Neural Crest - Peripheral Nervous System
| Embryology - 10 Mar 2026 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
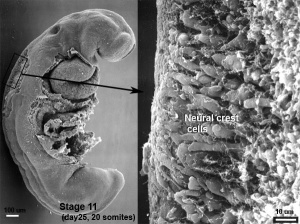
The neural crest are bilaterally paired strips of cells arising in the ectoderm at the margins of the neural tube. These cells migrate to many different locations and differentiate into many cell types within the embryo. This means that many different systems (neural, skin, teeth, head, face, heart, adrenal glands, gastrointestinal tract) will also have a contribution fron the neural crest cells.
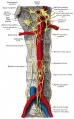
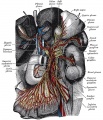
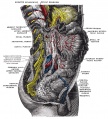
In the body region, neural crest cells also contribute the peripheral nervous system (both neurons and glia) consisting of sensory ganglia (dorsal root ganglia), sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia and neural plexuses within specific tissues/organs.
In the head region, neural crest cells migrate into the pharyngeal arches (as shown in movie below) forming ectomesenchyme contributing tissues which in the body region are typically derived from mesoderm (cartilage, bone, and connective tissue).General neural development is also covered in Neural Notes.
| Neural Crest Links: neural crest | Lecture - Early Neural | Lecture - Neural Crest Development | Lecture Movie | Schwann cell | adrenal | melanocyte | peripheral nervous system | enteric nervous system | cornea | cranial nerve neural crest | head | skull | cardiac neural crest | Nicole Le Douarin | Neural Crest Movies | neural crest abnormalities | Category:Neural Crest | |||
|
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Peripheral Nervous System Development <pubmed limit=5>Peripheral Nervous System Development</pubmed> Search term: Dorsal Root Ganglia Development <pubmed limit=5>Dorsal Root Ganglia Development</pubmed> Search term: Sympathetic Development <pubmed limit=5>Sympathetic Development</pubmed> |
Neural Crest Migration
<html5media height="380" width="410">File:Chicken-neural crest migration 01.mp4</html5media>
Movie Source: Original Neural Crest movies kindly provided by Paul Kulesa.[4]
Related Movies: Migration 01 | Migration 02 | Migration 03 | Migration 04 | Migration 05 | Migration 06 | Migration 07
Development Overview
The following cranial and trunk data is based upon 185 serially sectioned staged (Carnegie) human embryos.[5]
Cranial Neural Crest
- stage 9 - an indication of mesencephalic neural crest
- stage 10 - trigeminal, facial, and postotic components
- stage 11 - crest-free zones are soon observable in rhombomere 1, 3, and 5
- stage 12 - rhombomeres 6 and 7 neural crest migrate to pharyngeal arch 3 and then rostrad to the truncus arteriosus
- stage 13 - nasal crest and the terminalis-vomeronasal complex are last of the cranial crest to appear
stages 9-14 - otic vesicle primordium descends
Trunk Neural Crest
Spinal ganglia increase in number over time and are in phase with the somites, though not their centre. There are 3 migratory pathways: ventrolateral between dermatomyotome and sclerotome, ventromedial between neural tube and sclerotomes, and lateral between surface ectoderm and dermatomyotome.
- stage 13 - about 19 present
- stage 14 - about 33 present
- stage 15-23 - 30–35 ganglia
Animal Models
Mouse
| Model of trunk Neural Crest Cell migration to organise Mouse PNS neurons[6]
(A and B) NCC migration pathways at 9.5 dpc.
Figure and text modified from[6] |

Abbreviations: da, dorsal aorta; dm, dermomyotome; isv, intersomitic vessel; psv, perisomitic vessel; pcv, posterior cardinal vein; scl, sclerotome. |
References
- ↑ Vukojevic K, Filipovic N, Tica Sedlar I, Restovic I, Bocina I, Pintaric I & Saraga-Babic M. (2016). Neuronal differentiation in the developing human spinal ganglia. Anat Rec (Hoboken) , 299, 1060-72. PMID: 27225905 DOI.
- ↑ Hu ZL, Shi M, Huang Y, Zheng MH, Pei Z, Chen JY, Han H & Ding YQ. (2011). The role of the transcription factor Rbpj in the development of dorsal root ganglia. Neural Dev , 6, 14. PMID: 21510873 DOI.
- ↑ Kulesa PM, Bailey CM, Kasemeier-Kulesa JC & McLennan R. (2010). Cranial neural crest migration: new rules for an old road. Dev. Biol. , 344, 543-54. PMID: 20399765 DOI.
- ↑ Kulesa PM & Fraser SE. (2000). In ovo time-lapse analysis of chick hindbrain neural crest cell migration shows cell interactions during migration to the branchial arches. Development , 127, 1161-72. PMID: 10683170
- ↑ O'Rahilly R & Müller F. (2007). The development of the neural crest in the human. J. Anat. , 211, 335-51. PMID: 17848161 DOI.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Schwarz Q, Maden CH, Vieira JM & Ruhrberg C. (2009). Neuropilin 1 signaling guides neural crest cells to coordinate pathway choice with cell specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. , 106, 6164-9. PMID: 19325129 DOI.
Reviews
Krispin S, Nitzan E & Kalcheim C. (2010). The dorsal neural tube: a dynamic setting for cell fate decisions. Dev Neurobiol , 70, 796-812. PMID: 20683859 DOI.
Ernsberger U. (2009). Role of neurotrophin signalling in the differentiation of neurons from dorsal root ganglia and sympathetic ganglia. Cell Tissue Res. , 336, 349-84. PMID: 19387688 DOI.
Sarnat HB & Flores-Sarnat L. (2005). Embryology of the neural crest: its inductive role in the neurocutaneous syndromes. J. Child Neurol. , 20, 637-43. PMID: 16225807 DOI.
Chen HH, Hippenmeyer S, Arber S & Frank E. (2003). Development of the monosynaptic stretch reflex circuit. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. , 13, 96-102. PMID: 12593987
Schober A & Unsicker K. (2001). Growth and neurotrophic factors regulating development and maintenance of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Int. Rev. Cytol. , 205, 37-76. PMID: 11336393
Articles
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: Peripheral Neural Development | Dorsal Root Ganglia Development | Sympathetic Neural Development | Parasympathetic Neural Development | Neural Crest Development
Additional Images
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 10) Embryology Neural Crest - Peripheral Nervous System. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Neural_Crest_-_Peripheral_Nervous_System
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G