Genetics - Chromosome 17
Introduction
|
|
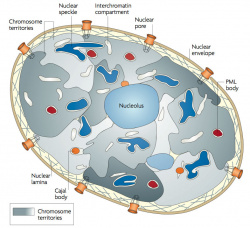
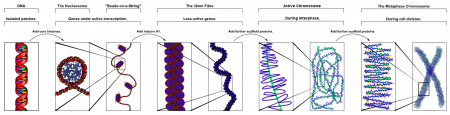
| Chromosome territories (interphase) | Chromosome (Chromatin) structure (mitosis) |
| Human Chromosomes: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | X | Y |
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Chromosome 17 |
Development Genes
TBX
| Table - Human Tbx Family | ||||
| Approved Symbol |
Approved Name | Previous Symbols | Synonyms | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBX2 | T-box 2 | 17q23.2 | ||
| TBX4 | T-box 4 | 17q23.2 | ||
| TBX21 | T-box 21 | "TBLYM, T-bet" | 17q21.32 | |
| Links: Developmental Signals - Tbx | OMIM Tbx3 | HGNC | Bmp Family | Sox Family | Tbx Family | ||||
| Human TBX Family | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hes7
Hairy/Enhancer Of Split, Drosophila, Homolog Of, 7 (HES7) 17p13.1 is a transcriptional repressor protein with the structure containing a basic helix-loop-helix-Orange domain. It is a direct target of the Notch signaling pathway and also part of a negative feedback required to attenuate Notch signaling. somitogenesis
Abnormalities
In 1994, two breast cancer susceptibility genes were identified BRCA1 on chromosome 17 and BRCA2 on chromosome 13.
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
| |
| Idiogram Chromosome Banding - The term refers to the light and dark pattern, seen after staining with a dye, of individual chromosomes identified in metaphase. It is only in meiosis and mitosis during metaphase that chromosomes can be easily identified, during the normal cell life (interphase) the chromosomes are unravelled and distributed within the nucleus in chromosome territories. A band is that part of a chromosome which is clearly distinguishable from nearby regions by appearing darker or brighter with one or more banding techniques. | |
| Genetic abnormality locations: 1-4 | 5-8 | 9-12 | 13-16 | 17-20 | 21-XY | sSMC | |
| |
| Links: Genetics | Abnormal Development - Genetic |
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 30) Embryology Genetics - Chromosome 17. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Genetics_-_Chromosome_17
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 30) Embryology Genetics - Chromosome 17. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Genetics_-_Chromosome_17
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ Jariwal R, Shoua B, Sabetian K, Natarajan P & Cobos E. (2018). Unmasking a Case of Asymptomatic Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT1A) With Vincristine. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep , 6, 2324709618758349. PMID: 29511693 DOI.
- ↑ Achyutuni S, Nadhan R, Sengodan SK & Srinivas P. (2017). The prodigious network of chromosome 17 miRNAs regulating cancer genes that influence the hallmarks of cancer. Semin. Oncol. , 44, 254-264. PMID: 29526253 DOI.
