2009 Lecture 17
Sensory Development - Hearing
Introduction
We use the sense of balance and hearing to position ourselves in space, sense our surrounding environment, and to communicate. Portions of the ear appear very early in development as specialized region (otic placode) on the embryo surface that sinks into the mesenchyme to form a vesicle (otic vesicle = otocyst) that form the inner ear.
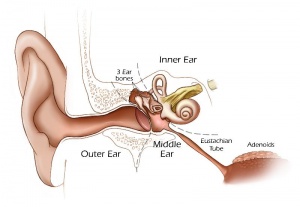
This region connects centrally to the nervous system and peripherally through specialized bones to the external ear (auricle). This organisation develops different sources forming the 3 ear parts: inner ear (otic placode, otocyst), middle ear (1st pharyngeal pouch and 1st and 2nd arch mesenchyme), and outer ear (1st pharyngeal cleft and 6 surface hillocks).
This complex origin, organisation, and timecourse means that abnormal development of any one system can impact upon the development of hearing.
Textbooks
- Human Embryology (2nd ed.) Larson Chapter 12: p375-409
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 19: p491-511
Objectives
- Understanding of structures and functions of the auditory pathway
- Understanding of inner, middle and external ear origins
- Understanding of timecourse of auditory development
- Understanding of abnormalities of auditory development
- Brief understanding of central auditory pathway and molecular development
Development Timing
- Week 3 - otic placode, otic vesicle
- Week 5 - cochlear part of otic vesicle elongates (humans 2.5 turns)
- Week 9 - Mesenchyme surrounding membranous labryinth (otic capsule) chondrifies
- Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labryinth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph
- Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
- 3rd Trimester - Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle response in fetus.
3 Sources:
- Inner ear - epidermal otic placode at level of hindbrain.
- Middle ear - cavity: 1st pharyngeal pouch, ossicles: mesenchyme 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches.
- Outer ear - external auditory meatus: 1st pharyngeal cleft, auricle: 6 hillocks 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches.
Inner Ear
- The inner ear is derived from a pair of surface sensory placodes (otic placodes) in the head region.
- These placodes fold inwards forming a depression, then pinch off entirely from the surface forming a fluid-filled sac or vesicle (otic vesicle, otocyst).
- The vesicle sinks into the head mesenchyme some of which closely surrounds the otocyst forming the otic capsule.
- The otocyst finally lies close to the early developing hindbrain (rhombencephalon) and the developing vestibulo-cochlear-facial ganglion complex.
Middle Ear
- The middle ear ossicles (bones) are derived from 1st and 2nd arch mesenchyme.
- The space in which these bones sit is derived from the 1st pharyngeal pouch.
References
Textbooks
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 20: p460-479
- Essentials of Human Embryology, Larson Chapter 12: p252-272
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology (6th ed.) Gilbert Chapter14 Intermediate Mesoderm
Search
- Bookshelf hearing development
- Pubmed hearing development
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 18) Embryology 2009 Lecture 17. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_17
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G