Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
Newborn Infant
- Some essential systems come online, others continue to develop.
The neonatal period is about the transition from an interuterine placenta and maternally supported life to life to relatively independent life in the external environment.
In developing a broad understanding of the neonatal period you need to think about the two different environments and the effects of loss of placental support. Remember that substantial postnatal development still has to occur in many systems. Identify these systems and the associated changes that occur.
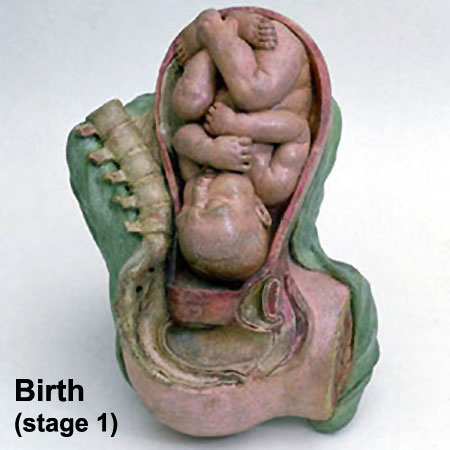
Birth
The median duration of gestation for first births from assumed ovulation to delivery was 274 days (just over 39 weeks). For multiple births, the median duration of pregnancy was 269 days (38.4 weeks).
Birth Weight
The primary causes of VLBW are premature birth (born <37 weeks gestation, and often <30 weeks) and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), usually due to problems with placenta, maternal health, or to birth defects. Many VLBW babies with IUGR are preterm and thus are both physically small and physiologically immature. See also DOHAD.
| Human Birth Weight Classifications
|
no colour
|
| Birth weight (grams)
|
less 500
|
500 – 999
|
1,000 – 1,499
|
1,500 – 1,999
|
2,000 – 2,499
|
2,500 – 2,999
|
3,000 – 3,499
|
3,500 – 3,999
|
4,000 – 4,499
|
4,500 – 4,999
|
5,000 or more
|
| Classification
|
Extremely Low Birth Weight
|
Very Low Birth Weight
|
Low Birth Weight
|
Normal Birth Weight
|
High Birth Weight
|
Newborn Homoeostasis
|
The newborn has to establish:
- lung function
- circulatory changes
- thermoregulation
- endocrine function
- nutrition
- gastrointestinal tract function
- waste
- kidney function
|
Australian Birth
Now briefly consider the current Australian trends in birth and the new reproductive technologies available.
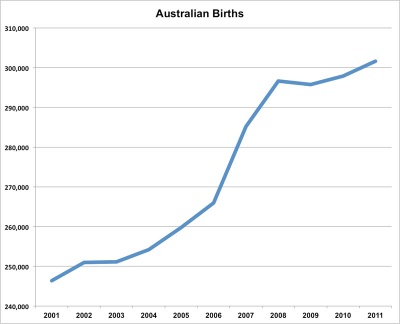
Australia’s mothers and babies 2016
- 310,247 women gave birth in Australia (an increase of 12% since 2006, 77,440 women).
- 62 per 1,000 women of reproductive age (15–44 years) giving birth (fluctuated between 2006 and 2016).
- 30.5 years of age, average age of all women who gave birth (continues to rise, 29.8 in 2006).
- 73% of mothers lived in major cities (most were themselves born in Australia).
- 66% of mothers (205,364) had a vaginal birth and 34% (104,839) had a caesarean section.
- Obesity in pregnancy contributes to increased risks of illness and death for both mother and baby.
- Maternal death most frequent causes were non-obstetric haemorrhage.
|
 Australia’s mothers and babies (2016) |
Assisted reproductive technology in Australia and New Zealand
 Assisted reproductive technology in Australia and New Zealand 2015 |
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) is a group of procedures that involve the in vitro (outside of body) handling of human oocytes (eggs) and sperm or embryos for the purposes of establishing a pregnancy.
Assisted Reproduction Technology (ART) is also used to identify in vitro fertilization (IVF), but now includes many new fertility techniques. Each ART treatment involves a number of stages and is generally referred to as an ART treatment cycle. The embryos transferred to a women can either originate from the cycle in which they were created (fresh cycle) or be frozen and thawed before transfer (thaw cycle).
- 77,721 ART treatment cycles reported from Australian and New Zealand clinics in 2015.
- 5.6% increase in Australia and 6.0% increase in New Zealand on 2014.
- 14.4 cycles per 1,000 women of reproductive age (15–44 years) in Australia.
- 94.5% of treatments used their own oocytes or embryos (autologous cycles).
- 37.4% of autologous cycles used embryos that had been frozen and thawed.
(More? Assisted Reproductive Technology)
|
Maternal Changes
- Puerperium - six weeks following birth, maternal reproductive organs and physiology return to pre-pregnancy state.
- Involution - process of tissue catabolism of uterus.
- Lochia - uterine (placental) discharge, blood plus mucous, continues for about 4 weeks.
- Mammary - glandular development and function.
Development does not finish at Birth
Many systems continue to grow and differentiate after birth, in particular neural, sensory, respiratory, renal, endocrine and genital.
|
|
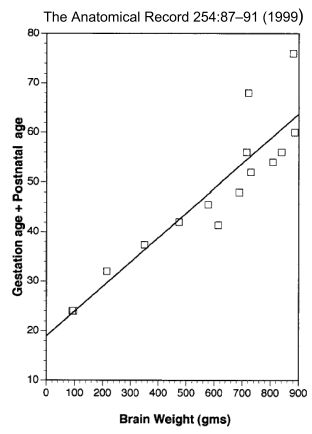
| Newborn Brain Changes - Complex and ongoing processes of neurological development continue postnatally. This can be seen at the very basic level by simply measuring the increase in overall brain weight.
|
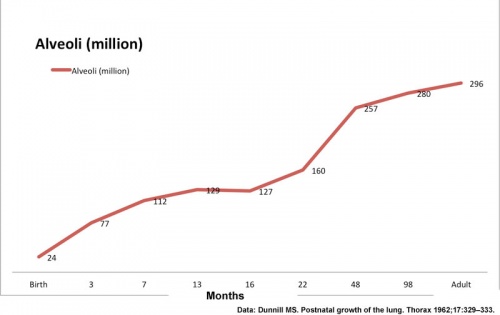
Postnatal lung growth - At birth about 15% of adult alveoli number have formed.
|
See also DOHAD.
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page.
|
Neonatal
Terms
Note - linked terms in the list below are external resources to the current class content.
| Birth Terms
|
- amniotomy - birth medical procedure thought to speed labor, where the amniotic sac is artificially ruptured using a tool (amniohook).
- birth - (parturition, partus, childbirth, labour, delivery). expulsion of the foetus from the uterus. (More? birth)
- Bishop score - (Bishop's score) A clinical test prior to birth named after the obstetrician/gynaecologist Edward H. Bishop (1913-1995) who published a 1964 paper "Pelvic Scoring For Elective Induction". (More? PMID 14199536)
- breech - fetal buttocks presented first and can also occur in different forms depending on presentation (complete breech, frank breech, footing breech, knee breech). (More? historic image)
- decidual activation - increased uterine proteolysis and extracellular matrix degradation.
- dilatation - opening of the cervix in preparation for birth (expressed in centimetres).
- effacement - shortening or thinning of the cervix, in preparation for birth.
- early cord clamping - placental cord clamping carried out in the first 60 seconds after birth.
- forceps - mechanical "plier-like" tool used on fetal head to aid birth.
- induction of labour - clinical procedure where labour starts artificially by using a membrane sweep, pessary or hormone drip.
- instrumental birth - birth process where the use of clinical instruments is required.
- labor - the maternal physiological process of birth. (More? birth)
- macrosomia - clinical description for a fetus that is too large, condition increases steadily with advancing gestational age and defined by a variety of birthweights. In pregnant women anywhere between 2 - 15% have birth weights of greater than 4000 grams (4 Kg, 8 lb 13 oz). (More? macrosomia)
- membrane rupture - breaking of the amniotic membrane and release of amniotic fluid (water breaking).
- morbidity - (Latin, morbidus = "sick" or "unhealthy") refers to a diseased state, disability, or poor health due to any cause.
- necrotising enterocolitis - clinical condition mainly seen in preterm infants, where portions of the bowel undergo necrosis.
- neonatal - the early postnatal period relating to the birth, it includes the period up to 4 weeks after birth.
- obstetric fistula - abnormal connection between the vagina and rectum or bladder caused by a prolonged obstructed labor.
- perinatal - the early postnatal period relating to the birth, statistically it includes the period up to 7 days after birth.
- presentation - how the fetus is situated in the uterus.
- presenting part - part of fetus body that is closest to the cervix.
- second stage of labour - passage of the baby through the birth canal into the outside world.
- tachycardia - rapid fetal heart rate (greater than 160 beats per minute) for the term fetus, usually determined by fetal monitoring.
- third stage of labour - interval from the birth of the baby to the expulsion of the placenta and membranes.
- tocolytic - a drug used to prevent or lessen uterine contractions.
- uterotonic - drug used to induce uterine contractions.
- umbilical cord acid-base analysis - clinical perinatal test used to assessing intrapartum hypoxia, measuring one or several indices: arterial umbilical cord blood pH, lactate, and base deficit. Hypoxia is indicated by a low pH, high base deficit and high lactate.
- vacuum extractor - (ventouse) rubber or metal suction cap device used on fetal head to aid birth.
- vertex presentation - (cephalic presentation) where the fetus head is the presenting part, most common and safest birth position.
- Z-score - (standard deviation scores) commonly used to assess growth of preterm infants. For an individual birth weight, a z-score of -1 is one standard deviation below the mean birth weight of the cohort.
- z-score differences - (Zdiff) uses standard deviation scores to analyze changes in growth for a particular observation period.
|
|
|
| Neonatal Terms
|
- Apgar test - neonatal test used in nearly all maternity clinics to assess the newborn infants well being assigned scores for each of 5 indicators: Heart Rate, Respiratory Effort, Reflex Irritability, Muscle Tone, Colour.
- Automated Auditory Brainstem Response - (AABR) neonatal hearing test that uses a trigger stimulus delivered through earphones and subsequent brain electrical activity then detected by scalp electrodes, averaging generates peaks reflecting signal passage activity through brain stem nuclei in the hearing central neural pathway.
- Babinski reflex - (plantar reflex) The up going toes or “Babinski reflex” is a normal reflex in the infant and may be present for the first year of life because at that developmental stage the incomplete myelination of the corticospinal tracts. Also found in a number of developmental and adult neural disorders. Video - plantar reflex
- birth weight - (birth-weight) the weight of the neonate measured as soon as possible after birth. The measurement can be indicative of a number of developmental abnormalities. DOHAD
- congenital hypothyroidism - (CH) Neonates born with this disorder typically have a normal appearance and no detectable physical signs. Thyroid hormone is required for normal postnatal neural (cognitive) development with newborn screening and thyroid therapy able to be begun within 2 weeks of birth. thyroid
- Maple syrup urine disease - (MSUD) metabolic disorder, clinical features include mental and physical retardation, feeding problems, and a maple syrup odour to the urine. The urine effects are due to the presence of keto acids of the branched-chain amino acids (branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme subunits). ICD-11 5C50.D0 Maple-syrup-urine disease
- Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency - (MCAD) metabolic disorder, most common inherited disorder of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in people from northern Europe, intolerance to prolonged fasting and an inability to generate energy during periods of increased energy demand and can be severe to fatal in infants.
|
|
|

Foundations Practical: Introduction | Week 1 and 2 | Week 3 and 4 | Week 1 to 8 | Week 9 to 36 | Neonatal | Critical Periods | Additional Resources | Quiz
Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 28) Embryology Foundations Practical - Neonatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Foundations_Practical_-_Neonatal
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G