Respiratory System - Histology
From Embryology
Introduction
This page contains information and images associated with respiratory system histology.
This can be initially divided into the 2 regions of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
- For the upper respiratory tract observe the epithelial specialisations, sensory regions and associated cartilages.
- For the lower respiratory tract observe the basic structure of the lung, alveoli and ducts, and associated cardiovascular elements.
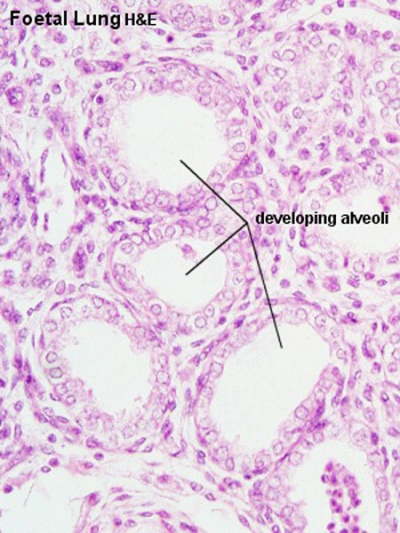
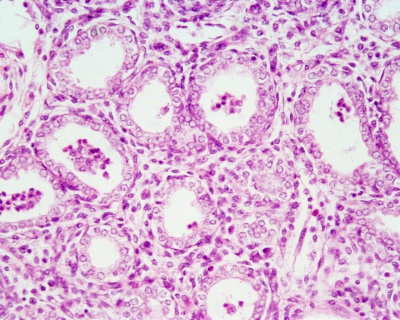
Fetal Histology
- Fetal Respiratory: late canalicular | unlabeled late canalicular | Hyaline cartilage | Respiratory Histology
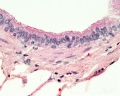
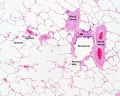
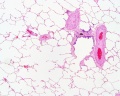
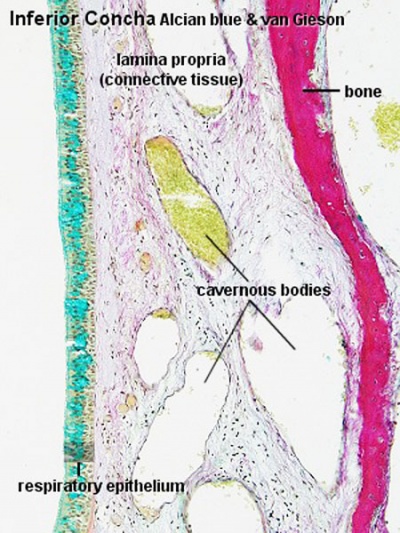
Upper Respiratory Tract - Nasal Cavity
Respiratory
|
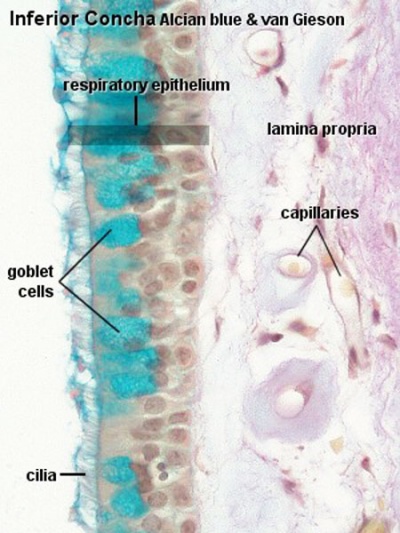
|
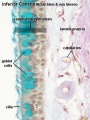
| Nasal respiratory epithelium (inferior concha) | Nasal respiratory epithelium (detail) |
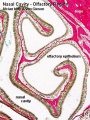
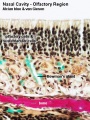
Olfactory
Nasal cavity olfactory epithelium cells
- Olfactory cells
- Sustentacular cells - located mainly in the superficial cell layer of the epithelium (difficult to distinguish from olfactory cells).
- Basal cells - identified by their location.
Epithelium
|
Lamina Propria
|
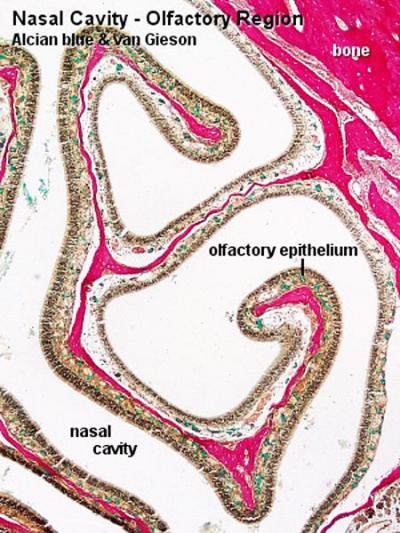
|
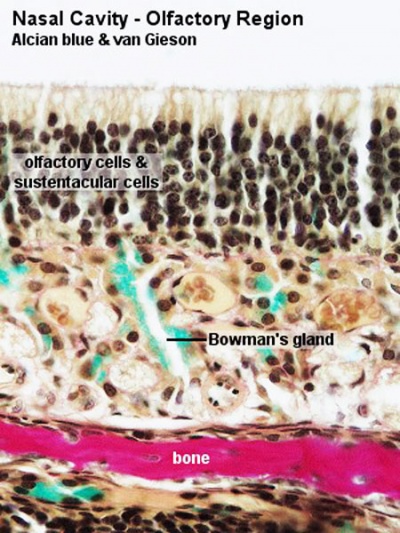
|
| Nasal cavity olfactory | Nasal cavity olfactory (detail) |
- Nasal Olfactory Histology: overview image | detail image | Smell Development | Histology | Histology Stains
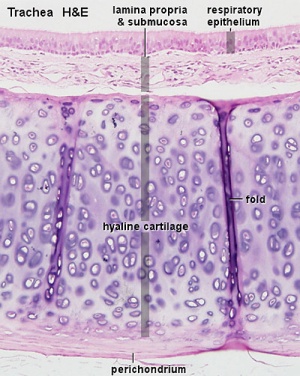
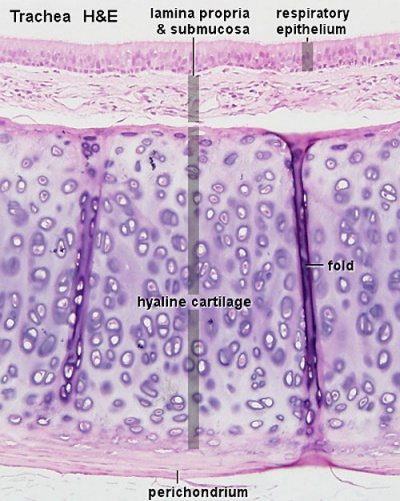
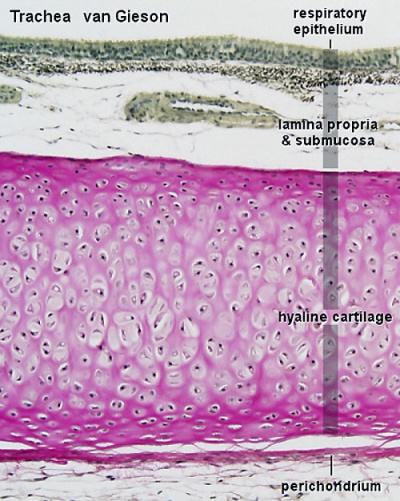
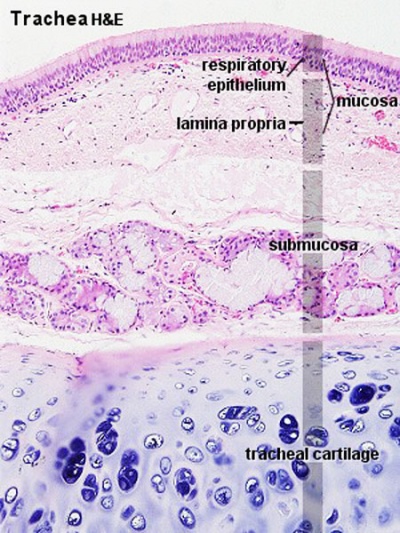
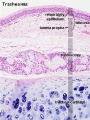
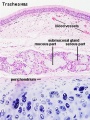
Trachea
Mucosa - formed by epithelium and underlying lamina propria.
- respiratory epithelium - (pseudostratified columnar and ciliated) ciliated cells, goblet cells, brush cells, endocrine cells, surfactant-producing cells (Clara cells), serous cells, basal cells, basement membrane.
- lamina propria - loose connective tissue, many elastic fibres.
- elastic lamina - forming the border between the mucosa and submucosa is not visible in H&E stained slides.
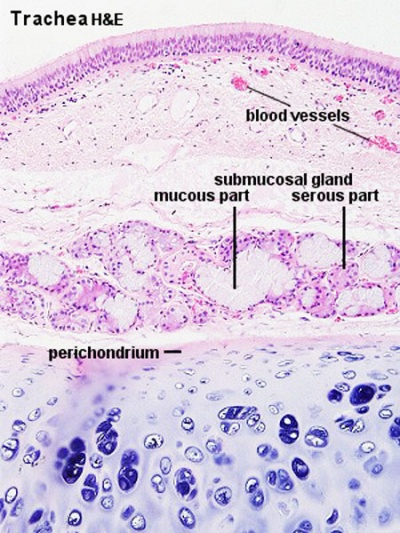
Submucosa - connective tissue and submucosal glands.
Submucosal Glands
(muco-serous) serous (dark) and mucous (light) parts have different staining appearance.
- Mucous secretions - "slimy" (high viscosity) mucous acini cells appear "foamy" or "frothy" and poorly stained (light). nuclei dark and smaller than serous.
- Serous secretions - "watery" (low viscosity) serous acini cell apical cytoplasm is usually well-stained (dark). nuclei round to ovoid located in cell basal cytoplasm.
Cartilage
- perichondrium - surface of cartilage.
- tracheal cartilage - hyaline cartilage, 16 to 20 C-shaped cartilages.
- trachealis muscle - (smooth muscle) Not visible in this section, together with connective tissue fibres, join ends of the cartilages together.
Hyaline Cartilage Development
- forms from mesenchymal cells.
- precursor cells become rounded and form densely packed cellular masses, chondrification centres.
- chondroblasts - (cartilage-forming cells) begin secreting the extracellular matrix components of cartilage.
- extracellular matrix - ground substance (hyaluronan, chondroitin sulfates and keratan sulfate) and tropocollagen (polymerises into fine collagen fibres, not visible).
- Trachea Histology Links: Overview HE | Overview VG | Detail 1 HE Detail 2 HE | Respiratory Histology | Histology Stains | Histology
- Trachea Histology Links: Overview HE | Overview VG | Detail 1 HE Detail 2 HE | Respiratory Histology | Histology Stains | Histology
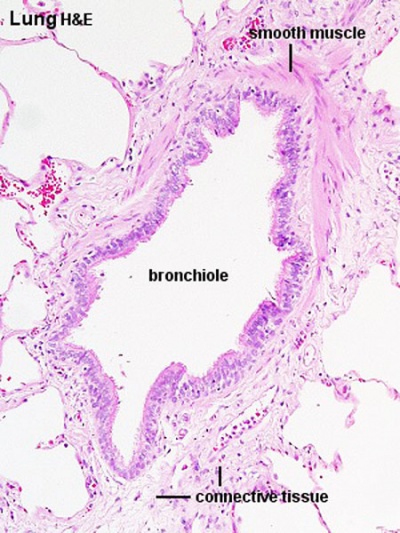
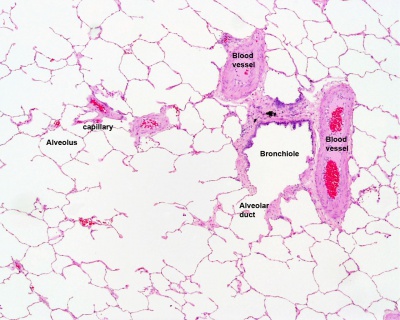
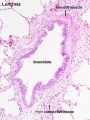
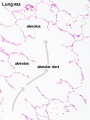
Bronchiole
Alveolar Ducts and Alveoli
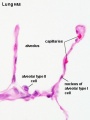
Alveolar type I cells
|
Alveolar type II cells
|
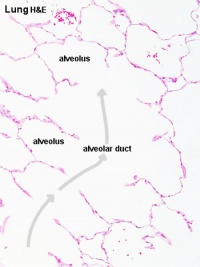
|
|
|
|
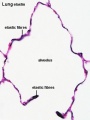
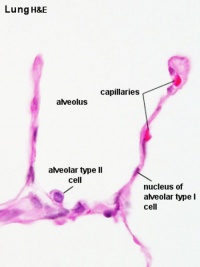
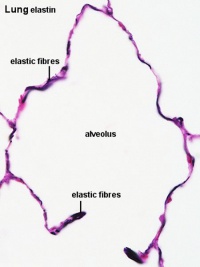
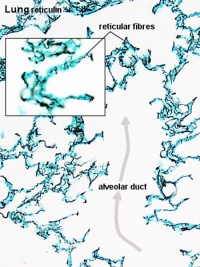
| Alveolar Duct | Alveoli | Alveoli Elastin | Lung Reticular Fibres |
Gallery
- Respiratory Histology: Bronchiole | Alveolar Duct | Alveoli | EM Alveoli septum | Alveoli Elastin | Trachea 1 | Trachea 2 | labeled lung | unlabeled lung | Respiratory Bronchiole | Lung Reticular Fibres | Nasal Inferior Concha | Nasal Respiratory Epithelium | Olfactory Region overview | Olfactory Region Epithelium | Histology Stains
Terms
- alveolar type I cell - (small alveolar cell, type I pneumocyte), extremely flattened and branched cell forming the bulk (95%) of the surface of the alveolar walls. Contain multiple cytoplasmic plates and relatively devoid of organelles, plates are the gas exchange surface in the alveolus. (More? Image - Respiratory Alveoli)
- alveolar type II cell - (large alveolar cell, type II pneumocyte) cuboidal to irregular shaped cells forming small bulges on the alveolar walls. Contain large number of granules (cytosomes or multilamellar bodies) precursors to pulmonary surfactant. (More? Image - Respiratory Alveoli)
- alveolar macrophage - (dust cell), irregular shaped cells lying with the fluid wall of the alveolar space. Monocyte-derived immune system cell that removes debris and microorganisms from the alveoli and may have immune roles. (More? Image - Respiratory Alveoli)
- Bowman's gland - (small mucous gland, olfactory gland) the main function of these glands is to moisturise the epithelium.
- cavernous body - (cavernous sinusoid) Thin-walled spaces located in the nasal cavity respiratory region lamina propria. The space is formed by veins in the lamina propria and may have a role in altering local nasal air flow in response to temperature, humidity and CO2-content of the inspired air.
- cilium - (plural cilia) An epithelial cell microtubule-based surface specialization. Cilia are thin, tail-like projections extending approximately 5–10 micrometers outwards from the cell body. There are two types of cilia, motile cilia and non-motile cilia. Motile cilia (respiratory epithelia, trachea, uterine tube, ependymal cells) move and constantly beat in a single direction, resulting in movement of the overlying fluid. Non-motile cilia lack dynein arms and are associated with sensory system epithelium (olfactory epithelium). (More? Movie - Respiratory Cilia Movement)
- dust cell - see alveolar macrophage.
- goblet cell - Named by the cell shape following histological preparation, cell produces membrane-bound secretory granules filled with mucus in the respiratory and intestinal epithelium. Mucus consists of mucins (highly glycosylated proteins) suspended in a solution of electrolytes.
- hyaline cartilage - Development from mesenchymal cells forming a chondrification centre. Mature cartilage contains chondrocytes lying in lacunae within isogenic groups surrounded (territorial matrix) and separated from other groups (interterritorial matrix) by the matrix. Cartilage surface is covered with perichondrium that merges with a layer of dense connective tissue. (More? Image - Hyaline Cartilage | Cartilage Histology)
- perichondrium - a layer of dense connective tissue surrounding the cartilage and blending with it's surface. Mesenchymal cells in the deep part of the perichondrium (chondrogenic layer) differentiate into chondroblasts. (More? Image - Hyaline Cartilage | Cartilage Histology)
- sustentacular cell - (supporting cell) provide mechanical and metabolic support for olfactory cells.
- type I pneumocyte - see alveolar type I cell.
- type II pneumocyte - see alveolar type II cell.
References
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed>17988208</pubmed> <pubmed>16415249</pubmed> <pubmed>2184755</pubmed>| Annu Rev Physiol.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 13) Embryology Respiratory System - Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Respiratory_System_-_Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G