2010 Foundations Lecture - Introduction to Human Development: Difference between revisions
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
[[File:Chorion 001 icon.jpg|120px|link=Development Animation - Chorionic Cavity]] | [[File:Chorion 001 icon.jpg|120px|link=Development Animation - Chorionic Cavity]] | ||
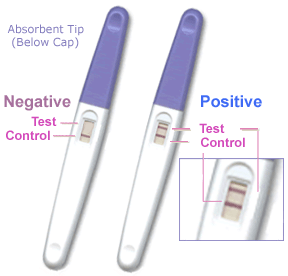
==Detect Pregnancy== | ==Pregnancy== | ||
===Detect Pregnancy=== | |||
[[File:Pregnancy_test.gif|thumb|pregnancy test]] | [[File:Pregnancy_test.gif|thumb|pregnancy test]] | ||
* Last Menstrual Period (LMP) - today ? | * Last Menstrual Period (LMP) - today ? | ||
* Birth Date - January 30, 2011 | * Birth Date - January 30, 2011 | ||
===Gestation Calculation=== | |||
* First pregnancy (primipara) 274 days, just over 39 weeks | |||
* Subsequent pregnancies (multipara) 269 days, 38.4 weeks | |||
Median duration of gestation assumed from ovulation to delivery | |||
* Historic - Franz Carl Naegele (1777-1851), first rule for estimating pregnancy length | |||
* Current - Ultrasound, the most accurate staging method | |||
Revision as of 11:51, 23 April 2010
Introduction
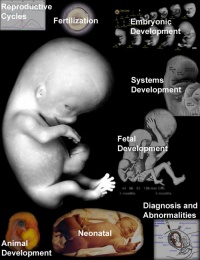
Human development is one of the most exciting topics to study not only as a medical student, but also for our fundamental understanding of the human body. This lecture is going to take you briefly through key concepts in human development, these will later be explored in more detail through the BGD course. The lecture will be followed by a practical class introducing online resources for independent study and working through similar embryology concepts.
Aims
- Purpose of learning embryology
- Basic facts about early human development
- Appreciate differences between the conceptus, embryo and fetus
- General understanding of the term “critical periods” of development
Concepts: Fertilization, Early conceptus, Germ layers, Embryo, Tissue origins, Timetable/stages of development, Fetus, Placenta
Background Lectures: Cell Structure (structure and function), Cell Division (mitosis, meiosis, lifespan, cell death), 4 Basic Tissues (Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous)
Links: Embryology Textbooks | 2009 Lecture | 2009 Lecture Slides
Animated overview
| <Flowplayer height="400" width="360" autoplay="true">Human development 001.flv</Flowplayer> | This animation begins at the two cell (blastomere) stage following fertilization and takes you through an overview of the entire 9 months of human development in just over a minute!
|
UNSW Embryology Online
- Original Website http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/
- New Website http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/
Textbooks
- There are many different excellent embryology textbooks
- I have included 2 that cover the clinical topics as well.
- More Textbooks?
The Developing Human: Clinically oriented embryology

|
Citation: The developing human : clinically oriented embryology 8th ed. Moore, Keith L; Persaud, T V N; Torchia, Mark G Philadelphia, PA : Saunders/Elsevier, c2008.
|
Larsen's human embryology
|
Citation: Larsen's human embryology 4th ed. Schoenwolf, Gary C; Larsen, William J, (William James). Philadelphia, PA : Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone, c2009.
|
Four Basic Tissue Types
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscular
- Nervous
- How do they develop?
- Where do they come from?
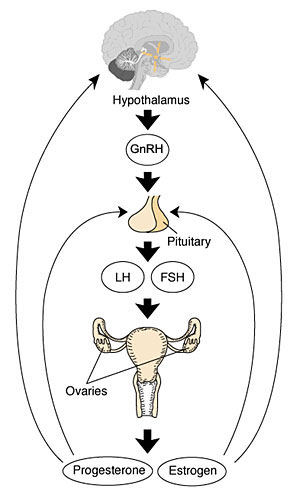
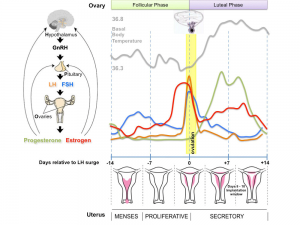
Human Reproductive Cycle
- Meiosis in gonad produces haploid gametes (egg and sperm)
Female
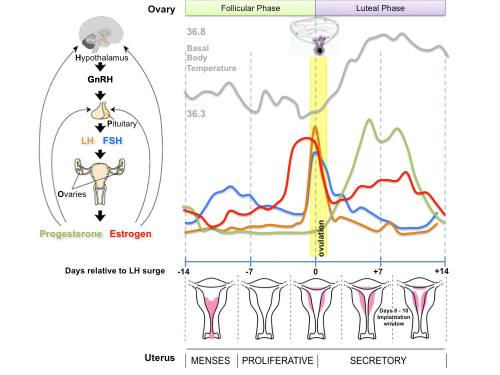
- Menstrual Cycle a regular cycle of reproduction (28 days)
- begins at puberty
- release of 1 egg (oocyte) every cycle
- Endocrine controlled (HPG axis)
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary
- Gonad
Male
- continuous production of spermatozoa
- begins at puberty
- release millions of spermatazoa
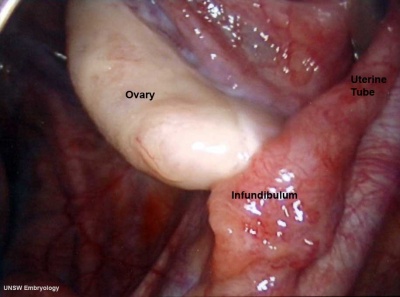
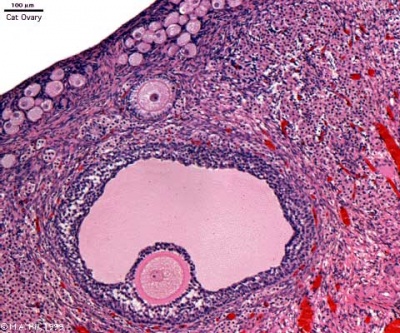
Ovary
- Paired organs
- lying in the peritoneal cavity
Ovulation
- ovulation is the release of the egg (oocyte)
- middle of the menstrual cycle
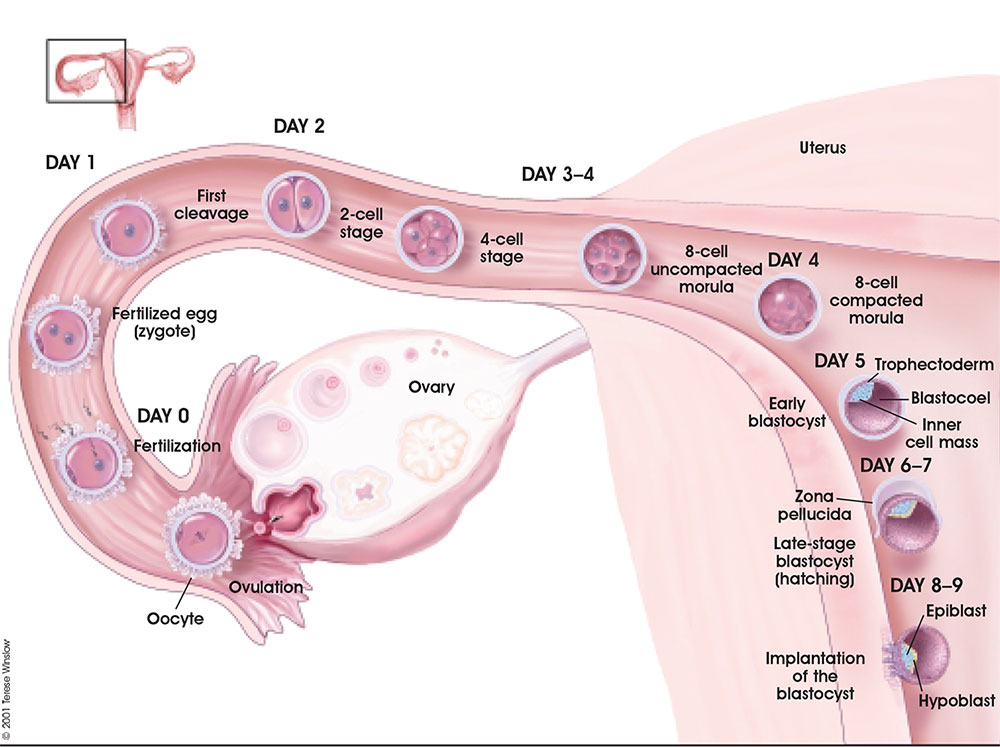
Fertilization
- the process of the 2 haploid gametes (egg and sperm) fusing and combining genetic material.
- conceptus - the entire product of fertilization
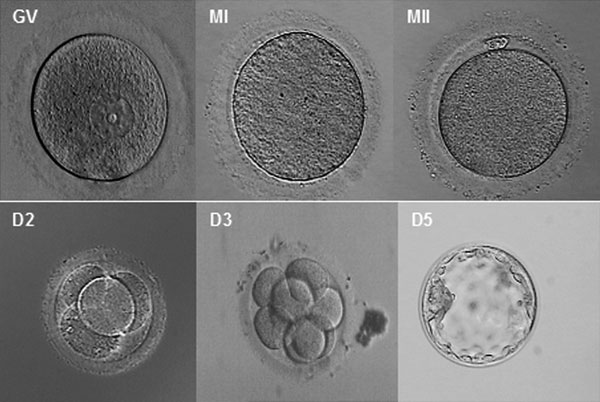
Early Development
- occurs during week 1 following fertilization
- last menstrual period (LMP) week 3
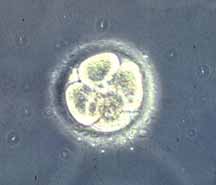
- mitosis to form solid ball of cells (morula), then hollow ball (blastocyst)
Week 1 Development
- occurs freely floating in uterus
Week 2 Development
- Implantation
- initial attachment to uterine wall
- invasion of uterine wall
Pregnancy
Detect Pregnancy
- Last Menstrual Period (LMP) - today ?
- Birth Date - January 30, 2011
Gestation Calculation
- First pregnancy (primipara) 274 days, just over 39 weeks
- Subsequent pregnancies (multipara) 269 days, 38.4 weeks
Median duration of gestation assumed from ovulation to delivery
- Historic - Franz Carl Naegele (1777-1851), first rule for estimating pregnancy length
- Current - Ultrasound, the most accurate staging method
Calculate a new Birth Date (I need to update calculator for 2010)
Revision Notes
- Don't confuse "germ cell layers" (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) with "germ cells" (egg, spermatazoa).
- Remember the difference between "clinical weeks" (last menstral period) and "embryonic weeks" (from fertilization, 2 weeks later).
- Revise meiosis and the difference between mechanism and timecourse for oogenesis and spermatogenesis in generating haploid gametes.
- With abnormalities, think about the types of prenatal dianostic techniques that are now available, the 2 major types (genetic and environmental) and the effect of maternal age/lifestyle.
2010 Foundations Practical - Introduction to Human Development
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology 2010 Foundations Lecture - Introduction to Human Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Foundations_Lecture_-_Introduction_to_Human_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G