Foundations Practical - Week 9 to 36
Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
The Fetal Period
- Growth and organ differentiation.
The fetal period is about continued differentiation of organs and tissues, most importantly this period is about growth both in size and weight.
Fetal Development - Page with an animation covering the fetal period showing changing proportions, not size, of the fetus.
The cartoon shows changes in the relative proportions of head and body and growth of the limbs, it does not show the overall growth in size.
Many different systems formed in the embryonic period (organogensesis) grow and differentiate further during the fetal period and do so at different times.
For example, the brain continues to grow and develop extensively during this period (and postnatally), the respiratory system differentiates (and completes only just before birth), the urogenital system further differentiates between male/female, endocrine and gastrointestinal tract begins to function.
Finally consider the systems (for example respiratory, cardiac, neural) that will still not have their final organization and function determined until after birth.
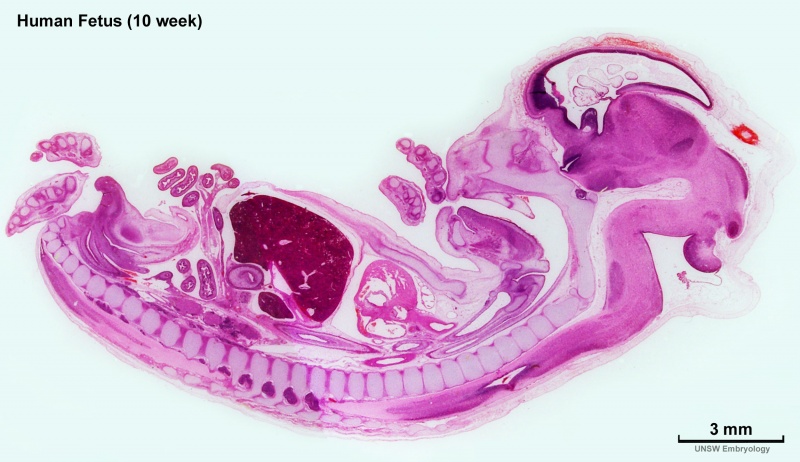
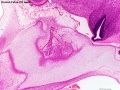
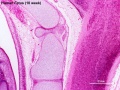
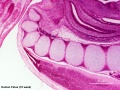
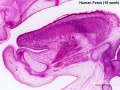
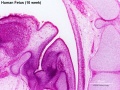
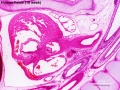
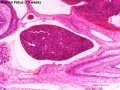
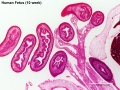
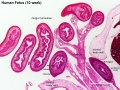
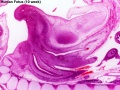
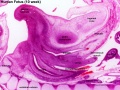
Human 10 Week
I do not expect detailed analysis of the following image, just observe the anatomical structures present at this early fetal stage.
This page is a link to images from a 10 week female fetus approximately 40 mm in size. This is showing an early stage of fetal development after the embryonic period (up to week 8).
3 mm scale bar
- Human Female Fetus (week 10)
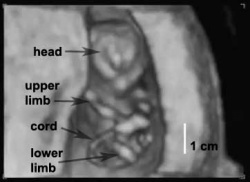
Human 12 Week 4D
| <html5media height="420" width="550">File:Ultrasound_Fetus_02.mp4</html5media> |
Ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique with many different applications
|
Fetal Growth
- First Trimester (1 - 12 weeks) - embryonic and early fetal
- Second Trimester (13 - 24 weeks) - organ development function and growth
- Third Trimester (25 - 40 weeks) - organ function and rapid growth
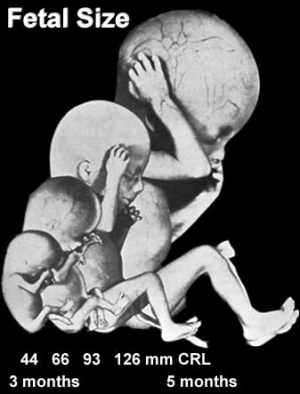
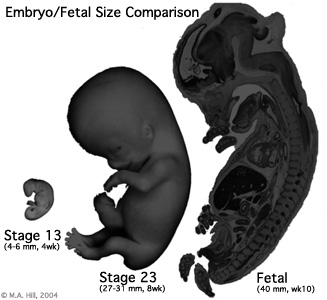
Embryo/Fetus Size Comparison
This is an enlarged image of the actual size comparison shown in the introduction of the Embryonic stage 13, 23 and Fetal stage 10 week 40mm.
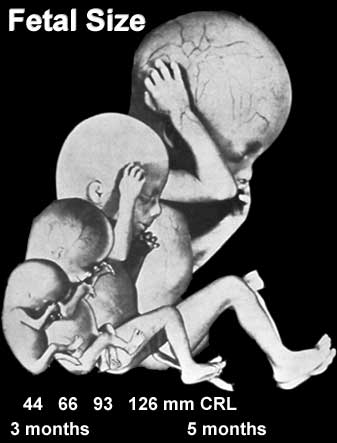
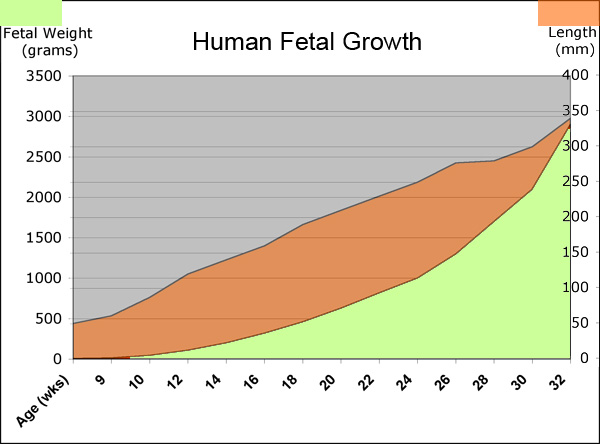
Fetal Length and Weight
Graph shows average Human Fetal Growth from Week 9 to 36. Weight is measured in grams, Length is crown/rump in millimeters.
During the fetal period there is a separation in changes in length and weight.
- Fetal length change increases through second and third trimesters.
- Fetal weight change is greatest in the final weeks of development (third trimester)
- Low birth weights can be an indicator of intrauterine growth restriction or retardation (IUGR), where the fetus that has not reached its growth potential because of genetic or environmental factors (less than 10th percentile for gestational age).
- High birth weights (macrosomia) can be an indicator of unregulated maternal diabetes.
- Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DoHaD) identifies maternal derived abnormalities relate to lifestyle, environment and nutrition and while some of these directly effect embryonic development, there is also growing evidence that some effects are more subtle and relate to later life health events, originally called the Developmental "Barker Hypothesis" and then the Fetal origins hypothesis.
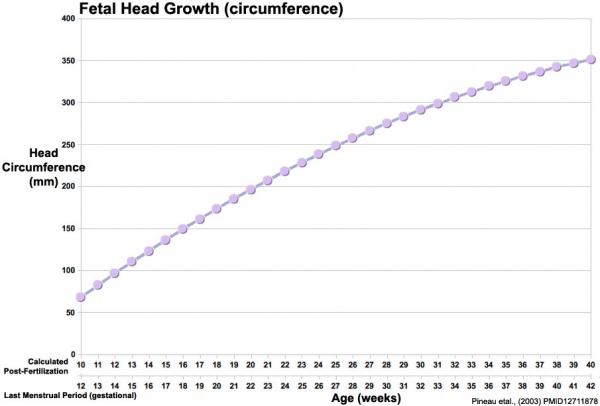
Fetal Head Growth
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
Embryo to Fetus

|
In 1949 the embryologist George Streeter[1] used the replacement of cartilage within the humerus by bone marrow as an arbitrary definition of the embryo to fetus transition.
|
| Fetal Links: fetal | Week 10 | Week 12 | second trimester | third trimester | fetal neural | Fetal Blood Sampling | fetal growth restriction | birth | birth weight | preterm birth | Developmental Origins of Health and Disease | macrosomia | BGD Practical | Medicine Lecture | Science Lecture | Lecture Movie | Category:Human Fetus | Category:Fetal | |||
|
- Fetal Graphs: Crown-Rump Length (CRL) | Third trimester CRL | Head Circumference | Head Circumference 2nd Trimester | Liver Weight | Pancreas Weight | Thymus Weight | Small Intestine Length | Large Intestine Length | Length and Weight Changes | Fetal Development
Take the Quiz
Open the table below, select your answers, click submit, then reopen the table to see your result.
| Quiz - Week 9 to 36 |
|---|
|
|
Terms
Note - linked terms in the list below are external resources to the current class content.
- fetal - (foetal) In mammals, term describes the period of development following the embryonic period. This term is also used non-scientifically to describe the human conceptus at both embryonic and fetal stages of development.
- fetal length - The measurement of crown to rump length of the developing fetus. The greatest growth in length occurs in the middle second trimester, of human development. There are a number of other growth parameters that can be measured, commonly determined by ultrasound, during the fetal period. (More? Fetal Development)
- fetal period - In humans, the development week 9 to 36 is the fetal stage (second and third trimester) and during this time organs formed in the embryonic period continue to develop and the fetus grows in size and weight. The first 8 weeks of development is considered the embryonic period and is divided into 23 Carnegie stages based upon developmental milestones. Note when searching an alternate spelling "foetal". (More? Fetal Development)
- fetal weight - The measurement of the weight of the developing fetus. The measurement is obtained by ultrasound calculation or clinically estimated by palpatation. The greatest addition of fetal weight occurs during and towards the end of the third trimester. (More? Fetal Development
- fundal height - Clinical measurement of distance from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus (fundus). Used during pregnancy as a general guide to fetal growth rate, the fundal height (cm) is n approximately equal to the the gestational age (GA) in weeks. (More? Fetal Development)
- intrauterine growth restriction - (IUGR) Term used to descibe clinically a fetus that has not reached its growth potential because of genetic or environmental factors. Abnormal development measured as less than 10th percentile for gestational age, not easy to detect before 32 weeks. This poor fetal growth can have fetal, placental or maternal causes. (More?Fetal Development | Medline Plus - IUGR)
- macrosomia - Term used to describe a newborn with an excessive birth weight. The definition is either a birth weight of 4000 to 4500 g (8 lb 13 oz to 9 lb 15 oz) or greater than 90% for gestational age after correcting for neonatal sex and ethnicity.
- ponderal index (PI) - Fetal calculation based upon ratio of body weight to length PI = [weight (in g) x 100] √∑ [length (in cm)] (More?Fetal Development)
- ultrasound - A noninvasive technique for visualizing the follicles in the ovaries and the gestational sac or fetus in the [U.htm#uterus uterus]. Uses high-frequency sound waves that are reflected off internal structures. These reflections can be analysed and displayed by computer.
- very low birth weight - (VLBW) This is defined as weight at birth of less than 1500 grams (3 lb, 5 oz).
Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 11) Embryology Foundations Practical - Week 9 to 36. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Foundations_Practical_-_Week_9_to_36
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ Streeter GL. Developmental horizons in human embryos (fourth issue). A review of the histogenesis of cartilage and bone. (1949) Carnegie Instn. Wash. Publ. 583, Contrib. Embryol., 33: 149-169. PMID: 18144445