File:Skin structure cartoon.jpg
From Embryology
Size of this preview: 583 × 600 pixels. Other resolution: 700 × 720 pixels.
Original file (700 × 720 pixels, file size: 52 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
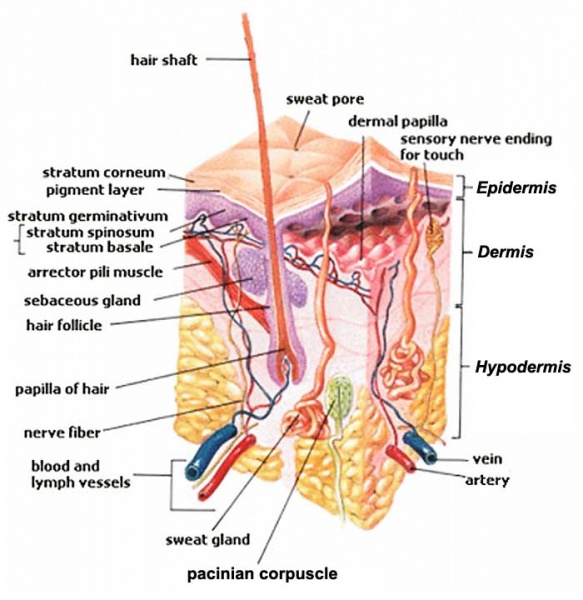
Skin Structure
- Basket cells - surround the base of hair follicles and can sense pressure. They are evaluated when assessing overall nerve health and condition.
- Blood Vessels - carry nutrients and oxygen-rich blood to the cells that make up the layers of skin and carry away waste products.
- Hair Erector Muscle (Arrector Pili Muscle) - tiny muscle connected to each hair follicle and the skin. When it contracts it causes the hair to stand erect, and a "goosebump" forms on the skin.
- Hair Follicle - tube-shaped sheath that surrounds the part of the hair that is under the skin and nourishes the hair. It is located in the epidermis and the dermis.
- Hair Shaft - the part of the hair that is above the skin.
- Langerhans Cells - cells attach themselves to antigens that invade damaged skin and alert the immune system to their presence.
- Melanocyte- cell that produces melanin, and is located in the basal layer of the epidermis.
- Merkel Cells - tactile cells of neuroectodermal origin located in the basal layer of the epidermis.
- Pacinian Corpuscle - a nerve receptor located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue that responds to pressure and vibration.
- Sebaceous Gland - small, sack-shaped glands which release an oily substance onto the hair follicle that coats and protects the hair shaft from becoming brittle. These glands are located in the dermis.
- Sensory Nerves - epidermis is innervated with sensory nerves. These nerves sense and transmit heat, pain, and other noxious sensations. When they are not functioning properly sensations such as numbness, pins-and-needles, pain, tingling, or burning may be felt. When evaluating a skin biopsy, total number, contiguity, diameter, branching, swelling, and overall health of the sensory nerves are assessed.
- Stratum Corneum - outermost layer of the epidermis, and is comprised of dead skin cells. It protects the living cells beneath it by providing a tough barrier between the environment and the lower layers of the skin. The stratum corneum is useful for diagnosis because in some conditions it will become thinner than normal.
- Sweat Gland (Sudoriferous Gland) - located in the epidermis and produce moisture (sweat) that is secreted through tiny ducts onto the surface of the skin (stratum corneum). When sweat evaporates, skin temperature is lowered.
Image Source: SEER Training Modules http://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/anatomy/
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:31, 14 February 2012 |  | 700 × 720 (52 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 18:25, 28 September 2009 |  | 396 × 407 (63 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Image Source: SEER Training Modules http://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/anatomy/ |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 14 pages use this file:
- 2009 Lecture 18
- 2010 Lecture 22
- A
- ANAT2241 Nervous Tissue
- ANAT2511 Basic Tissues
- ANAT2511 Integumentary System
- Foundations - Histology Cells and Tissues
- Foundations - Histology Epithelia and Skin
- H
- Human System Development
- Integumentary System - Hair Development
- Integumentary System Development
- Lecture - Integumentary Development
- P