2009 Lab 9
Sensory Development
Introduction
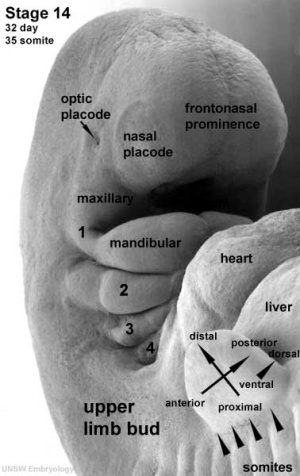
This laboratory is a introduction to development of senses (sight, smell, hearing and balance) through the development of the specialized sense organs (eye, nose and ear). Portions of the eye, nose and ear appear very early in development as specialized surface regions (placodes) on the embryo, these regions must be connected to the central nervous system by neural pathways that originate as extensions of the central nervous system.
The laboratory will also allow time for work on the group online project.
Also with the reorganization of the timetable, if we have time I will briefly review the integumentary system.
Begin by working through the computer activities listed below.
Objectives
- Understand the early development of the eye, defining optic vesicles, optic stalks, optic fissure, optic cups, lens placodes and lens vesicles.
- Understand the development of the retina, ciliary body, iris, lens, choroid, sclera and cornea.
- Understand the development of external, middle and internal ear, including otic placode, otocyst, endolymphatic duct and semicircular canals.
Computer Activities
Embryo Images Unit
Eye Development - Eye Development Unit
- Eye Fields-Optic Vesicle (Weeks 3-4)
- Optic Cup, Lens Vesicle, Choroid Fissure, Hyaloid Artery (Weeks 5-6)
- Cornea, Anterior Chamber, Pupillary Membrane, Lens, Retina (Weeks 7-8)
- Iris, Cilliary Body (Weeks 9-15)
- Eyelids (Weeks 8-10)
Ear Development - Ear Development Unit
UNSW Embryology
EarHearing Notes | Inner Ear | Middle Ear | Outer Ear
Eye Components of the Eye | Human Selected | optic nerve, optic retina, lens | Stage 22 Head Images | Stage 13/14 Head Images | Human Systems
Group Online Project
- Second part of Laboratory, do not work on this in first half.
- Each group project should now have individual peer assessment feedback added to the discussion page.
- No assessment or signature on your comment - no marks! All individual assessments need to be signed in order to get your mark for this component.
- I will explain in the laboratory how as a group to respond to the assessment comments, before final submission for co-ordinator assessment.
Listed below are key points:
- Critically read and assess the comments added to your discussion page. Is there a common comment positive/negative from several peers?
- Prepare a priority list of changes that are possible and feasible in the next 2 weeks. I will also be making some constructive comments after the first week.
- Allocate updates to members of the group (several people can work on major changes).
- Keep a list of all changes your group has made to your project on the basis of peer feedback under a title at the top of your discussion "Project Updates". Do not identify the original peer assessors when you make your changes.
- Finally, are there additional changes, not suggested by peers or not included because of the earlier deadline, that you would like to now incorporate. The should be identified as "Additional Changes".
UNSW Embryology Links
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2026, February 27) Embryology 2009 Lab 9. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lab_9
- © Dr Mark Hill 2026, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G