File:Adult cochlea nerve glia cartoon.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Adult Human Cochlea Nerve Glia cartoon== | ==Adult Human Cochlea Nerve Glia cartoon== | ||
Schematic illustration of the | Schematic illustration of the peripheral glial cells in the adult human cochlea. Satellite glial cells (green) envelop all spiral ganglion neuron (SGN) cell bodies. Non-myelinating Schwann cells (light blue) ensheath both the central and peripheral processes of the type II SGNs (yellow) that innervate the outer hair cells (OHC). Myelinating Schwann cells (dark blue) ensheath and myelinate both processes of the type I SGNs (red) that innervate the inner hair cells (IHC). Beyond the habenula perforata, in the organ of Corti, neither Schwann cell types ensheath the most distal part of the peripheral processes of type I and type II SGNs. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[Category:Senses]] [[Category:Hearing]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Inner Ear]] [[Category:Neural]] | [[Category:Senses]] [[Category:Hearing]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Inner Ear]] [[Category:Neural]][[Category:Adult]] | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 7 February 2014
Adult Human Cochlea Nerve Glia cartoon
Schematic illustration of the peripheral glial cells in the adult human cochlea. Satellite glial cells (green) envelop all spiral ganglion neuron (SGN) cell bodies. Non-myelinating Schwann cells (light blue) ensheath both the central and peripheral processes of the type II SGNs (yellow) that innervate the outer hair cells (OHC). Myelinating Schwann cells (dark blue) ensheath and myelinate both processes of the type I SGNs (red) that innervate the inner hair cells (IHC). Beyond the habenula perforata, in the organ of Corti, neither Schwann cell types ensheath the most distal part of the peripheral processes of type I and type II SGNs.
- Links: Adult cochlea cartoon | Adult cochlea nerve glia cartoon | Cochlea glial lineage cartoon | Inner Ear Development | Hearing
Reference
<pubmed>24498246</pubmed>| PLoS One.
Copyright
© 2014 Locher et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Locher H, de Groot JCMJ, van Iperen L, Huisman MA, Frijns JHM, et al. (2014) Distribution and Development of Peripheral Glial Cells in the Human Fetal Cochlea. PLoS ONE 9(1): e88066. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088066
Image: Figure 1. Capturing PGCs in the human cochlea. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088066.g001
Panel C cropped, resized and relabelled from original figure. Text modified from figure legend.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:34, 7 February 2014 | 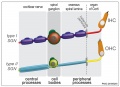 | 1,000 × 725 (85 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: