Endocrine - Adrenal Development
Adrenal
The developing adrenal gland has both an interesting origin and an intruiging fetal role.
The adrenal gland and placenta also act in synergy, and the notes endocrine placenta should also be read.
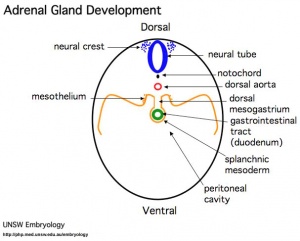
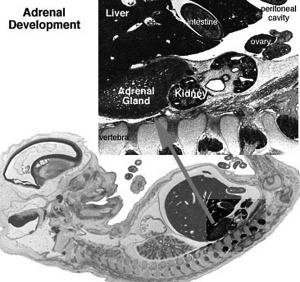
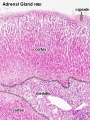
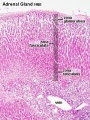
The 2 adrenal glands (suprarenal gland, glandulæ suprarenales) are named by their anatomical postion sitting above the 2 kidneys (renal). The 2 main parts of the adrenals have different embryonic origins. The inside core adrenal medulla is neural crest in origin. Mesenchyme surrounding these cells differentiates to form a fetal cortex. This fetal cortex is later replaced by the adult cortex. The outside adrenal cortex is derived from mesothelium and can be further divided into 3 distinct layers (zona reticularis, zona fasiculata, zona glomerulosa) each with distinct hormonal functions.
During fetal development, adrenal hormones are involved with the maturation of the lung and other developing systems.
| Lecture - Neural Crest Development | original page
- Richly vascularized - arterioles passing through cortex, capillaries from cortex to medulla, portal-like circulation
- Fetal Cortex - produces a steroid precursor (DEA), converted by placenta into estrogen
- Adult Medulla - produces adrenalin (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
- Fetal adrenal hormones - influence lung maturation
Adrenal cortical hormones - (steroids) Cortisol, Aldosterone, Dehydroepiandrosterone
- zona glomerulosa - regulated by renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system controlled by the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidney.
- zona fasciculata - regulated by hypothalamo-pituitary axis with the release of CRH and ACTH respectively.
Adrenal medullary hormones - (amino acid derivatives) Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
Adrenal Development
- Fetal Adrenals - fetal cortex later replaced by adult cortex
- Week 6 - fetal cortex, from mesothelium adjacent to dorsal mesentery; Medulla, neural crest cells from adjacent sympathetic ganglia
- Adult cortex - mesothelium mesenchyme encloses fetal cortex
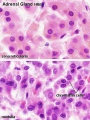
Adrenal Cortex
- Late Fetal Period - differentiates to form cortical zones
- Birth - zona glomerulosa, zona fasiculata present
- Year 3 - zona reticularis present
Endocrinology - Adrenal Cortex Development
Adrenal Medulla
- neural crest origin, migrate adjacent to coelomic cavity, initially uncapsulated and not surrounded by fetal cortex, cells have neuron-like morphology
- 2 cell types - secrete epinepherine (adrenaline) 80%; secrete norepinepherine (noradrenaline* 20%
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search April 2010
- Endocrine Development - All (14277) Review (4620) Free Full Text (3140)
Search Pubmed: adrenal development
Additional Images
Adult Histology
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 1) Embryology Endocrine - Adrenal Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Endocrine_-_Adrenal_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G