BGDB Gastrointestinal - Late Embryo: Difference between revisions
(→Week 8) |
(→Week 8) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
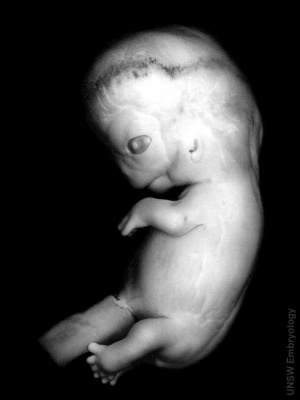
| Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 22, week 8 | | Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 22, week 8 | ||
| A 3D reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract of this embryo stage. | | A 3D reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract of this embryo stage. | ||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | |||
|+ Stage 22 Embryo - Gastrointestinal Tract | |||
! Section | |||
! Name | |||
! Description | |||
|- | |||
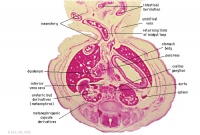
| width= 160px|[[File:Stage_22 image 083.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 083.jpg|E6L]] | |||
| Liver. Ductus venosus. | |||
Cardio-oesophageal junction (cf. E5). | |||
Inferior vena cava. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 084.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 084.jpg|E7L]] | |||
| Stomach body, with mucosa, submucosa and muscularis externa. | |||
Lesser sac. Lesser omentum. Pyloroduodenal junction. Folded duodenal mucosa. | |||
Inferior vena cava. Portal vein. Hepatic ducts. Gallbladder. | |||
|- | |||
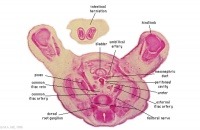
| [[File:Stage_22 image 085.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 085.jpg|F1L]] | |||
| Stomach body. Spleen. Pyloric canal. Duodenum. | |||
Pancreas. | |||
Small intestine loop (jejunum) cut tangentially, ventral to liver. | |||
Portal vein. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 086.jpg|200px]] | |||
[[File:Stage_22 image 087.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 086.jpg|F2L]] | |||
[[:File:Stage_22 image 087.jpg|F3L]] | |||
| Stomach, spleen. Superior mesenteric artery. | |||
Superior mesenteric vein crossing cranial to body of pancreas. | |||
Tail of pancreas. | |||
Duodenum. | |||
Small intestinal loop herniating from abdominal cavity into the coelom of the umbilical cord (remnant of extra-embryonic coelom). | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 088.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 088.jpg|F4L]] | |||
| Greater curvature of stomach (tangential section). Lesser sac. Greater omentum. Duodenal/jejunal junction. | |||
Note colon (small lumen, darkly-staining wall) and its mesocolon. | |||
Note the sections of small and large intestine within the umbilical cord coelom and their mesenteries. | |||
Note the thickened jelly to one side of the umbilical cord, containing umbilical vein and R umbilical artery. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 089.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 089.jpg|F5L]] | |||
| Lesser sac. Greater omentum. Duodenum. Jejunum (cut twice with mesentery in between). Colon and mesocolon. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 090.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 090.jpg|F6L]] | |||
| Greater omentum and lesser sac. | |||
Jejunum with mesentery. | |||
Colon with mesocolon. | |||
Three layers of abdominal muscles. | |||
Both umbilical arteries now inside abdominal cavity with urachus between them. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 091.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 091.jpg|F7L]] | |||
| In abdominal cavity - colon with mesocolon, jejunum. Greater omentum and lesser sac. | |||
Umbilical cord - containing umbilical arteries and small dark allantois. Umbilical cord coelom containing mainly, small intestinal loops with their mesentery. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 092.jpg|200px]] | |||
[[File:Stage_22 image 093.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 092.jpg|G1L]] | |||
[[:File:Stage_22 image 093.jpg|G2L]] | |||
| Umbilical cord and coelom containing small intestine loops. | |||
Colon and mesocolon. Jejunum (G1 only). | |||
Bladder with umbilical arteries either side. | |||
Knees. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 094.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 094.jpg|G3L]] | |||
| Rectum. | |||
Bladder. | |||
Umbilical arteries arising from common iliac arteries. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 095.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 095.jpg|G4L]] | |||
| Rectum. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Stage_22 image 096.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 096.jpg|G5L]] | |||
| Recto-anal junction with rectovesical pouch of peritoneal cavity. | |||
|- | |||
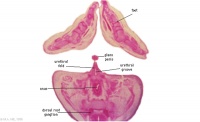
| [[File:Stage_22 image 097.jpg|200px]] | |||
[[File:Stage_22 image 098.jpg|200px]] | |||
| [[:File:Stage_22 image 097.jpg|G6L]] | |||
[[:File:Stage_22 image 098.jpg|G7L]] | |||
| Anal canal with triangular lumen. | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 15 April 2011
| Practical 1: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Lecture | Quiz |
Week 8
We have now reached late embryonic development. Start by looking briefly the process of how the definitive GIT tube is formed and then at the overview of the Carnegie stage 22 embryo GIT from one end to the other.
Then work through the listed specific serial sections of the embryo identifying the GIT features. Alternatively step through the serial sections yourself identifying the tract, its associated mesentries, organs and spaces. Note you should also be comparing the GIT appearance with the earlier embryonic (13/14) Carnegie stage.
Observe: GIT tube has a different appearance at different levels; stomach, duodenum, midgut and hindgut midgut herniated at the umbilicus, lying outside the ventral body wall, connected by mesentry large liver lying directly under the diaphragm and occupying the entire ventral body cavity with organs "embedded" within it the developing pancreas lying in the loop between stomach and duodenum
|
|
| Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 22, week 8 | A 3D reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract of this embryo stage. |
| Section | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
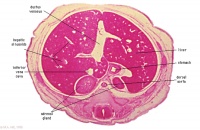
|
E6L | Liver. Ductus venosus.
Cardio-oesophageal junction (cf. E5). Inferior vena cava. |
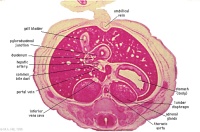
|
E7L | Stomach body, with mucosa, submucosa and muscularis externa.
Lesser sac. Lesser omentum. Pyloroduodenal junction. Folded duodenal mucosa. Inferior vena cava. Portal vein. Hepatic ducts. Gallbladder. |
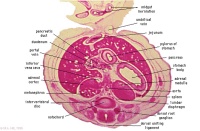
|
F1L | Stomach body. Spleen. Pyloric canal. Duodenum.
Pancreas. Small intestine loop (jejunum) cut tangentially, ventral to liver. Portal vein. |
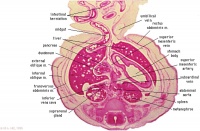
|
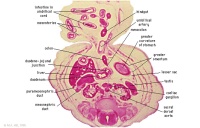
F2L | Stomach, spleen. Superior mesenteric artery.
Superior mesenteric vein crossing cranial to body of pancreas. Tail of pancreas. Duodenum. Small intestinal loop herniating from abdominal cavity into the coelom of the umbilical cord (remnant of extra-embryonic coelom). |
|
F4L | Greater curvature of stomach (tangential section). Lesser sac. Greater omentum. Duodenal/jejunal junction.
Note colon (small lumen, darkly-staining wall) and its mesocolon. Note the sections of small and large intestine within the umbilical cord coelom and their mesenteries. Note the thickened jelly to one side of the umbilical cord, containing umbilical vein and R umbilical artery. |

|
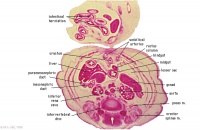
F5L | Lesser sac. Greater omentum. Duodenum. Jejunum (cut twice with mesentery in between). Colon and mesocolon. |
|
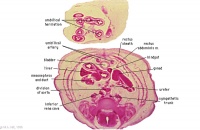
F6L | Greater omentum and lesser sac.
Jejunum with mesentery. Colon with mesocolon. Three layers of abdominal muscles. Both umbilical arteries now inside abdominal cavity with urachus between them. |
|
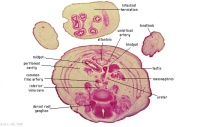
F7L | In abdominal cavity - colon with mesocolon, jejunum. Greater omentum and lesser sac.
Umbilical cord - containing umbilical arteries and small dark allantois. Umbilical cord coelom containing mainly, small intestinal loops with their mesentery. |
|
G1L
|
Umbilical cord and coelom containing small intestine loops.
Colon and mesocolon. Jejunum (G1 only). Bladder with umbilical arteries either side. Knees. |
|
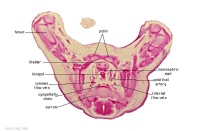
G3L | Rectum.
Bladder. Umbilical arteries arising from common iliac arteries. |
|
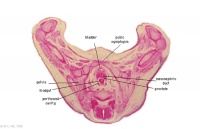
G4L | Rectum. |
|
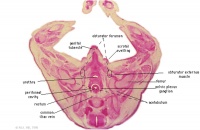
G5L | Recto-anal junction with rectovesical pouch of peritoneal cavity. |
|
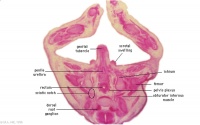
G6L | Anal canal with triangular lumen. |
Lumen Development
| width=252px|height=460px|controller=true|autoplay=false</qt> |
This is a simplified animation showing how the gastrointestinal tract wall changes during the late embryonic period.
Week 8 - By the end of this week the GIT endoderm tube is a tube once more. Week 9 - (early fetal) the endoderm of this now hollow tube differentiates into the mucosal epithelium (endoderm).
|
| Practical 1: Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Lecture | Quiz |
BGDB: Lecture - Gastrointestinal System | Practical - Gastrointestinal System | Lecture - Face and Ear | Practical - Face and Ear | Lecture - Endocrine | Lecture - Sexual Differentiation | Practical - Sexual Differentiation | Tutorial
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology BGDB Gastrointestinal - Late Embryo. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/BGDB_Gastrointestinal_-_Late_Embryo
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G