File:Epigenetics cartoon.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:16688142}} | |||
====Copyright==== | ====Copyright==== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:31, 2 September 2018
Epigenetic Mechanisms
Epigenetics are inheritance mechanisms that lie outside the DNA sequence of our genes.
- DNA methylation - usually associated with 5-methylcytosine (m5C), leads to transcriptional silencing in vertebrates.
- Modification of nucleosomal histones.
Reference
Qiu J. (2006). Epigenetics: unfinished symphony. Nature , 441, 143-5. PMID: 16688142 DOI.
Copyright
Image: Nature 441, 143-145 (11 May 2006), with permission.
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v441/n7090/full/441143a.html
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Epigenetics cartoon.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Epigenetics_cartoon.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:52, 29 June 2010 | 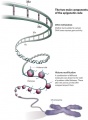 | 500 × 684 (53 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Epigenetic Mechanisms Epigenetics are as the name implies, inheritance mechanisms that lie outside the DNA sequence of our genes. One of the initial discoveries was the effects of DNA methylation upon gene expression and then modifications of nucleosomal |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 6 pages use this file: