File:Zebrafish nephrogenesis signaling01.jpg
Zebrafish_nephrogenesis_signaling01.jpg (508 × 324 pixels, file size: 29 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
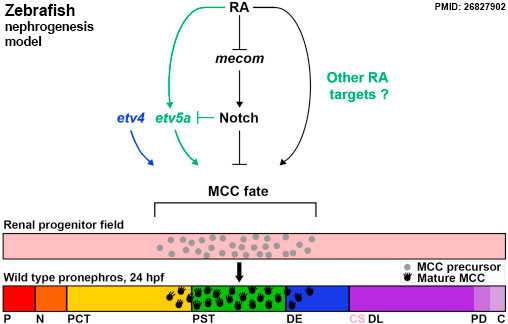
Zebrafish Nephrogenesis Signaling
Transportive cells - occupy distinct tubule segments and are characterized by the expression of various solute transporters
multiciliated cells (MCCs) - function in fluid propulsion and are dispersed in a "salt-and-pepper" fashion within the tubule.
| Model of etv5a and etv4 function in MCC patterning during Nephrogenesis | Abbreviations |
|---|---|
| Interplay between retinoic acid (RA), etv5a, and Notch signaling in the renal progenitor field mediates multiciliated cell (MCC) formation during nephrogenesis.
etv5a responds downstream of RA signaling to promote MCC fate, although it is likely that etv5a is not the only target of RA in this pathway. Conversely, Notch signaling inhibits etv5a activity to restrict MCC formation and favor transportive cell identity. In addition, etv4 promotes MCC fate, although it is not resolved if etv4 acts within renal progenitors or neighboring tissues, and whether other known MCC specification factors impact etv4 in other embryonic locales to affect pronephros development. |
|
- Links: Renal System - Molecular | Retinoic acid | Notch | Zebrafish Development
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Reference
Marra AN & Wingert RA. (2016). Epithelial cell fate in the nephron tubule is mediated by the ETS transcription factors etv5a and etv4 during zebrafish kidney development. Dev. Biol. , 411, 231-245. PMID: 26827902 DOI.
Copyright
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Fig. 7. 1-s2.0-S0012160615301068-gr7.jpg PMID and title added to original
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology Zebrafish nephrogenesis signaling01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Zebrafish_nephrogenesis_signaling01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:22, 31 August 2016 |  | 508 × 324 (29 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Zebrafish nephrogenesis signaling== ===Reference=== <pubmed>26827902</pubmed> ====Copyright==== https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Fig. 7. 1-s2.0-S0012160615301068-gr7.jpg PMID and title added to original |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: