2010 BGD Lecture - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 2
Introduction
--Mark Hill 20:54, 3 May 2010 (EST) I am currently updating the notes that will appear here for 2010. Previous 2008 Lecture
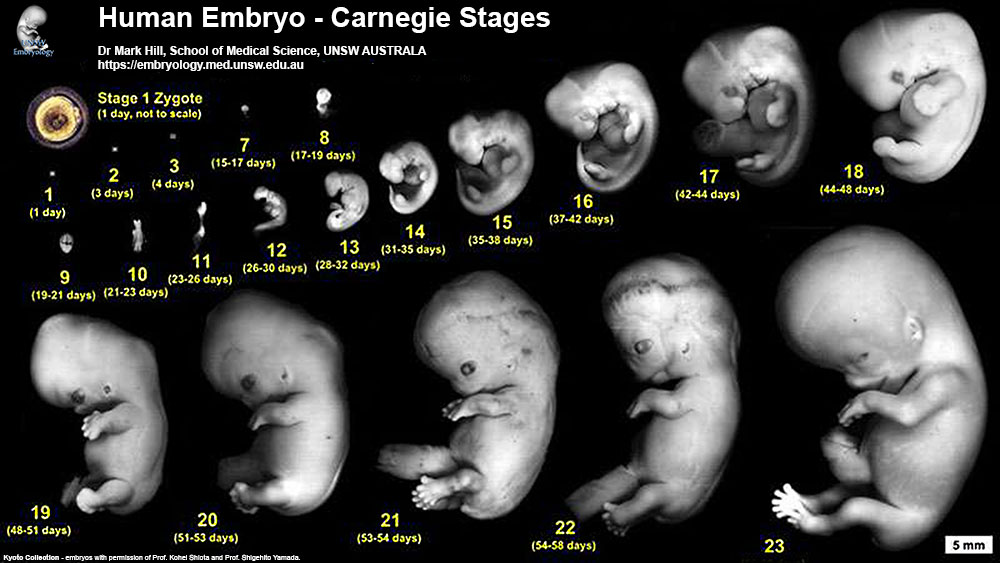
This lecture covers the period of Embryonic development, in Humans from week 3 to week 8 and is divided into 23 Carnegie stages of embryonic development. There will also be a brief introduction to fetal development.
This period of development will also be covered in your Practical, which is currently being updated for 2010 and will be available online. Note, the period from week 9 to week 38 is considered Fetal development and will be covered in detail in the Laboratory 11.
- Embryonic Development
- Organ and System formation (Functioning / Not Functional)
- Dynamic changes internal and external
- Carnegie stages illustrate external development
First 8 Weeks
Week 3
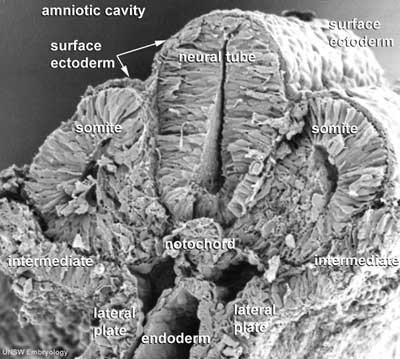
Mesoderm means the "middle layer" and it is from this layer that nearly all the bodies connective tissues are derived. In early mesoderm development a number of transient structures will form and then be lost as tissue structure is patterned and organised. Humans are vertebrates, with a "backbone", and the first mesoderm structure we will see form after the notochord will be somites.
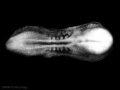
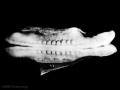
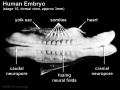
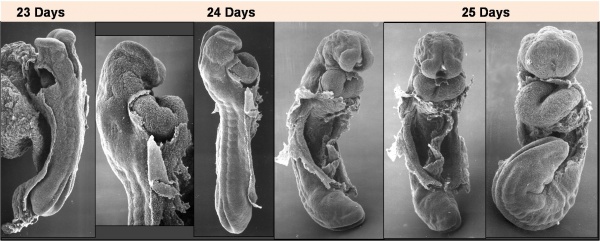
Facts: Week 4, 22 - 23 days, 2 - 3.5 mm, Somite Number 4 - 12
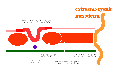
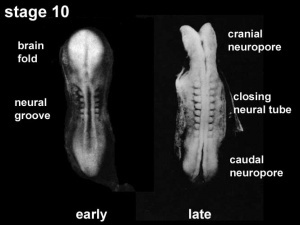
View: This is a dorsal view of the human embryo, the amniotic membrane has been removed. Top embryo is an early stage 10, bottom is late stage 10.
Mesoderm organization: lateral plate - intermediate mesoderm - paraxial mesoderm - axial mesoderm - paraxial mesoderm - intermediate mesoderm - lateral plate
Axial Mesoderm
- notochord
- mechanical role in embryonic disc folding
- molecular role in patterning surrounding tissues
Adult - contributes to the nucleus pulposis of the intervertebral disc
Paraxial Mesoderm
- differentiates rostro-caudally (head to tail)
- remains unsegmented in the head region.
- segments in the body region to form pairs of somites along the length of the embryo.
Adult - contributes vertebral column (vertebra and IVD), dermis of the skin, skeletal muscle of body and limbs
Intermediate Mesoderm
- named by position (between paraxial and lateral plate)
- differentiates rostro-caudally (head to tail)
- forms 3 sets of "kidneys" in sequence
- pronephros
- mesonephros
- metanephros
Adult - metanephros forms the kidney
Lateral Plate Mesoderm
- a "horseshoe shaped" space forms in the middle
- somatic mesoderm - closest to ectoderm
- space - forms the 3 body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal)
- splanchnic mesoderm - closest to endoderm
Adult - body connective tissues, gastrointestinal tract (connective tissues, muscle, organs), heart
Somite Development
Somite initially forms 2 main components
- ventromedial- sclerotome forms vertebral body and intervertebral disc
- dorsolateral - dermomyotome forms dermis and skeletal muscle
Sclerotome
- sclerotome later becomes subdivided
- rostral and caudal halves separated laterally by von Ebner's fissure
- half somites contribute to a single vertebral level body
- other half intervertebral disc
- therefore final vertebral segmentation “shifts”
Myotome
- Body - epaxial and hypaxial muscles
- Limbs - flexor and extensor muscles
Dermatome
- connective tissue underlying epidermis
- begins as a dorsal thickening
- spreads throughout the body
Week 4
Heart
- forms initially in splanchnic mesoderm of prechordal plate region - cardiogenic region
- growth and folding of the embryo moves heart ventrallly and downward into anatomical position
- week 3 begins as paired heart tubes that fuse to form single heart tube
- begins to beat in Humans- day 22-23
- heart tube connects to blood vessels forming in splanchnic and extraembryonic mesoderm
Week 2-3 pair of thin -walled tubes
Week 3 tubes fused, truncus arteriosus outflow, heart contracting
Week 4 heart tube continues to elongate, curving to form S shape
Week 5 Septation starts, atrial and ventricular
Septation continues, atrial septa remains open, foramen ovale
Neural
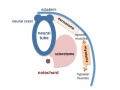
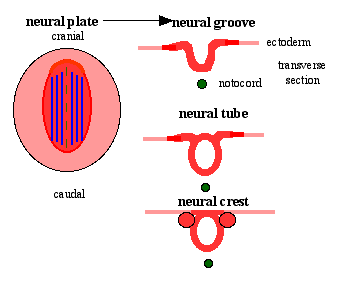
Neural Plate
- extends from buccopharyngeal membrane to primitive node
- forms above notochord and paraxial mesoderm
- neuroectodermal cells
- broad brain plate
- narrower spinal cord
- 3 components form: floor plate, neural plate, neural crest
Neural Groove
- forms in the midline of the neural plate (day 18-19)
- either side of which are the neural folds which continues to deepen until about week 4
- neural folds begins to fuse, beginning at 4th somite level
Neural Tube
- the neural tube forms the brain and spinal cord
- fusion of neural groove extends rostrally and caudally
- begins at the level of 4th somite
- closes neural groove "zips up" in some species.
- humans appear to close at multiple points along the tube.
- leaves 2 openings at either end - Neuropores
- cranial neuropore closes before caudal
Failure for the neural tube to close correctly or completely results in a neural tube defect.
Neural Crest
- population of cells at the edge of the neural plate that lie dorsally when the neural tube fuses
- dorsal to the neural tube, as a pair of streaks
- pluripotential, forms many different types of cells
- cells migrate throughout the embryo
Neural Crest Derivatives: dorsal root ganglia, autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla, drg sheath cells, glia, pia-arachnoid sheath, skin melanocytes, connective tissue of cardiac outflow, thyroid parafollicular cells, craniofacial skeleton, teeth odontoblasts
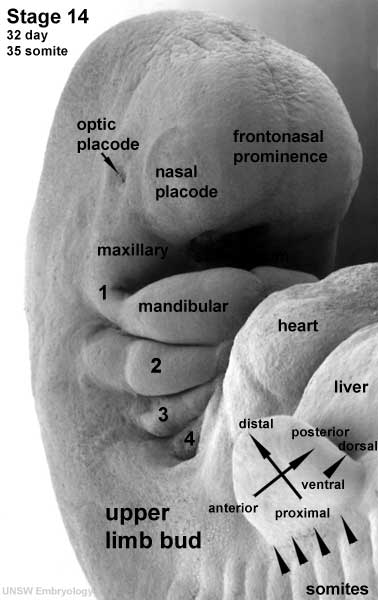
Head
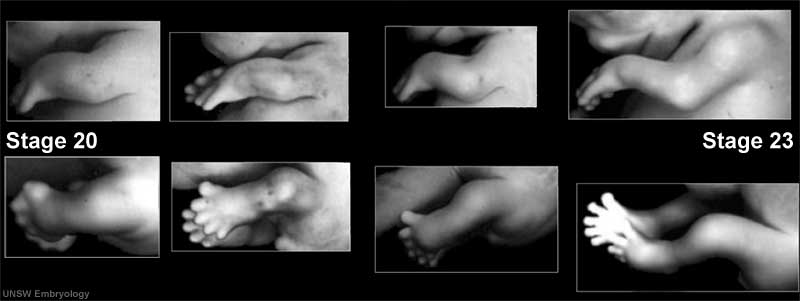
Upper and Lower Limb
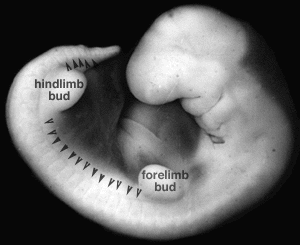
Limb development occurs at different times for forelimbs and hindlimbs. In the mid-4th week, human upper limb buds first form and lower limbs about 2 days later. The limbs form at vertebra segmental levels C5-C8 (upper limbs) L3-L5 (lower limbs).
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
- 2010 BGD: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 17) Embryology 2010 BGD Lecture - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 2. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_BGD_Lecture_-_Development_of_the_Embryo/Fetus_2
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G