Introduction
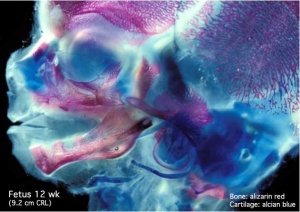
Fetal Head (12 weeks) showing bone and cartilage
The Skull is a unique skeletal structure in several ways: embryonic cellular origin (neural crest), form of ossification (intramembranous and endochondrial) and flexibility (fibrous sutures).
- The cranial vault (which encloses the brain) bones are formed by intramembranous ossification.
- While the bones that form the base of the skull are formed by endochondrial ossification.
- The bones enclosing the brain have large flexible fibrous joints (sutures) which allow:
- the head to pass through the birth canal
- postnatal brain growth
- ossification continues postnatally, through puberty until mid 20s.
- in old age the sutures separating the vault plates are often completely ossified.
- Flexible fibrous sutures allow growth of the brain to be accomodated by calvarial plate growth.
- Recent molecular studies have show that noggin (a BMP antagonist) is involved in closure of these sutures.
Postnatal Skull
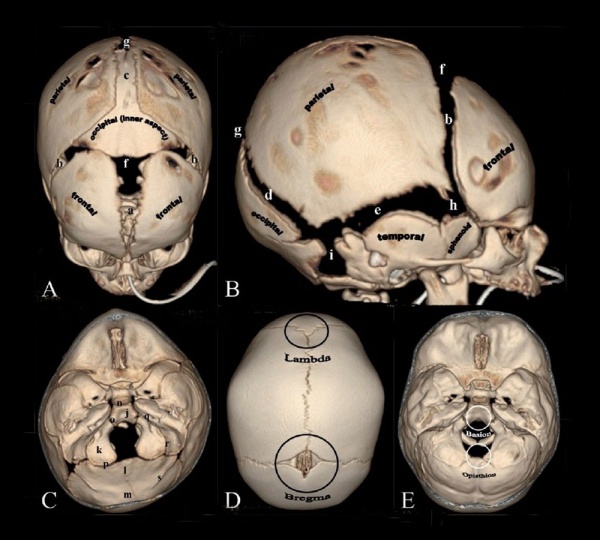
Skull CT Vertex, later and basal views.[1]
|
- rapid brain growth in the early years of life (growth of the neurocranium stopping at about 7 years of age).
- fontanels usually close by the second year of life
- posterior fontanel by about 3 months.
- anterior fontanel by about 20 months.
- Complete sutural fusion occurs after the third decade of life.
Sutures and Fontanels
- a - Metopic suture
- b - coronal sutures
- c - sagittal suture
- d - lambdoid suture
- e - squamosal suture
- f - anterior fontanel
- g - posterior fontanel
- h - sphenoidal fontanel
- i - mastoid fontanel
|
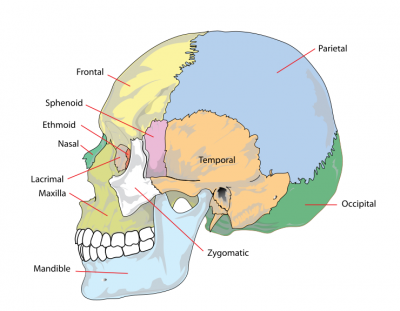
Adult Skull
Additional Information
| Additional Information - Content shown under this heading is not part of the material covered in this class. It is provided for those students who would like to know about some concepts or current research in topics related to the current class page.
|
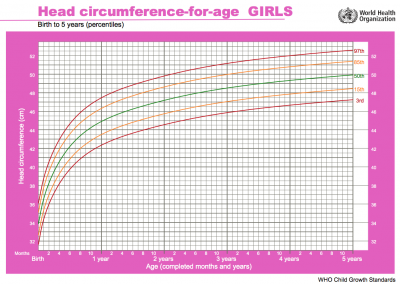
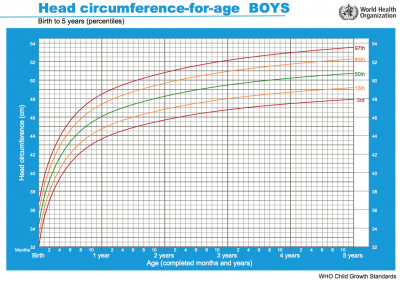
Head Growth
Head growth and corresponding charts differ slightly for girls and boys. Given as head circumference-for-age Birth to: 13 weeks, 2 years, 5 years.
- Links: Growth Charts | Neural Exam Movies | - Standard Head circumference-for-age | WHO Growth Standards
- Links: Growth Charts | Neural Exam Movies | - Standard Head circumference-for-age | WHO Growth Standards
Bone Histology
A histological image of a skull bone formation by Intramembranous ossification.

References
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 27) Embryology ANAT2341 Lab 6 - Postnatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2341_Lab_6_-_Postnatal
- What Links Here?
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G