences of the rhesus monkey embryo during primary palate formation. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 13, 236-49. PMID: 8288731
Diewert VM, Lozanoff S & Choy V. (1993). Computer reconstructions of human embryonic craniofacial morphology showing changes in relations between the face and brain during primary palate formation. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 13, 193-201. PMID: 8227291
Diewert VM & Lozanoff S. (1993). Growth and morphogenesis of the human embryonic midface during primary palate formation analyzed in frontal sections. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 13, 162-83. PMID: 8227289
Diewert VM & Lozanoff S. (1993). A morphometric analysis of human embryonic craniofacial growth in the median plane during primary palate formation. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 13, 147-61. PMID: 8227288
Diewert VM, Wang KY & Tait B. (1993). A new threshold model for cleft lip in mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. , 678, 341-3. PMID: 8494279
Wang KY & Diewert VM. (1992). A morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth in cleft lip and noncleft mice. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 12, 141-54. PMID: 1517393
Diewert VM & Wang KY. (1992). Recent advances in primary palate and midface morphogenesis research. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. , 4, 111-30. PMID: 1457684
Diewert VM & Shiota K. (1990). Morphological observations in normal primary palate and cleft lip embryos in the Kyoto collection. Teratology , 41, 663-77. PMID: 2353315 DOI.
Lozanoff S & Diewert VM. (1989). Developmental morphology of the solum nasi in the mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus). J. Morphol. , 202, 409-24. PMID: 2600973 DOI.
Lozanoff S & Diewert VM. (1989). A computer graphics program for measuring two- and three-dimensional form change in developing craniofacial cartilages using finite element methods. Comput. Biomed. Res. , 22, 63-82. PMID: 2914426
Richman JM & Diewert VM. (1988). The fate of Meckel's cartilage chondrocytes in ocular culture. Dev. Biol. , 129, 48-60. PMID: 3044881
Lozanoff S, Diewert VM, Sinclair B & Wang KY. (1988). Surface modeling of craniofacial form in human embryos with a limited graphics terminal. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 8, 101-9. PMID: 3182967
Richman JM & Diewert VM. (1987). An immunofluorescence study of chondrogenesis in murine mandibular ectomesenchyme. Cell Differ. , 21, 161-73. PMID: 3308120
Lozanoff S & Diewert VM. (1986). Measuring histological form change with finite element methods: an application using diazo-oxo-norleucine (DON)-treated rats. Am. J. Anat. , 177, 187-201. PMID: 3788820 DOI.
Ciriani D & Diewert VM. (1986). A comparative study of development during primary palate formation in A/WySn, C57BL/6, and their F1 crosses. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 6, 369-77. PMID: 3793861
Diewert VM. (1986). Craniofacial growth during human secondary palate formation and potential relevance of experimental cleft palate observations. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol Suppl , 2, 267-76. PMID: 3491117
Diewert VM. (1985). Development of human craniofacial morphology during the late embryonic and early fetal periods. Am J Orthod , 88, 64-76. PMID: 3860013
Diewert VM. (1985). Growth movements during prenatal development of human facial morphology. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. , 187, 57-66. PMID: 3903766
Pratt RM, Dencker L & Diewert VM. (1984). 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced cleft palate in the mouse: evidence for alterations in palatal shelf fusion. Teratog., Carcinog. Mutagen. , 4, 427-36. PMID: 6150558
Diewert VM & Juriloff DM. (1983). Abnormal head posture associated with induction of cleft palate by methylmercury in C57BL/6J mice. Teratology , 28, 437-47. PMID: 6665742 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1983). A morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth and changes in spatial relations during secondary palatal development in human embryos and fetuses. Am. J. Anat. , 167, 495-522. PMID: 6624691 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1982). A comparative study of craniofacial growth during secondary palate development in four strains of mice. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. , 2, 247-63. PMID: 7183704
Diewert VM. (1982). Contributions of differential growth of cartilages to changes in craniofacial morphology. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. , 101, 229-42. PMID: 7156139
Diewert VM & Pratt RM. (1981). Cortisone-induced cleft palate in A/J mice: failure of palatal shelf contact. Teratology , 24, 149-62. PMID: 7336358 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1981). Correlation between alterations in Meckel's cartilage and induction of cleft palate with beta-aminoproprionitrile in the rat. Teratology , 24, 43-52. PMID: 7302872 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1980). Differential changes in cartilage cell proliferation and cell density in the rat craniofacial complex during secondary palate development. Anat. Rec. , 198, 219-28. PMID: 7212306 DOI.
Pratt RM, Salomon DS, Diewert VM, Erickson RP, Burns R & Brown KS. (1980). Cortisone-induced cleft palate in the brachymorphic mouse. Teratog., Carcinog. Mutagen. , 1, 15-23. PMID: 6119797
Diewert VM. (1979). Experimental induction of premature movement of rat palatal shelves in vivo. J. Anat. , 129, 597-601. PMID: 541242
Diewert VM & Pratt RM. (1979). Selective inhibition of mandibular growth and induction of cleft palate by diazo-oxo-norleucine (DON) in the rat. Teratology , 20, 37-51. PMID: 515963 DOI.
Diewert VM & Tait B. (1979). Palatal process movement in the rat as demonstrated in frozen sections. J. Anat. , 128, 609-18. PMID: 381268
Diewert VM. (1979). Correlation between mandibular retrognathia and induction of cleft palate with 6-aminonicotinamide in the rat. Teratology , 19, 213-27. PMID: 157558 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1978). A quantitative coronal plane evaluation of craniofacial growth and spatial relations during secondary palate development in the rat. Arch. Oral Biol. , 23, 607-29. PMID: 281896
Diewert VM. (1976). Graphic reconstructions of craniofacial structures during secondary palate development in rats. Teratology , 14, 291-313. PMID: 996777 DOI.
Diewert VM. (1974). A cephalometric study of orofacial structures during secondary palate closure in the rat. Arch. Oral Biol. , 19, 303-15. PMID: 12692913
Diewert VM. (1973). The course of the palatine arteries during secondary palate development in the rat. J. Dent. Res. , 52, 1273-80. PMID: 4522822 DOI.
Wragg LE, Diewert VM & Klein M. (1972). Spatial relations in the oral cavity and the mechanism of secondary palate closure in the rat. Arch. Oral Biol. , 17, 683-90. PMID: 4558302
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 26) Embryology Virginia Diewert. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Virginia_Diewert
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
