2015 Group Project 1: Difference between revisions
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
=Technical Progression= | =Technical Progression= | ||
Three-person ''in-vitro'' fertilization is a process where a small proportion of genetic information encoded within mitochondria are replaced to prevent mitochondrial disease passing through generations. Main approaches to achieve this goal involve the replacement of mitochondrial genome between gametes or embryos <ref name=pmid24382342><pubmed> 24382342</pubmed></ref> <ref><pubmed> 25573721 </pubmed></ref>. | Three-person ''in-vitro'' fertilization is a process where a small proportion of genetic information encoded within mitochondria are replaced to prevent mitochondrial disease passing through generations. Main approaches to achieve this goal involve the replacement of mitochondrial genome between gametes or embryos <ref name=pmid24382342><pubmed> 24382342</pubmed></ref> <ref name=PMID25573721><pubmed> 25573721 </pubmed></ref>. | ||
*The first proposed treatment is '''cytoplasmic transfer''', which transfers a small part of ooplasm from one oocyte to another. however, this approach are then considered to be inadequate to prevent the inheritance of diseased mitochondrial. because it adds in donor mitochondria without removing the mutated mtDNA, which will then generate a 'heteroplasmic oocyte' with both mitochondria haplotypes <ref name=pmid24382342/>. | *The first proposed treatment is '''cytoplasmic transfer''', which transfers a small part of ooplasm from one oocyte to another. however, this approach are then considered to be inadequate to prevent the inheritance of diseased mitochondrial. because it adds in donor mitochondria without removing the mutated mtDNA, which will then generate a 'heteroplasmic oocyte' with both mitochondria haplotypes <ref name=pmid24382342/>. | ||
| Line 219: | Line 219: | ||
==Spindle-Chromosome Transfer== | ==Spindle-Chromosome Transfer== | ||
Spindle-choromosome transfer is a modified cloning technique which transfers the meiotic spindle and attached chromosomes (spindle-chromosome complex, SCC) from one mature oocyte to another to select for a cytoplasm or mtDNA background <ref><pubmed>25444504</pubmed></ref>. Comparing to cytoplasmic transfer, the '''advantage''' of spindle transfer is the reduction in heteroplasmy risk, thus offering a better reproductive option to prevent mtDNA disease transmission in affected families <ref><pubmed>23103867</pubmed></ref>. This technology has been used to generate both cattle and mice after subsequent fertilization (Bai et al, 2006, Bao et al, 2003, Wakayama et al, 2004 and Wang et al, 2001), and has generated live monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after sperm injection <ref name=PMID25573721 | Spindle-choromosome transfer is a modified cloning technique which transfers the meiotic spindle and attached chromosomes (spindle-chromosome complex, SCC) from one mature oocyte to another to select for a cytoplasm or mtDNA background <ref><pubmed>25444504</pubmed></ref>. Comparing to cytoplasmic transfer, the '''advantage''' of spindle transfer is the reduction in heteroplasmy risk, thus offering a better reproductive option to prevent mtDNA disease transmission in affected families <ref><pubmed>23103867</pubmed></ref>. This technology has been used to generate both cattle and mice after subsequent fertilization (Bai et al, 2006, Bao et al, 2003, Wakayama et al, 2004 and Wang et al, 2001), and has generated live monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after sperm injection <ref name=PMID25573721/>. Spindle transfer between human oocytes has also result in blastocyst development and embryonic stem cell derivation with very low levels of heteroplasmy <ref><pubmed> 25973765 </pubmed></ref>. | ||
| Line 276: | Line 276: | ||
===What is the procedure?=== | ===What is the procedure?=== | ||
[[File:Pronuclear transfer.jpg|600px|thumb|right|Diagram of pronuclear transfer <ref | [[File:Pronuclear transfer.jpg|600px|thumb|right|Diagram of pronuclear transfer <ref name=PMID25573721/>]] | ||
The nuclear genome from the pronuclear stage zygote of an affected woman is transferred to an enucleated donor zygote <ref name ='humanmodel2003'/> | The nuclear genome from the pronuclear stage zygote of an affected woman is transferred to an enucleated donor zygote <ref name ='humanmodel2003'/> | ||
# It begins with creating an embryo using the parents’ sperm and eggs. | # It begins with creating an embryo using the parents’ sperm and eggs. | ||
| Line 337: | Line 337: | ||
Polar body transfer has been adopted in mice models to prevent the transmission of mtDNA variants. They also compare the effects of different types of germline genome transfer, including spindle-chromosome transfer, pronuclear transfer, and first and second polar body transfer, in mice. Their pre-clinical model indicate that polar body transfer has better potential in preventing the inheritance of mitochondrial diseases<ref><pubmed> 24949971 </pubmed></ref>. | Polar body transfer has been adopted in mice models to prevent the transmission of mtDNA variants. They also compare the effects of different types of germline genome transfer, including spindle-chromosome transfer, pronuclear transfer, and first and second polar body transfer, in mice. Their pre-clinical model indicate that polar body transfer has better potential in preventing the inheritance of mitochondrial diseases<ref><pubmed> 24949971 </pubmed></ref>. | ||
The other group coupled Polar body transfer with Pronuclei transfer or Spindle-choromosome transfer on a mice model which increased the yield of reconstructed embryos with low mtDNA carryover. <ref | The other group coupled Polar body transfer with Pronuclei transfer or Spindle-choromosome transfer on a mice model which increased the yield of reconstructed embryos with low mtDNA carryover. <ref name=PMID25573721/> | ||
==Other Approaches== | ==Other Approaches== | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 23 October 2015
| 2015 Student Projects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 Projects: Three Person Embryos | Ovarian Hyper-stimulation Syndrome | Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | Male Infertility | Oncofertility | Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis | Students | ||||
| 2015 Group Project Topic - Assisted Reproductive Technology | ||||
| This page is an undergraduate science embryology student and may contain inaccuracies in either description or acknowledgements. | ||||
Three Person Embryos
Three Person Embryos are embryos from oocytes that contain maternal and paternal DNA, and mitochondria from a third donor. Collectively, the techniques for the creation of Three Person Embryos are referred to as Mitochondrial Donation or Mitochondrial replacement-assisted IVF. Mitochondrial donation is used for the prevention of maternal inheritance of Mitochondrial disorders that occur due to the mutation of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). It is considered a germ-line therapy, with the donated mitochondria being passed maternally to the next generation. Because of this it has generated debate in the media and scientific community over the ethics of its use, since the first techniques were developed in the 1980s. Recently, with the development of safer techniques, the United Kingdom and United States have begun the process of legalizing its clinical use.
<html5media width="560" height="315">https://www.youtube.com/embed/0Zs2KntZ7vU</html5media>
Teenage Girl Has Three Biological Parents [1]
History
Timeline Of Mitochondrial Donation
1980s
- 1981, United Kingdom - Complete sequencing of human mitochondrial genome[2]
- 1982, United Kingdom - Muggleton-Harris's group at MRC Laboratory Animals Center in Surrey, developed the technique and reported the first successful mammalian cytoplasmic transfer in mice [3].
- 1984, United Kingdom - Publication of the Warnock Report on IVF technologies and embryo research in reaction to 1978s first IVF baby. Becomes blueprint for regulation worldwide.
- 1988, US and UK - First pathogenic mitochondrial mutations in humans identified [4][5]
1990s
- 1990, United Kingdom - Implamentation of the Human fertilization and embryology act 1990. Governs the legal requirements around research and clinical use of IVF technologies until present.[6]
- 1996, United Kingdom - Dolly the sheep born from nuclear transfer. Generates public interests in genetic modification and clinical embryology[7].
- 1997, United States - Jacques Cohen, Richard Scott, Tim Schimmel, Jacob Levron, and Steen Willadsen at the Institute for Reproductive Medicine and Science of St. Barnabas in West Orange, New Jersey, announced the birth of a baby girl after the first successful human cytoplasmic transfer [8].
- 1998, United States - FDA ban use of cytoplasmic transfer techniques.
- 1998, United States - First oocyte with DNA transferred from a first polar body fertilized brought to term in a mouse model. [9]
2000s
- 2002 United States - One of the children conceived through ooplasmic transfer were diagnosed with pervasive developmental disorder, and indicated mild developmental delays to severe autism.
- 2008, United Kingdom - Changes to the Human Fertilization and Embryology Act allows research into the techniques of three person IVF.
- 2009, United States - First success-full trails of spindle transfer in rhesus monkeys [10]
2010s
- 2014 United States - Public meetings to discuss mitochondrial manipulation techniques were held by FDA. There was no formal decision made on the efficacy, but agreements were made on further practice in animal models to provide scientific data.
- 2015 United Kingdom - Regulations to allow the open use of three person IVF via pronuclear transfer in fertility clinics comes into affect in the UK.
Mitochondrial mutation and benefits of mitochondrial donation
Mitochondria are generally known as the ATP production sites of the cell. Although they are also involved in signalling, differentiation, cell cycle, cell development, Neuronal function and many other functions [5]. In mammals mitochondria contain their own circular genome encoding for 37 genes of which 13 are vital to oxidative phosphorylation and hence the respiratory chain. The remainder of mtDNA encodes for tRNAs and rRNAs[11]. Each mitochondria contain 2-10 identical copies of their mtDNA at birth in a healthy person and average 100 mitochondria per cell. In addition to mtDNA over 1000 nuclear DNA (nDNA) encoded genes have so far been identified as involved in the life-cycle and function of mitochondria[12]. In normal mammalian mating all mtDNA is maternally inherited[13].
Mutations in mtDNA or nDNA mitochondrial genes can lead to abnormalities in normal function. The level of dysfunction in non-X-linked maternally inherited disorders is related to the copy number mutated mtDNA molecules in individual mitochondria and the percentage of mitochondria in a cell that contain mutated mtDNA. Because mitochondria cover a wide range of functions in varying regions of the body clinical presentations are also wide ranging[11].
Mitochondrial donation can benefit anyone that is at risk of passing on to their offspring a mitochondrial disorder that is caused by a mtDNA mutation. It cannot however prevent inheratence of nDNA derived disorders. Because mitochondrial replacement is a germ line treatment any future generations will also be free from mtDNA mutations.
Extrapolation from small studies estimate that per year 152 women in the UK and 778 in the United State, are at risk of passing on mtDNA disorders[14]. Prevalence in the population of mtDNA associated disorders is estimated to be 1 in 10,000.[15].
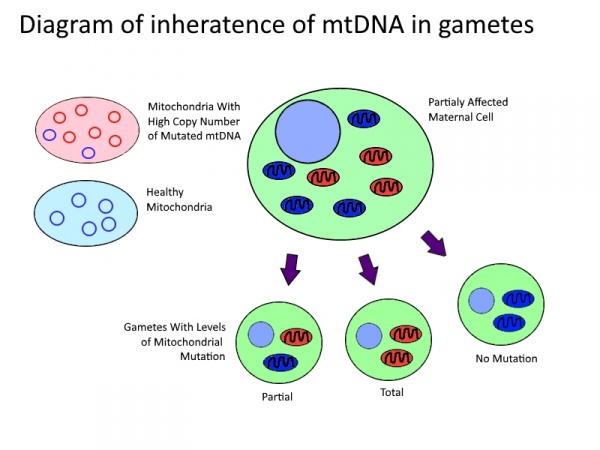
Inheritance of mitochondrial disorder
Although mtDNA is entirely maternally inherited, offspring of a pathogenic mother may have substantially different pathology and level of mutated mtDNA. Clinical presentation of disease only occurs once levels of mutated mtDNA pass a threshold within a cell[16]. Fission and fusion of mitochondria inside of the cell leads to transmission of copies of mtDNA and hence an uneven distribution on mutated mtDNA. This then leads to a distribution of functional, semi-functional and dysfunctional mitochondria within each cell. During cell division these mitochondria are then randomly distributed among the daughter cells as described in the table bellow. The higher the level of mtDNA mutation in the parent cell the greater the likelihood of the daughter cell to receive a random distribution mutated mtDNA above the thresh hold[16]. When this occurs during meiotic cell division the mtDNA in the daughter cell will go on to form the entire mtDNA of the offspring. Although poorly understood there has been shown to be a selective pressure against germ-line cells with an accumulation deleterious mutations[17] as well as a tendency for hetroplasmic blastomeres to shift towards homoplasmy before implantation[18] suggesting some mechanisms mtDNA selection post division.
Hereditary Mitochondrial Disorders
Mitochondrial disorders cover a broad range of clinical symptoms and affected organs. Predominantly they present as neurologic and myopathic diseases owing to the retardation of ATP production but symptoms can include deafness, vision loss, diabetes and organ failure among others. The following is an inexhaustive list of the most notable disorders.
| Mitochondrial disorder | Disease Type | Clinical Pathology | Mutation | Preventable with mitochondrial donation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpers disease[19] | Degenerative disease of CNS | Psychomotor retardation, epilepsy, liver failure, cortical necrosis | nDNA gene mutation | "No" |
| Kearns-Sayre Sydrome (KSS)[20] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Causes pigmentary retinopathy, conduction block, ataxia. Can cause mental reardation/deterioration, delayed sexual maturation. | mtDNA deletion | "Yes" |
| Leigh Syndrome[21] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Necrotizing lesions in the brain-stem, developmental delays, muscle weakness, hypotonia, respiratory distress and death before the age of five. | 30 X-linked Recessive genes. mtDNA mutation. | "20% of Cases" |
| Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome (MDS)[22] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Muscle weakness, liver failure and developmental retardation. Can cause brain abnormalities, pigmentary retinopathy and seizures. | nDNA mutation | "No" |
| Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis and Stoke-like episodes (MELAS)[23] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Prolonged focal seizures and epilepsia. Pigmentary retinopathy, muscle weakness, hearing loss,diabetes. | mtDNA point mutation | "yes" |
| Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalomyopathy (MNGIE)[24] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Peripheral neuropathy. | nDNA TYMP gene mutation | "No" |
| Myoclonus epilepsy with ragged red fibres (MERFF)[25] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Seizures, ataxia, myopathy linked to diabetes, optic atrophy peripheral neuropathy, hearing loss and dimentia. | mtDNA point mutation | "yes" |
| Neuropathy, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP)[26] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Rod-Cone dystrophy of the eye, muscle weakness, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa | mtDNA 6-gene mutation | "yes" |
| Pearson syndrome[27] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Bone marrow failure and pancreatic insufficiency. If survival past childhood develops into Kearns-Sayre syndrome. | mtDNA rearrangement, deletion. | "yes" |
| Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO)[28] | Mitochondrial Myopathy | Progressive paralysis of the eye muscles. Can be distinct syndrome or part of greater mitochondrial disorder | mtDNA and nDNA mutations | "Most Cases" |
Technical Progression
Three-person in-vitro fertilization is a process where a small proportion of genetic information encoded within mitochondria are replaced to prevent mitochondrial disease passing through generations. Main approaches to achieve this goal involve the replacement of mitochondrial genome between gametes or embryos [29] [30].
- The first proposed treatment is cytoplasmic transfer, which transfers a small part of ooplasm from one oocyte to another. however, this approach are then considered to be inadequate to prevent the inheritance of diseased mitochondrial. because it adds in donor mitochondria without removing the mutated mtDNA, which will then generate a 'heteroplasmic oocyte' with both mitochondria haplotypes [29].
- New emerged approaches of mitochondrial transmission are pronuclear transfer(PNT), spindle transfer (ST) and Polar body transfer (PBT). however, none of this techniques have been proved on generating healthy human offspring due to the technical difficulty, as well as the ethics issues being recognized worldwide [31].
- Major breakthroughs of these techniques rely on the practice on animal models (mice and primate) [32], early stage human embryo and stem cell studies [33].
Cytoplasmic Transfer
Cytoplasmic transfer is also named Ooplasmic transfer. It is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique,which introduce a small amount of ooplasm from a donor oocyte or zygote into compromised oocyte or zygote from patients.
Why do cytoplasmic transfer?
The quality of the oocyte cytoplasm is critical for the future of the embryo [34].Following ovulation, the survival of zygote depends almost exclusively on maternal messenger RNA and proteins that accumulated during oocyte growth and maturation within the ooplasm. It is not until the maternal-to-zygotic transition (MZT) stage, during the 4–8‐cell stage in humans, where the new zygote genome is activated and replace the maternal cytoplasm to be predominant in regulating the zygote development [35] . The maternal transcripts are thus responsible for the first few cleavage divisions and for transition of the maternally controlled zygote into an activated embryonic genome [36].
Researches are still investigating the molecular and cellular mechanisms how ooplasm regulates the maturation and activation of human oocytes and zygotes[37]. The ooplasmic factors involved in this regulation are messenger RNA, maternally stored proteins, stockpiles of energy substrates, other energy-production components and many additional factors yet to be determined. The benefits of cytoplasm transfer are revealed by two hypothesized biochemical mechanisms: correction of a putative imbalance between anti-and pro-apoptotic factors and/or correction of defective mitochondrial membrane potential[38].
What is the procedure?
Cytoplasmic transfer can be performed either as a repair of oocyte or repair of Embryo [29] [39]
In method one, the cytoplasm is withdrew from a donor’s oocyte, and then injected into a patient’s oocyte together with the sperm cells which will then fertilize the oocyte. In Method two, the cytoplasm from donor is injected into a patient’s fertilized oocyte.
 Simplified Cell Structure [39] |
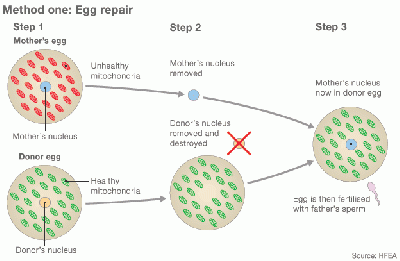 Egg repair by Cytoplasmic transfer [39] |
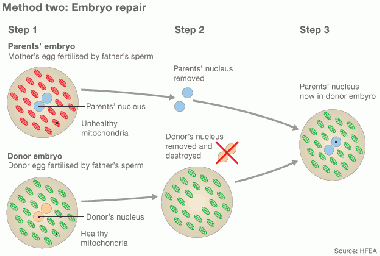 repair by Cytoplasmic transfer [39] |
Key Events of Cytoplasmic Transfer
- 1982, United Kingdom - Audrey Muggleton-Harris's group at MRC Laboratory Animals Center in Surrey, developed the technique and reported the first successful mammalian cytoplasmic transfer in mice [3].
- 1982 United Kingdon - Muggleton-Harris's group transferred cytoplasm from mice strains whose oocytes divide past the two-cell stage in vitro into mice to overcome the two-cell barrier [3].
- 1997, United States - Jacques Cohen, Richard Scott, Tim Schimmel, Jacob Levron, and Steen Willadsen at the Institute for Reproductive Medicine and Science of St. Barnabas in West Orange, New Jersey, announced the birth of a baby girl after the first successful human cytoplasmic transfer [8].
- 1998 United States – The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) banned the procedure.
- 2002 United States - one of the children conceived through ooplasmic transfer were diagnosed with pervasive developmental disorder, and indicated mild developmental delays to severe autism.
- 2014 United States - public meetings to discuss mitochondrial manipulation techniques were held by FDA. There was no formal decision made base on the efficacy of Cytoplasmic transfer, but agreements were made on further practice on animal models to provide scientific data.
| Type of Cytoplasm Transferred to recipient oocytes | No. of Procedures | Pregnancies achieved | Offspring delivered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synchronized fresh oocytes by electrofusion [41] | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Synchronized fresh oocytes by injection (USA) [8] [42] [43] [44] [45] | 30 | 13 | 16 |
| Synchronized fresh oocytes by injection (Israel) [40] | 15 | 5 | 6 |
| Synchronized frozen oocytes by injection [46] | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Asynchronous 3-PN zygotes by injection [47] | 9 | 4 | 5 |
Risk of Cytoplasmic Transfer -- Heteroplasmy
Heteroplasmy is defined as the mixture of more than one Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) type within the cytoplasm of an individual [48] [49]. Previously it was believed to have been a rare heteroplasmic mutation in healthy individuals . However, human mtDNA sequencing has now shown that each person has some low-frequency, variant mtDNA types, mixed with the maternally inherited dominant type. These low-frequency variants arise from mutations during growth and mitosis of individual cell. The two types of heteroplasmy are length heteroplasmy and sequence (or site) heteroplasmy [50] .
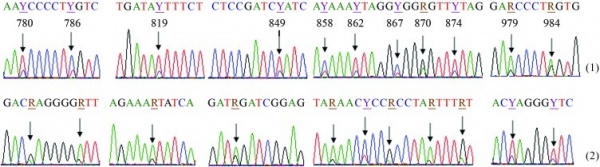
- Length heteroplasmy is the presence of mtDNA molecules that differ in length.
- Sequence (site) heteroplasmy is the presence of mtDNA molecules that have different nucleotides at the same site.
The low frequency mtDNA mutation is quite common and cells can contain varying proportions of mutated and wild-type mtDNA [51]. Cells can usually tolerate the level of mutations. Only if the mutation is pathogenic, and the percentage of variants exceeds the biochemical threshold will defects will be induced[52].
Cytoplasmic transfer in IVF procedure has the risk of manifesting the mutations as it combines the mtDNA from donor with the maternally inherited mtDNA of the recipient. Heteroplasmy is thus one of the major concerns arise regarding cytoplasmic transfer in IVF procedure [53]. Severe disease can occur due to heteroplasmy in the offspring’s mitochondria. They may affect the development of the muscle, brain and endocrine system [54]. They could also result in mitochondrial disease developing either in the child or in future generations [55].
Spindle-Chromosome Transfer
Spindle-choromosome transfer is a modified cloning technique which transfers the meiotic spindle and attached chromosomes (spindle-chromosome complex, SCC) from one mature oocyte to another to select for a cytoplasm or mtDNA background [56]. Comparing to cytoplasmic transfer, the advantage of spindle transfer is the reduction in heteroplasmy risk, thus offering a better reproductive option to prevent mtDNA disease transmission in affected families [57]. This technology has been used to generate both cattle and mice after subsequent fertilization (Bai et al, 2006, Bao et al, 2003, Wakayama et al, 2004 and Wang et al, 2001), and has generated live monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after sperm injection [30]. Spindle transfer between human oocytes has also result in blastocyst development and embryonic stem cell derivation with very low levels of heteroplasmy [58].
What is the procedure?
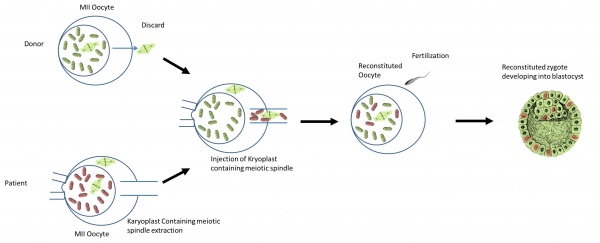 Diagram of spindle-chromosomal transfer [30] |
Assisted reproductive technologies are used to extract the patient’s egg from her ovaries. The cytoplasm of the egg contains the unhealthy mitochondria. Chromosomes, the nuclear DNA material, are found in the patient’s eggs are grouped together in a spindle-like formation.
|
Primate model
Due to the uncertainty of the health risks related to spindle-chromosome transfer, experiments in non-human primates are required to asses the safety of this procedure. Tachibana et al(2009) carried out maternal spindle transfer using healthy eggs from non-human primates (rhesus macaques)[10].
Some of the resulting embryos were successful and produced healthy offspring with low mtDNA carryover. However it is still too early to determine whether spindle-chromosome transfer is a safe procedure. Because defects may develop later in life, or in their offspring. Thus long-term studies are required to access the effects of this procedure, which includes life-long monitoring and multi-generational tracking. |
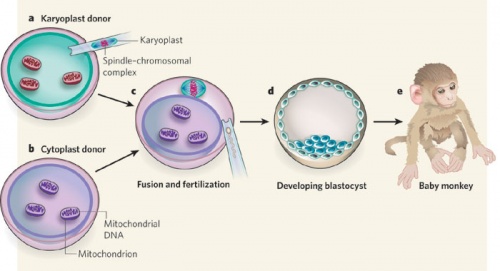 Primate model of spindle-chromosome transfer [10] |
Current Research
Currently, researchers at Newcastle University in the United Kingdom are collaborating with the Oregon researchers who successfully generated the first primate model in 2009. They are now testing the maternal spindle transfer technique on human oocytes. Fertilization rate in ST oocytes (73%) was similar to controls (75%); however, a significant portion of ST zygotes (52%) showed abnormal fertilization as determined by an irregular number of pronuclei. Among normally fertilized ST zygotes, blastocyst development (62%) and embryonic stem cell isolation (38%) rates were comparable to controls. All embryonic stem cell lines derived from ST zygotes had normal euploid karyotypes and contained exclusively donor mtDNA. Thus they concluded that the mtDNA can be efficiently replaced in human oocytes, although some ST oocytes displayed abnormal fertilization[59].
Limitations
Experiments showed minimal mutated mtDNA carryover in nonhuman primate offspring and human preimplantation embryos. However, the spindle is very sensitive to micromanipulation, which frequently induces premature activation of oocytes and results in karyotype abnormalities [60] [61].
Pronuclear transfer
Pronuclear Transfer is similar to Maternal Spindle Transfer but performed as a repair of embryo. it fertilizes the mother’s egg first and then transfers the nuclear DNA to the fertilised donor egg containing healthy mitochondria, from which the original nuclear DNA has been removed [30].
- pronuclear transfer procedures was first performed on mice in the 1990s, suggesting the possibility of preventing the transmission of mutated mitochondrial DNA [62].
- In 2003 scientists at Sun Yat-Sen University in China first attempted this procedure on human embryos. Five genetically modified embryos were implanted into a 30-year-old woman. She became pregnant with triplets, and doctor removed one to give the other two foetuses better chance of survival. After some months, the woman suffered miscarriages and lost both foetuses [63].
- In 2010 researchers at Newcastle University reported that pronuclear-transferred human embryos developed normally to the blastocyst stage in six to eight days, this marked the procedure as a success in preventing mitochondrial disease [15].
What is the procedure?
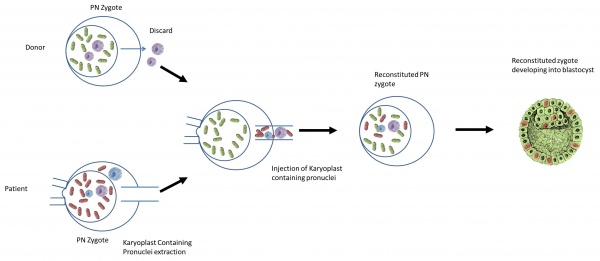
The nuclear genome from the pronuclear stage zygote of an affected woman is transferred to an enucleated donor zygote [63]
- It begins with creating an embryo using the parents’ sperm and eggs.
- At the same time, a second embryo is created using a donor egg with healthy mitochondria and the father’s (or donor) sperm.
- The pronuclei are removed from the single-cell stage embryo (day one). The leftover enucleated embryo with diseased mitochondria is discarded.
- The pronuclei of the second embryo are removed and discarded.
- The parents’ pronuclei can be placed into the second embryo for development.
- The developed embryo will then be transferred into the mother.
Human Embryo Model
Research Group in New Castle University performed pronuclear transfer on human mebryo model[15]:
- Pronuclear transfer was performed using abnormally fertilised human zygotes generated following in vitro fertilisation (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
- Abnormal zygotes were identified on day 1 of development by the presence of one pronucleus (unipronucleate) or three pronuclei (tripronucleate) 18-19 hours after insemination.
- Karyoplasts containing pronuclei and surrounding cytoplasm were removed from the donor zygote using a biopsy pipette and transferred to a recipient zygote.
- Following fusion, the reconstituted zygotes were either cultured for 6-8 days to monitor development to the blastocyst stage or were cultured before being disaggregated for analysis of mtDNA in individual blastomeres'.
The safety effects of this procedure (zygote mtDNA carry-over) were tested by sequencing of non-coding control region. The sequence of donor and recipient mtDNA were then compared. Based on the data provided, they believe pronuclear transfer has the potential to prevent the transmission of mtDNA disease in humans. However, Further studies are required to ensure the safety of different techniques when modifying human oocytes and zygotes due to the potential of causing chromosomal or epigenetic abnormalities
<html5media width="560" height="315">https://www.youtube.com/embed/Sr7Jnr9qn44</html5media>
Healing broken batteries: The Wellcome Trust Centre for Mitochondrial Research [64]
Limitations
Pronuclear transfer (PNT) between zygotes can correct mtDNA-related phenotypes in mice model. However, it is reported that PNT-generated mice possessed 6%–21% heteroplasmic mtDNA at the weaned stage, and the average increase was 12% to possess 5%–44% heteroplasmic mtDNA at Day 300 after birth [65] . Human embryo model study showed that PNT between zygotes resulted in minor donor mtDNA carryover (<2.0%) in early embryos [15]. However, one disadvantage of PNT is that the manipulation, which requires both donor and recipient fertilized eggs, discards half of the embryos.
Polar Body Transfer
Polar bodies are small cells formed during the meiotic reductive division of the oocyte. They contain complementary chromosomes (to the mature oocyte) and small amount of cytoplasmic segregation[66].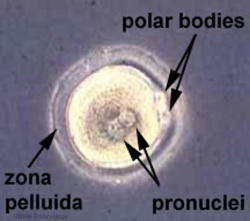
- Polar body 1 is formed and released during ovulation. It contains a diploid set of chromosomes.
- Polar body 2 is formed during fertilization and can be identified in the zygote. It contains a haploid set of chromosomes.
- Both polar bodies are unable to be fertilized and disintegrate eventually.
Due the unique feature of polar bodies, which can provide beneficial information about the genetic background of the oocyte without potentially destroying it, polar body biopsies have been applied in preimplantation genetic diagnosis to detect inheritable chromosomal or genetic abnormalities. More recently the role of polar bodies in assisted reproductive technology are: single-cell sequencing of the polar body genome to deduce the genomic information of its sibling oocyte and polar body transfer to prevent the transmission of mtDNA-associated diseases [68].
The advantages of polar body transfer have been reported as[68]:
- Polar body 1 and 2 contain minimum mitochondria but carries the entire genome.
- Polar body 1 and 2 are separate from the oocyte, thus can be easily manipulated without damage to the chromosome.
- each donor will have three offers (polar body 1, body 2, maternal pronucleus), which significant increase the efficiency of using donor egg.
What is the procedure?
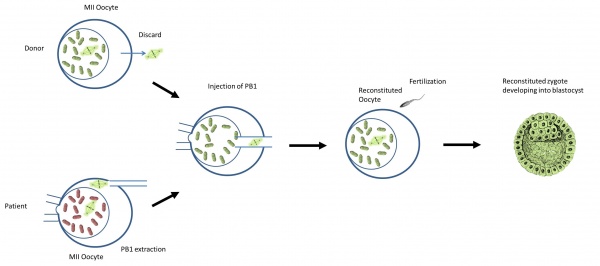 Diagram of Polar body 1 transfer [68] |
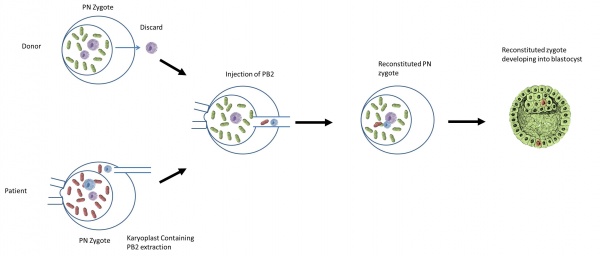 Diagram of Polar body 2 transfer [68] |
Mice Model
Polar body transfer has been adopted in mice models to prevent the transmission of mtDNA variants. They also compare the effects of different types of germline genome transfer, including spindle-chromosome transfer, pronuclear transfer, and first and second polar body transfer, in mice. Their pre-clinical model indicate that polar body transfer has better potential in preventing the inheritance of mitochondrial diseases[69]. The other group coupled Polar body transfer with Pronuclei transfer or Spindle-choromosome transfer on a mice model which increased the yield of reconstructed embryos with low mtDNA carryover. [30]
Other Approaches
Germinal Vesicle Nuclear Transfer
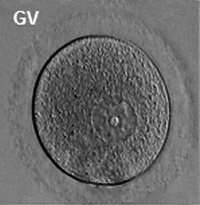
The germinal vesicle (GV) is the large nucleus of an immature oocytes arrested naturally in the first meiotic prophase. The oocyte undergoes GVBD soon after MPF activation, and its material (or nucleoplasm) mixes with the cytoplasm (or ooplasm) of maturing oocytes. The germinal vesicle contains a number of proteins, such as histones and DNA polymerases, that are used immediately after fertilization [71][72].
Germinal Vesicle Transfer (GVT) is the transfer of a GV from an unfertilised into an enucleated recipient oocyte. Following reconstruction, the GV is allowed to develop to Metaphase II through in vitro maturation (IVM) and is then fertilised through either IVF or ICSI. The resultant zygotes are then allowed to develop in culture before transfer to patients [73]. These procedures have been proposed as potential treatments for those women whose oocytes fail to fertilise, arrest during development or are associated with aneuploidy. Studies in humans have shown that GVT from aged oocytes introduced into the enucleated ooplasm of young oocytes or sibling oocytes can overcome oocyte aneuploidy, and produced the majority of reconstructions with normal karyotypes[74] [75].
Similar to the other techniques,A major concern of GVT is still that the transferred GV is still surrounded by a population of tightly packed mitochondria which will also be introduced into the donor ooplasm. These mitochondria remain close to center of the immature reconstruction and disperse throughout the cytoplasm as maturation progresses[73].
Ethics
Some people believe that the Mitochondrial Gene Transfer techniques are ethical. The Nuffield Council on Bioethics in the UK examined the ethical issues and wrote in a report that “Due to the health and social benefits to individuals and families of living free from mitochondrial disorders, … we believe that if these novel techniques are adequately proven to be acceptably safe and effective as treatments, it would be ethical for families to use them, if they wish to do so and have been offered an appropriate level of information and support.”. [76]
Others hold an opposite opinion. They doubt the safety of Mitochondrial Gene Transfer techniques and believe that other safe means of reproduction already exist can be used instead. They argue that unlike the use of donor eggs or embryos, children born with Mitochondrial Gene Transfer techniques would have a genetic connection to three parents due to the fact that such therapies involve modification of the germline. Some mothers may feel that it is important to have a genetic link with their future child and that having this genetic link outweighs most disadvantages (e.g. health risks and high financial cost) associated with Mitochondrial Gene Transfer techniques. Thus for these intending mothers, using egg or embryo donation is not a suitable alternative. From the childrens point of view, there are also two concerns. First, children may have a troubled relationship with their parents or struggle to develop their identity they are aware that they share a mitochondrial genome with a donor. Second, Mitochondrial Gene Transfer conceived children may be exposed to some risks to their physical well-being such as the failure of donor’s mtDNA to function properly with the nuclear genes contributed by the intending parents. [77]
Legal Status
Permitted
Britain is the only country that legally allows the inheritable genetic modification of humans. On February 24 2015, the House of Lords approved regulations. Earlier in the month, the UK House of Commons also approved the techniques that would allow the creation of an embryo with genetic material from three different people and result in inheritable genetic modification. It was passed with 382 votes in favor and 128 against. [78]
Under Discussion
In USA the legality of mitochondrial manipulation techniques is still under discussion. On February 25 and 26, 2014, public meetings that included discussion of mitochondrial manipulation techniques were held by The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). None of the seven members of the public who had contacted the FDA in advance spoke in favor of the techniques. There was no formal decision made on the efficacy of Cytoplasmic transfer, but agreements were made on further practice on animal models to provide scientific data. On January 27 2015, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) held the first in a series of meetings to fulfill the FDA’s request to consider the Ethical and Social Policy of Novel Techniques for Prevention of Maternal Transmission of Mitochondrial DNA Diseases.
Prohibited
- These countries have the same law "Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine" due to their ratification of the Council of Europe's Convention
Further Reading
useful publications:
The ethics of creating children with three genetic parents. [79] PMID 23608245
Three-Parent IVF: Gene Replacement for the Prevention of Inherited Mitochondrial Diseases.[29] PMID 24382342
Mitochondrial function in the human oocyte and embryo and their role in developmental competence.[80] PMID 20933103
Mitochondrial reshaping accompanies neural differentiation in the developing spinal cord.[81] PMID 26020522
The impact of mitochondrial function/dysfunction on IVF and new treatment possibilities for infertility.[82] PMID 25421171
Risks inherent to mitochondrial replacement.[83] PMID 25807984
Glossary
Cortical necrosis Break down of the kidney tisssue.
Hetroplasmy When a cell line contains two dissimilar mitochondrial DNA elements
Homoplasmy When a cell line contains only one mitochondrial DNA
Maternal Spindle Transfer: The transfer of nuclear DNA from a patient egg into a donor egg with its nuclear DNA removed, which is then fertilized and implanted via standard IVF.
Myopathy A disease of the muscle tissue
Ooplasmic Transfer: The injection of ooplasm from a donor egg into a patient egg. Leads to mitochondrial heteroplasmy.
Pigmentary retinopathy Migration and proliferation of the retinal pigment cell into the retina. Produces blindness.
Pronuclear Transfer: The pre-fertilized nuclear DNA form a patient is transferred into a donor egg with its nuclear DNA removed, which is then fertilized and implanted via standard IVF.
References
- ↑ GeoBeats News. (2013, December 19) Teenage Girl Has Three Biological Parents. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/0Zs2KntZ7vU
- ↑ <pubmed> 7219534 </pubmed>
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 <pubmed> 6896904 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 3201231 </pubmed>
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 <pubmed> 2830540 </pubmed>
- ↑ Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act 1990 c.37, retrieved from http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1990/37/contents 23/10/15
- ↑ <pubmed> 9039911 </pubmed>
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 <pubmed> 9250192</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 9674999 </pubmed>
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 <pubmed> 19710649 </pubmed>
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 <pubmed> 16814712 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 19651984 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 17506638 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25629662 </pubmed>
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 <pubmed> 20393463 </pubmed>
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 <pubmed>1463006</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 18695671 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 22701816 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>20220442</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>25539952</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>18651330</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23385875</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>25038129</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26264513</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>12876264</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11730668</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>25691415</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26251896</pubmed>
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 <pubmed> 24382342</pubmed>
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.5 <pubmed> 25573721 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24373414</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25229667 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 23103869 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 15140871 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 3352746 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 10429238 </pubmed>
- ↑ J A.Barritt, S Willadsen Epigenetic and experimental modifications in early mammalian development: part II Cytoplasmic transfer in assisted reproduction Human Reproduction Update 2001 Vol.7, No.4 pp.428-435
- ↑ <pubmed> 23602680 </pubmed>
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 Charlotte Pritchard The girl with three biological parents1 September 2014 http://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-28986843 retrieved September 2015
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 J A.Barritt, S Willadsen Epigenetic and experimental modifications in early mammalian development: part II Cytoplasmic transfer in assisted reproduction Human Reproduction Update 2001 Vol.7, No.4 pp.428-435
- ↑ <pubmed> 9570273 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 9570273 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 10973657 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11228222 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11041526</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>10065803</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>10521114</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>20735895</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24135157</pubmed>
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 <pubmed>23271951</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23077218</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23271951</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>16939888</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26281784</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24709341</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>25444504</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23103867</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25973765 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 23103867</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25472922</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 23254936</pubmed>
- ↑ Mado Vandewoestyne , Jitesh Neupane , Björn Heindryckx , Sylvie Lierman ,Dieter Deforce and Petra De Sutter (2012) Pronuclear transfer in mice yields minimal mitochondrial DNA carry-over Mado Vandewoestyne FERTILITY AND STERILITY. 98(3, suppl.). p.S289-S289
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Three-Parent Baby Pioneer Jamie Grifo: The Brits Will be Ahead of the World 16 January 2015 http://www.geneticsandsociety.org/article.php?id=8314. Retrived 15 Oct 2015
- ↑ The Wellcome Trust Centre for Mitochondrial Research, A film by Barry J Gibb. (2012, September 15) Healing broken batteries: The Wellcome Trust Centre for Mitochondrial Research. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sr7Jnr9qn44
- ↑ <pubmed>16275929</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 24949971 </pubmed>
- ↑ Hill, M.A. (2015) Embryology Early zygote labelled.jpg. Retrieved October 16, 2015, from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Early_zygote_labelled.jpg
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 68.2 68.3 <pubmed> 25472922 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 24949971 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19924284</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 12193404 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 21234179 </pubmed>
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 Scientific and Clinical Advances Group 24 Nov 2005 Germinal vesicle transfer SCAG(11/05)04 retrieved from http://www.hfea.gov.uk/docs/SCAG_Germinal_vesicle_transfer_nov05.pdf at 16 Oct 2015
- ↑ <pubmed>25985993</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>25515532</pubmed>
- ↑ http://nuffieldbioethics.org/project/mitochondrial-dna-disorders/
- ↑ <pubmed>26239841</pubmed>
- ↑ Gallagher, James (03 February 2015) MPs say yes to three-person babies BBC News Retrieved 09 October 2015.
- ↑ <pubmed> 23608245</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 20933103 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 26020522 </pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25421171</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 25807984</pubmed>