Template:Main Page News: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
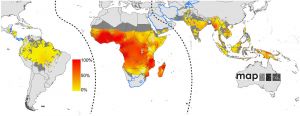
:"On the impact of climate change on human disease epidemiology, Dr. Henriette De Valk and Prof. Ana Maria de Roda Husman presented informative and sobering overviews on changes in vector-borne, water-borne, and other diseases that have been observed and can be expected to occur in the future. Warming temperatures in Europe create opportunities for mosquitos and other disease vectors to spread further North, reaching new human populations, as has been the case with {{West Nile virus}}. The conclusion drawn from their talks is that time is running out and action is needed now to stop things becoming much worse later down the line." | :"On the impact of climate change on human disease epidemiology, Dr. Henriette De Valk and Prof. Ana Maria de Roda Husman presented informative and sobering overviews on changes in vector-borne, water-borne, and other diseases that have been observed and can be expected to occur in the future. Warming temperatures in Europe create opportunities for mosquitos and other disease vectors to spread further North, reaching new human populations, as has been the case with {{West Nile virus}}. The conclusion drawn from their talks is that time is running out and action is needed now to stop things becoming much worse later down the line." | ||
:'''Links:''' {{abnormal environmental}} | {{West Nile virus}} | {{Malaria}} | :'''Links:''' {{abnormal environmental}} | {{West Nile virus}} | {{Malaria}} | {{zoonotic infection}} | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | ||
! Older News Articles | ! Older News Articles | ||
Revision as of 10:11, 29 January 2020
| News - Climate Change Abnormal Development - Environmental |
|
European Scientific Conference on Applied Infectious Disease Epidemiology (ESCAIDE, Nov 2019)
|