2009 Lecture 13: Difference between revisions
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Online Textbooks=== | ===Online Textbooks=== | ||
* '''Developmental Biology''' by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 | * '''Developmental Biology''' by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 | ||
* '''Molecular Biology of the Cell''' Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi? | * '''Molecular Biology of the Cell''' Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=mboc4.TOC&depth=2 Search Molecular Biology of the Cell][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.section.4177#4187 Bone Is Continually Remodeled by the Cells Within It][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.figgrp.4191 Image: Figure 22-52. Deposition of bone matrix by osteoblasts.][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.figgrp.4196 Image: Figure 22-56. The development of a long bone.] | ||
===Search === | ===Search === | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 11 September 2009
Musculoskeletal Development
Introduction
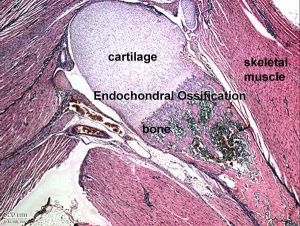
This lecture is an introduction to the process of musculoskeletal development. In the body, this is mainly about mesoderm differentiation beginning with an embryonic connective tissue structure, the mesenchyme. In the head, this is a mixture of mesoderm and neural crest differentiation, from mesenchyme and ectomesenchyme respectively. The lecture will cover mainly cartilage and bone, as muscle will be covered in the limb lecture and in this week's laboratory.
Lecture Objectives
- Understanding of mesoderm and neural crest development.
- Understanding of connective tissue development.
- Understanding of muscle, cartilage and bone development.
- Understanding of the two forms of bone development.
- Brief understanding of bone molecular development.
- Brief understanding of other bone roles.
- Brief understanding of bone abnormalities.
Textbook References
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 15 the skeletal system
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 11 Limb Dev (bone not well covered in this textbook)
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch16,17: p379-397, 399-405
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Ch11 p207-228
Early Development and Neural Derivatives
Abnormalities
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240.
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418.
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000
- Molecular Biology of the Cell Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 Search Molecular Biology of the CellBone Is Continually Remodeled by the Cells Within ItImage: Figure 22-52. Deposition of bone matrix by osteoblasts.Image: Figure 22-56. The development of a long bone.
Search
- Bookshelf neural crest
- Pubmed neural crest
UNSW Embryology Links
- Notes: Bone Development | Limb Development | Axial Skeleton Development | Bone Development | Skull | Development Limb | Axial Skeleton| Human Bone | Endochondral Ossification | Skeletal Muscle | Cartilage | Joints
- Lectures: ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 16
- Movies: Neural Movies
External Links
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 3) Embryology 2009 Lecture 13. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_13
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G