2009 Lecture 16: Difference between revisions
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
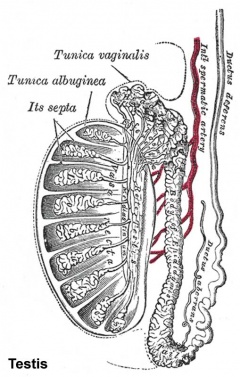
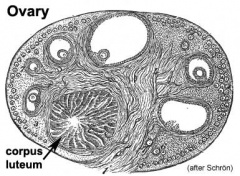
[[File:Historic-testis.jpg|240px]] [[File:Historic-ovary.jpg|240px]] | [[File:Historic-testis.jpg|240px]] [[File:Historic-ovary.jpg|240px]] | ||
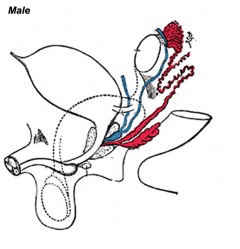
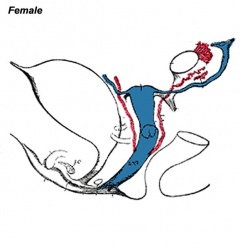
This section of notes covers genital development. Differences in development are dependent on a protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. Mesonephric duct (Wolffian Duct) and paramesonephric (Mullerian Duct) contribute the majority of male and female internal genital tract respectively. | This section of notes covers genital development. Differences in development are dependent on a protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. Mesonephric duct (Wolffian Duct) and paramesonephric (Mullerian Duct) contribute the majority of male and female internal genital tract respectively. | ||
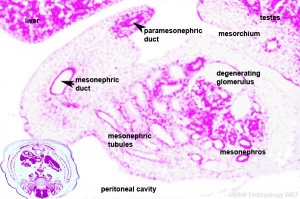
[[File:Stage22 mesonephros.jpg|thumb|Stage 22 mesonephros]] | [[File:Stage22 mesonephros.jpg|thumb|Stage 22 mesonephros]] | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 21 September 2009
Genital Development
Introduction
This section of notes covers genital development. Differences in development are dependent on a protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. Mesonephric duct (Wolffian Duct) and paramesonephric (Mullerian Duct) contribute the majority of male and female internal genital tract respectively.
Objectives
- Understand the role of the Y chromosome in sex determination.
- Understand the differences in male/female duct develpoment (mesonephric/paramesonephric).
- Compare the development of the cloaca in the male and female.
- Understand the developmental abnormalities in male and female development.
Textbooks
- Human Embryology (2nd ed.) Larson Ch10 p261-306
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 13 p303-346
Three Stages
The mesonephric/paramesonephric duct changes are one of the first male/female differences that occur in development, while external genitaila remain indeterminate in appearance for quite a while.
- Differentiation of gonad (Sex determination)
- Differentiation of internal genital organs
- Differentiation of external genital organs
The 2nd and 3rd stages dependent on endocrine gonad. Reproductive development has a long maturation timecourse, begining in the embryo and finishing in puberty. (More? Puberty)
Development Overview
Sex Determination
- Humans (week 5-6)
- Germ cells migrate into gonadal ridge
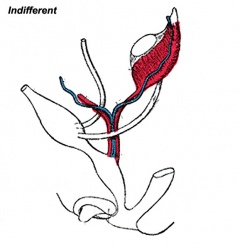
- Gonads (male/female) identical at this stage, indifferent
Gonad development
- dependent on sex chromosome
- Y testes
- No Y ovary
SRY
- SRY protein (Testes determining factor, TDF) binds DNA
- Transcription factor, Bends DNA 70-80 degrees
Internal Genital Organs
- All embryos form paired
- Mesonephric duct, see kidney development
- Paramesonephric duct, Humans 7th week Invagination of coelomic epithelium Cord grows and terminates on urogenital sinus
- Male Gonad (testes) secretes Mullerian duct inhibitory factor (MDIF) which causes regression of paramesonephric duct
- Male Gonad (testes) secretes Testosterone which retains mesonephric duct
External Genital Organs
- All embryos initially same (indifferent)
- Testosterone differentiates male
References
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 14 p289-326
- Essentials of Human Embryology, Larson Ch10 p173-205
- Human Embryology, Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Ch21-22 p134-152
- Developmental Biology (6th ed.) Gilbert Ch14 Intermediate Mesoderm
Online Links
- UNSW Embryology Abnormalities | Y chromosome | X chromosome | Ovary | Stage 13/14 Embryo | Stage 22 Embryo | Stage 22 Highpower
- UNSW Embryology Movies: Urogenital Movies
- Embryo Images Unit: Embryo Images Online | Urongenital Development | Internal Genitalia | Definitive Kidney | External Genitalia
- Histology: Male Reproductive System | Female Reproductive System
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 2) Embryology 2009 Lecture 16. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_16
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G