ANAT2341 Lab 9: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= | =Muscle Development = | ||
[[File:Actin_myosin_crossbridge_3D_animation.gif]] [[File:Actin_myosin_crossbridge_3D_animation.jpg]][[File:Muscle fiber types.jpg]] | |||
== Introduction == | |||
This laboratory concerns the development and differentiation of skeletal muscle, muscle stem cells, hypertrophy, fibre type differentiation and plasticity. | |||
==Objectives== | |||
# Understand the origin, differentiation and development of skeletal muscle tissue. | |||
# Know what is meant by patterning, conversion and adult plasticity of muscle fibre type. | |||
# Develop an understanding of research methods for studying skeletal muscle development and function. | |||
[[File:Sarcomere_animation.gif]] | |||
[[File: | |||
[http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Muscle/Muscle.htm#SKELETAL Skeletal Muscle Histology] | |||
=== | == Lab 7 Assessment Questions== | ||
TBA | |||
== Terms == | |||
''' | '''anterior tibialis''' - (tibialis anterior) skeletal muscle situated on the lateral side of the tibia and is a direct flexor of the foot at the ankle-joint. | ||
''' | '''cis-acting elements''' - DNA sequences that through transcription factors or other trans-acting elements or factors, regulate the expression of genes on the same chromosome. | ||
''' | '''enhancer''' - A cis-regulatory sequence that can regulate levels of transcription from an adjacent promoter. Many tissue-specific enhancers can determine spatial patterns of gene expression in higher eukaryotes. Enhancers can act on promoters over many tens of kilobases of DNA and can be 5' or 3' to the promoter they regulate. | ||
''' | '''extensor digitorum longus''' - (EDL) skeletal muscle situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg and extend the phalanges of the toes, and, continuing their action, flex the foot upon the leg. | ||
'''Gtf2ird1''' - General Transcription Factor 2 -I Repeat domain-containing protein 1. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=604318 OMIM: Gtf2ird1] | |||
'''MusTRD1''' - muscle TFII-I repeat domain-containing protein 1. | |||
'''MyHC''' - acronym for myosin heavy chain. | |||
'''myoblast''' - the undifferentiated mononucleated muscle cell progenitor, which in skeletal muscle fuses to form a myotube, that in turn expresses contractile proteins to form a muscle fibre. | |||
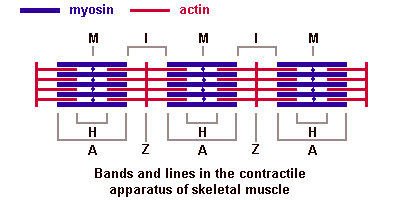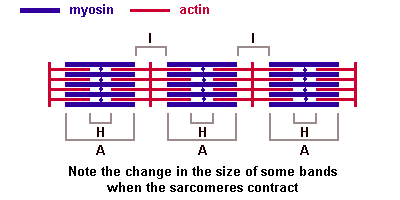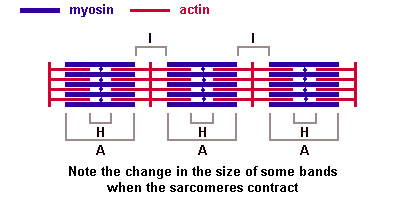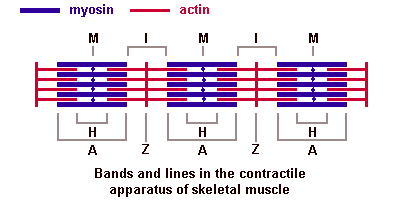
:''' | '''myosin heavy chain''' - protein forming the thick filament of the sarcomere and the motor for actin-myosin contraction. There are 17 different myosin classes. | ||
'''myotube''' - the initial multinucleated cell formed by fusion of myoblasts during skeletal muscle development. | |||
'''promoter''' - A regulatory region a short distance upstream from the 5' end of a transcription start site that acts as the binding site for RNA polymerase II. A region of DNA to which RNA polymerase IIbinds in order to initiate transcription. | |||
'''regulatory sequence''' - (regulatory region, regulatory area) is a segment of DNA where regulatory proteins such as transcription factors bind preferentially. | |||
'''soleus''' - skeletal muscle situated immediately in front of the gastrocnemius and when standing taking its fixed point from below, steadies the leg upon the foot and prevents the body from falling forward. | |||
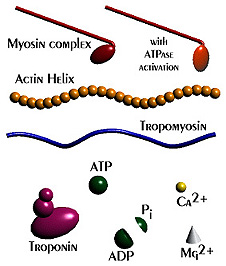
'''Troponin''' - striated muscle contraction is regulated by the calcium-ion-sensitive, multiprotein complex troponin and the fibrous protein tropomyosin. Troponin has 3 subunits (TnC, TnI, TnT) and is located on the actin filament. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=191040 OMIM: Troponin I slow] | |||
'''visuospatial deficiency''' - performing the Delis hierarchical processing task, subjects are asked to copy a large global figure made of smaller local forms. Both Down syndrome (DS) and William-Beuren syndrome (WBS) groups fail but in different ways. WBS individuals produce the local elements and DS individuals produce only the global forms. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12952863?dopt=Abstract PMID: 12952863] [http://hmg.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/12/suppl_2/R229#DDG299F2 Hum Mol Genet.] | |||
'''William-Beuren syndrome''' - (WBS) rare developmental disorder (1/20,000–1/50,000 live births). A contiguous gene deletion syndrome resulting from the hemizygous deletion of several genes on chromosome [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/getmap.cgi?l194050 7q11.23]. The syndrome has associated craniofacial abnormalities, hypersociability and visuospatial defects. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=194050 OMIM: William-Beuren syndrome] | |||
===Search === | |||
* '''Bookshelf''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books&cmd=search&term=muscle_development muscle development] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books&cmd=search&term=muscle_fiber_type muscle fiber type] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books&cmd=search&term=troponin troponin] | |||
* '''Pubmed''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/gquery?itool=toolbar&cmd=search&term=muscle_fiber_type muscle fiber type] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/gquery?itool=toolbar&cmd=search&term=troponin troponin] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/gquery?itool=toolbar&cmd=search&term=Gtf2ird1 Gtf2ird1] | | |||
==UNSW Embryology Links== | |||
* [[File:Muscle_development_1-Talk1_muscle_development.pdf]] | |||
* [[File:Talk1_muscle_development_4_per_page.pdf]] | |||
* [[File:Part_2_Muscle_Development.pdf]] | |||
* [[File:Part_2_Muscle_Development_4_per_page.pdf]] | |||
== External Links == | |||
{{External Links}} | |||
* Blue Histology [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Muscle/Muscle.htm#SKELETAL Skeletal Muscle histology] | |||
* Primer [http://www.plosbiology.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.0020348 Skeletal Muscle Fiber Type: Influence on Contractile and Metabolic Properties] | |||
* Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body - [http://www.bartleby.com/107/129.html The Muscles and Fasciæ of the Leg] | [http://www.bartleby.com/107/illus440.html Cross-section through middle of leg] | |||
* Wiki [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skeletal_muscle Skeletal muscle] | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Troponin Troponin] | |||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=604318 OMIM: Gtf2ird1] | |||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=194050 OMIM: William-Beuren syndrome] | |||
==Individual Assessment== | ==Individual Assessment== | ||
TBA | |||
==Group Project== | ==Group Project== | ||
* Peer Assessment of | * Peer Assessment of projects. | ||
===Plagiarism=== | ===Plagiarism=== | ||
| Line 120: | Line 101: | ||
* The Research Support Committee is pleased to announce that it will again be offering Summer Research Awards (SRAs). | * The Research Support Committee is pleased to announce that it will again be offering Summer Research Awards (SRAs). | ||
* These awards are for undergraduate students carrying out supervised research in SOMS between November | * These awards are for undergraduate students carrying out supervised research in SOMS between November 2014 and February 2015. | ||
* Successful students will receive a stipend each week for 6 weeks of research. [http://medicalsciences.med.unsw.edu.au/students/undergraduate/summer-research-awards More Information?] | * Successful students will receive a stipend each week for 6 weeks of research. [http://medicalsciences.med.unsw.edu.au/students/undergraduate/summer-research-awards More Information?] | ||
| Line 127: | Line 108: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
{{ | {{2014ANAT2341}} | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 7 October 2014
Muscle Development
Introduction
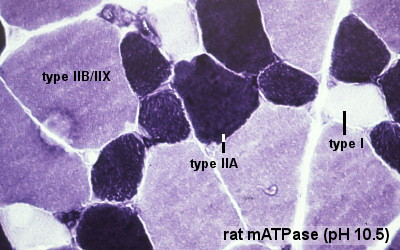
This laboratory concerns the development and differentiation of skeletal muscle, muscle stem cells, hypertrophy, fibre type differentiation and plasticity.
Objectives
- Understand the origin, differentiation and development of skeletal muscle tissue.
- Know what is meant by patterning, conversion and adult plasticity of muscle fibre type.
- Develop an understanding of research methods for studying skeletal muscle development and function.
Lab 7 Assessment Questions
TBA
Terms
anterior tibialis - (tibialis anterior) skeletal muscle situated on the lateral side of the tibia and is a direct flexor of the foot at the ankle-joint.
cis-acting elements - DNA sequences that through transcription factors or other trans-acting elements or factors, regulate the expression of genes on the same chromosome.
enhancer - A cis-regulatory sequence that can regulate levels of transcription from an adjacent promoter. Many tissue-specific enhancers can determine spatial patterns of gene expression in higher eukaryotes. Enhancers can act on promoters over many tens of kilobases of DNA and can be 5' or 3' to the promoter they regulate.
extensor digitorum longus - (EDL) skeletal muscle situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg and extend the phalanges of the toes, and, continuing their action, flex the foot upon the leg.
Gtf2ird1 - General Transcription Factor 2 -I Repeat domain-containing protein 1. OMIM: Gtf2ird1
MusTRD1 - muscle TFII-I repeat domain-containing protein 1.
MyHC - acronym for myosin heavy chain.
myoblast - the undifferentiated mononucleated muscle cell progenitor, which in skeletal muscle fuses to form a myotube, that in turn expresses contractile proteins to form a muscle fibre.
myosin heavy chain - protein forming the thick filament of the sarcomere and the motor for actin-myosin contraction. There are 17 different myosin classes.
myotube - the initial multinucleated cell formed by fusion of myoblasts during skeletal muscle development.
promoter - A regulatory region a short distance upstream from the 5' end of a transcription start site that acts as the binding site for RNA polymerase II. A region of DNA to which RNA polymerase IIbinds in order to initiate transcription.
regulatory sequence - (regulatory region, regulatory area) is a segment of DNA where regulatory proteins such as transcription factors bind preferentially.
soleus - skeletal muscle situated immediately in front of the gastrocnemius and when standing taking its fixed point from below, steadies the leg upon the foot and prevents the body from falling forward.
Troponin - striated muscle contraction is regulated by the calcium-ion-sensitive, multiprotein complex troponin and the fibrous protein tropomyosin. Troponin has 3 subunits (TnC, TnI, TnT) and is located on the actin filament. OMIM: Troponin I slow
visuospatial deficiency - performing the Delis hierarchical processing task, subjects are asked to copy a large global figure made of smaller local forms. Both Down syndrome (DS) and William-Beuren syndrome (WBS) groups fail but in different ways. WBS individuals produce the local elements and DS individuals produce only the global forms. PMID: 12952863 Hum Mol Genet.
William-Beuren syndrome - (WBS) rare developmental disorder (1/20,000–1/50,000 live births). A contiguous gene deletion syndrome resulting from the hemizygous deletion of several genes on chromosome 7q11.23. The syndrome has associated craniofacial abnormalities, hypersociability and visuospatial defects. OMIM: William-Beuren syndrome
Search
- Bookshelf muscle development | muscle fiber type | troponin
- Pubmed muscle fiber type | troponin | Gtf2ird1 |
UNSW Embryology Links
- File:Muscle development 1-Talk1 muscle development.pdf
- File:Talk1 muscle development 4 per page.pdf
- File:Part 2 Muscle Development.pdf
- File:Part 2 Muscle Development 4 per page.pdf
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Blue Histology Skeletal Muscle histology
- Primer Skeletal Muscle Fiber Type: Influence on Contractile and Metabolic Properties
- Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body - The Muscles and Fasciæ of the Leg | Cross-section through middle of leg
- Wiki Skeletal muscle | Troponin
- OMIM: Gtf2ird1
- OMIM: William-Beuren syndrome
Individual Assessment
TBA
Group Project
- Peer Assessment of projects.
Plagiarism
Currently all students originally assigned to each group are listed as equal authors/contributors to their project. If you have not contributed the content you had originally agreed to, nor participated in the group work process, then you should contact the course coordinator immediately and either discuss your contribution or request removal from the group author list. Remember that all student online contributions are recorded by date, time and the actual contributed content. A similar email reminder will be sent to all current students.
Please note the Universities Policy regarding Plagiarism
In particular this example:
- "Claiming credit for a proportion of work contributed to a group assessment item that is greater than that actually contributed;"
Academic Misconduct carries penalties. If a student is found guilty of academic misconduct, the penalties include warnings, remedial educative action, being failed in an assignment or excluded from the University for two years.
SOMS Summer Research Awards
- The Research Support Committee is pleased to announce that it will again be offering Summer Research Awards (SRAs).
- These awards are for undergraduate students carrying out supervised research in SOMS between November 2014 and February 2015.
- Successful students will receive a stipend each week for 6 weeks of research. More Information?
References
- 2014 Course: Week 2 Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lab 1 | Week 3 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lab 2 | Week 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lab 3 | Week 5 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lab 4 | Week 6 Lecture 9 Lecture 10 Lab 5 | Week 7 Lecture 11 Lecture 12 Lab 6 | Week 8 Lecture 13 Lecture 14 Lab 7 | Week 9 Lecture 15 Lecture 16 Lab 8 | Week 10 Lecture 17 Lecture 18 Lab 9 | Week 11 Lecture 19 Lecture 20 Lab 10 | Week 12 Lecture 21 Lecture 22 Lab 11 | Week 13 Lecture 23 Lecture 24 Lab 12
Student Projects - Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | Group 7 | Group 8 | Moodle