2009 Lecture 13: Difference between revisions
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
* '''Lectures:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Science/ANAT2341lecture16.htm ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 16] | * '''Lectures:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Science/ANAT2341lecture16.htm ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 16] | ||
* '''Movies:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/ | * '''Movies:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/mesoderm.htm Mesoderm Movies] | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 11 September 2009
Musculoskeletal Development
Introduction
This lecture is an introduction to the process of musculoskeletal development. In the body, this is mainly about mesoderm differentiation beginning with an embryonic connective tissue structure, the mesenchyme. In the head, this is a mixture of mesoderm and neural crest differentiation, from mesenchyme and ectomesenchyme respectively. The lecture will cover mainly cartilage and bone, as muscle will be covered in the limb lecture and in this week's laboratory.
Lecture Objectives
- Understanding of mesoderm and neural crest development.
- Understanding of connective tissue development.
- Understanding of muscle, cartilage and bone development.
- Understanding of the two forms of bone development.
- Brief understanding of bone molecular development.
- Brief understanding of other bone roles.
- Brief understanding of bone abnormalities.
Textbook References
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 15 the skeletal system
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 11 Limb Dev (bone not well covered in this textbook)
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch16,17: p379-397, 399-405
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Ch11 p207-228
Summary
Abnormalities
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240.
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418.
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 Paraxial and intermediate mesoderm | Myogenesis: The Development of Muscle | Osteogenesis: The Development of Bones | Figure 14.10. Conversion of myoblasts into muscles in culture
- Molecular Biology of the Cell Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 Search Molecular Biology of the CellBone Is Continually Remodeled by the Cells Within ItImage: Figure 22-52. Deposition of bone matrix by osteoblasts.Image: Figure 22-56. The development of a long bone.
Search
- Bookshelf mesoderm | somite | myogenesis | chondrogenesis | osteogenesis
- Pubmed mesoderm | somite | myogenesis | chondrogenesis | osteogenesis
UNSW Embryology Links
- Notes: Bone Development | Limb Development | Axial Skeleton Development | Bone Development | Skull | Development Limb | Axial Skeleton| Human Bone | Endochondral Ossification | Skeletal Muscle | Cartilage | Joints
- Lectures: ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 16
- Movies: Mesoderm Movies
External Links
- UWA Blue Histology Skeletal Tissues - Bone
- University of Kansas Histoweb Bone
- Loyola University Medical Education Network Part 9: Specialized Connective Tissue: Cartilage and Bone | Part 10: Endochondral Ossification
- UNSW Embryology Cartilage and Bone
Terms
annulus fibrosus - the circularly arranged fibers (derived from sclerotome)that together with the nucleus pulposus (derived from notochord) form the intervertebral disc (IVD) of the vertebral column.
axial mesoderm - (=notochord)
cartilage - connective tissue from mesoderm in the embryo forms the initial skeleton which is replaced by bone. In adult, found on surface of bone joints.
centrum - the primordium of the [#vertebral body vertebral body] formed initially by the sclerotome.
clavicle - (L. little key) bone which locks sholder to body.
cloacal membrane- at caudal (anal) end of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) where surface ectoderm and GIT endoderm meet forms the openings for GIT, urinary, reproductive tracts. (see also [#buccopharyngeal membrane buccopharyngeal membrane])
connective tissue-
costotransverse -
costovertebral -
dermatome -
dermomyotome - dorsolateral half of each somite that forms the dermis and muscle.
ectoderm - the layer (of the 3 germ cell layers) which form the nervous system from the neural tube and neural crest and also generates the epithelia covering the embryo.
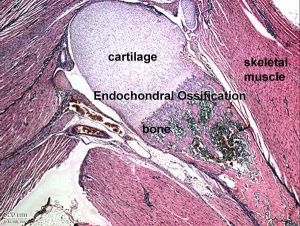
endochondrial ossification - the process of replacement of the cartilagenous framework by osteoblasts with bone.
epaxial myotome - the dorsal portion of the myotome that generates dorsal skeletal muscles (epaxial muscles).
erector spinae -
extracellular matrix - material secreted by and surrounding cells. Consists if fibers and ground substance.
fibroblast growth factors - (FGF) a family of at least 10 secreted proteins that bind membrane tyrosine kinase receptors. A patterning switch with many different roles in different tissues. (FGF8 = androgen-induced growth factor (AIGF)
fibroblast growth factor receptor - receptors comprise a family of at least 4 related but individually distinct tyrosine kinase receptors (FGFR1- 4). They have a similar protein structure, with 3 immunoglobulin-like domains in the extracellular region, a single membrane spanning segment, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain.
growth factor - usually a protein or peptide that will bind a cell membrane receptor and then activates an intracellular signaling pathway. The function of the pathway will be to alter the cell directly or indirectly by changing gene expression. (eg shh)
hox - (=homeobox) family of transcription factors that bind DNA and activate gene expression. Expression of different Hox genes along neural tube defines rostral-caudal axis and segmental levels.
hypaxial myotome - the ventral portion of the myotome that generates ventral skeletal muscles (hypaxial muscles).
intercostal- the region between adjacent ribs, usually comprising intercostal muscles and connective tissue.
intervertebral disc- (IVD) the annulus fibrosus+nucleus pulposus together form the intervertebral disc (IVD) of the vertebral column. This is the flexible region between each bony vertebra that allows the column to be bent.
intervertebral foramina-
lumbar plexus - mixed spinal nerves innervating the lower limb form a complex meshwork (crossing).
mesenchymal progenitor cells - (MPCs) cells able to differentiate in various types of connective tissue, including cartilage, bone and adipose tissue.
mesoderm - the middle layer of the 3 germ cell layers of the embryo. Mesoderm outside the embryo and covering the amnion, yolk and chorion sacs is extraembryonic mesoderm.
myoblast - the undifferentiated mononucleated muscle cells that will fuse together to form a multinucleated myotube, then mature into a muscle fibre.
MyoD - transcription factor involved in the determination of muscle cells in the somite. A basic helix-loop-helix factor which binds DNA.
myotome - the portion of the dermamyotome that generates skeletal muscle. Has 2 components epaxial (dorsal muscles ) hypaxial (ventral muscles).
neural crest - cell region at edge of neural plate, then atop the neural folds, that remains outside and initially dorsal to the neural tube when it forms. These paired dorsal lateral streaks of cells migrate throughout the embryo and can differentiate into many different cell types(=pluripotential). Those that remain on the dorsal neural tube form the sensory spinal ganglia (DRG). Neural crest cells migrate into the somites.
osteoblast - The mesenchymal cells that differentiate to form the cellular component of bone and produce bone matrix. Mature osteoblasts are called osteocytes. (More? Musculoskeletal Development - Bone)
osteoclast - Cells that remove bone (bone resorption) by enzymatically eroding the bone matrix. These cells are monocyte-macrophage in origin and fuse to form a multinucleated osteoclast. These cells allow continuous bone remodelling and are also involved in calcium and phosphate metabolism. The erosion cavity that the cells lie iwithin and form is called Howship's lacuna. (More? Musculoskeletal Development - Bone)
osteocyte - The mature bone-forming cell, which form the cellular component of bone and produce bone matrix. Differentiate from osteoblasts, mesenchymal cells that differentiate to form bone. (More? Musculoskeletal Development - Bone)
osteon - The anatomical (histological) unit structure (principal structure) of compact bone. (More? Musculoskeletal Development - Bone)
Pax - name derived from Drosophila gene 'paired' (prd) the 'paired box' is a amino end 124 amino-acid conserved domain (signature aa 35-51: P-C-x(11)-C-V-S). Transcription factor of the helix-turn-helix structural family, DNA binding, and activating gene expression. In human, nine member proteins from Pax-1 to Pax-9. Regulate differentiation of many different tissues. Some members of the family (PAX3, PAX4, PAX6, PAX7) also contain a functional homeobox domain.
pedicle -
primary centre of ossification - the first area where bone growth occurs between the periosteum and cartilage.
sacrum -
sclerotome - ventromedial half of each somite that forms the vertebral body and intervertebral disc.
segmentation - to break a solid structure into a number of usually equal size pieces.
somatic mesoderm - derived from lateral mesoderm closest to the ectoderm and separated from other component of lateral mesoderm (splanchnic, near endoderm) by the intraembryonic coelom.
somite - segmental block (ball) of mesoderm formed from paraxial mesoderm adjacent to notochord (axial mesoderm). Differentiates to form initially sclerotome and dermamyotome (then dermotome and myotome).
somitic mesoderm-
somitocoel - a transient cavity that appears within each of the the early forming somites then is lost.
somitogenesis - the process of segmentation of the paraxial mesoderm to form "mesoderm balls" beginning cranially (humans day20) and extending caudally at 1 somite/90 minutes until approx. 44 pairs have been formed.
sonic hedgehog - (=shh) secreted growth factor that binds patched (ptc) receptor on cell membrane. SHH function is different for different tissues in the embryo. In the nervous system, it is secreted by the notochord, ventralizes the neural tube, inducing the floor plate and motor neurons. In the Limb it is secreted by the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) organizing limb axis formation.
tarsal -
Tbx - T-box genes (transcription factor) involved in mouse forelimb (Tbx4) and hindlimb (Tbx5) specification.
transcription factor- a factor (protein or protein with steroid) that binds to DNA to alter gene expression, usually to activate. (eg steroid hormone+receptor, Retinoic acid+Receptor, Hox, Pax, Lim, Nkx-2.2).
transverse abdominal m.-
trochanter-
vertebral body- formed by centrum, vertebral arch, facets for ribs. It is the mature vertebral structure formed by the 5 secondary ossification centers after puberty.
vertebral column - name given to the complete structure formed from the alternating segments of vertebra and intervertebral discs which support the spinal cord.
vertebral foramen - the dorsal cavity within each vertebra, generated by the vertebral arch that surrounds the spinal cord.
vertebral canal -
Wnt7a - The designation 'Wnt' was derived from 'wingless' and 'int'. The Wnt gene was first defined as a protooncogene, int1. Humans have at least 4 Wnt genes: Wnt7a gene is at 3p25 encoding a 349aa secreted glycoprotein. A patterning switch with different roles in different tissues. The mechanism of Wnt distribution (free diffusion, restricted diffusion and active transport) and all its possible cell receptors are still being determined. At least one WNT receptor is Frizzled (FZD). The Frizzled gene family encodes a seven-transmembrane receptor.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 5) Embryology 2009 Lecture 13. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_13
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G