BGDA Practical 3 - Extraembryonic Spaces
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |
Introduction
The conceptus is now fully implanted witin the endometrial wall and the uterine epithelium has reformed over the site of implanation.
Note that all future development will now occur within the wall of the uterus, not within the cavity of the uterine body.
As the conceptus continues to implant and grow a series of fluid-filled cavities form both outside and inside the implanting conceptus.
- Outside the Conceptus - maternal blood-filled lacunae
- Inside the Conceptus - 3 separate spaces - amniotic sac, yolk sac, chorionic sac (but outside the embryo, therefore "extra-embryonic coeloms")
Conceptus Cavities Week 2 and Week 3
| <html5media height="580" width="500">File:Chorion 001.mp4</html5media> | Animation shows the events following implantation and focuses on changes in the the spaces surrounding the embryonic disc, the extraembryonic coelom.
The blastoceol cavity is converted into two separate spaces: the yolk sac and the chorionic cavity. The third space lies above the epiblast layer of the embryonic disc, the amniotic cavity.
|
| Stage 7 - Implanted Conceptus |
| Stage 7 | Embryo Slides |
Outside
Continued expansion of syncitiotrophoblasts within the endometrial wall opens both uterine glands and uterine blood vessels. These spaces outside the conceptus fill with uterine gland secretions and maternal blood forming maternal blood-filled lacunae. These lacunae provide the initial nutrition to the growing conceptus, which will later be provided through the placenta.
Inside
A cavity forms now between the inner cell mass and the trophoblast (cytotrophoblasts) wall. This cavity is the amniotic cavity.
A new cell layer forms from cells proliferating and lining the inside of the blastoceol cytotrophoblastic layer (extraembryoic mesoderm). This extraembryoic mesoderm layer continues to proliferate and then vacuolates, splitting into two separate cavities.
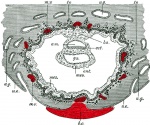
Overview of blastocyst implantation in uterine wall during the second week of development. (Image: Moore & Persaud, 1998)
Beginning of Carnegie Stage 6, blastocyst fully implanted in endometrial wall.
Continued expansion of the cavities in the extraembryonic mesoderm, allow the primary yolk sac to collapse. The collapsed space later becomes lined with endodermal cells and forms the yolk sac.
The space formed outside is lined with extraembryonic mesoderm and forms the third cavity the chorionic cavity.
A section of extraembryonic mesoderm links the now bilaminar embryonic disc to surrounding shell and is called the connecting stalk.
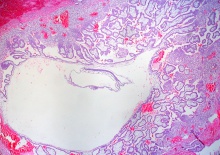
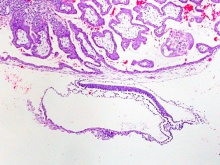
Human Conceptus Implantation 2nd and 3rd Week of Development
| Identify chorionic sac, yolk sac and amniotic sac, all containing different fluids.
Identify secondary chorionic villi, maternal blood "spaces" (empty) and uterine tissue (maternal decidua).
Nishimura H. Semba R. Tanimura T. and Tanaka O. Prenatal development of the human with special reference to craniofacial structures : An atlas. (1977) U.S. Dept. of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health ; Washington. Bethesda, Md. (Image: Nishimura etal., 1977) |

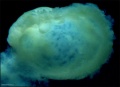
Human conceptus approximately Carnegie stage 6-7 (16-18 days). This is about the time of the first missed menstrual period. |
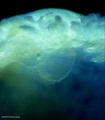
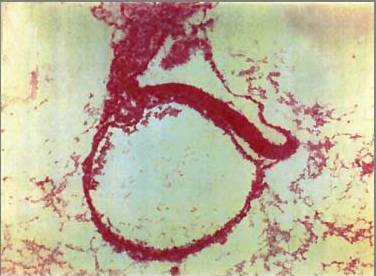
Human Conceptus (high power view)
Human Conceptus (high power view)
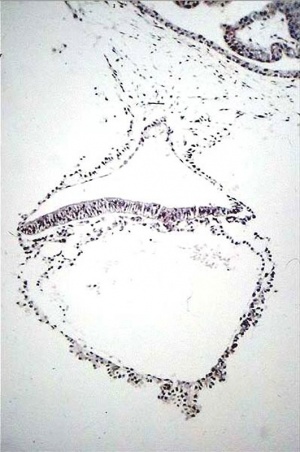
|
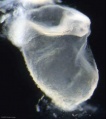
Approximate cross-section of an 18 day human conceptus.
(Image: Nishimura etal., 1977)
|
Extraembryonic Spaces Interactive Component
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |
Terms
- bilaminar- having 2 layers
- blastocyst - the developmental stage following morula, as this stage matures, the zona pellucia is lost allowing the conceptus to adplant and then implant into the uterine wall.
- inner cell mass- the clump of cells found inside the blastocyst. These cells will go in to form the embryo, these are the "stem cells" (we here about in the media) that are totipotential, they can form any tissue in the embryo. Mature oocyte-the female germ cell released at ovulation from the ovary.
- parental genomes- the male (sperm) and female (oocyte) DNA which contributes to the embryo's cells.
- trilaminar embryonic disc- the 3 layered embryo stage.
- trophoblasts- (Gr. trophe = nutrition) outer layer of cells on blastocyst that will generate the embryonic part of the placenta.
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page. |
|
|
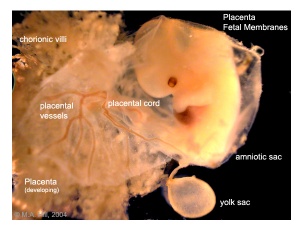
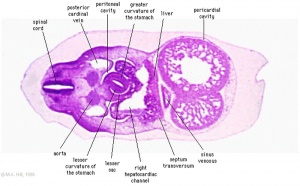
| Week 7 fetal membranes | Week 5 pericardial and peritoneal cavities |
| Extra-embryonic Coeloms | Intra-embryonic Coeloms |
|
|
References
BGDA: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12 | Lecture Neural | Practical 14 | Histology Support - Female | Male | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, March 1) Embryology BGDA Practical 3 - Extraembryonic Spaces. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDA_Practical_3_-_Extraembryonic_Spaces
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G