File:Hyaline cartilage 03.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Trachea Hyaline Cartilage== {{Cartilage Histology}} {{Blue Histology}}) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Trachea Hyaline Cartilage== | ==Respiratory Trachea - Layers== | ||
'''Mucosa''' - formed by epithelium and underlying lamina propria. | |||
* respiratory epithelium - (pseudostratified columnar and ciliated) ciliated cells, goblet cells, brush cells, endocrine cells, surfactant-producing cells (Clara cells), serous cells, basal cells, basement membrane. | |||
* lamina propria - loose connective tissue, many elastic fibres | |||
* elastic lamina - forming the border between the mucosa and submucosa is not visible in H&E stained slides. | |||
'''Submucosa''' - connective tissue and submucosal glands | |||
* submucosal gland - serous (dark) and mucous (light) parts have different staining appearance. | |||
==Tracheal Cartilage== | |||
* tracheal cartilage - hyaline cartilage, 16 to 20 C-shaped cartilages. | |||
* perichondrium - surface of cartilage. | |||
* trachealis muscle - (smooth muscle) Not visible in this section, together with connective tissue fibres, join ends of the cartilages together. | |||
===Hyaline Cartilage Development=== | |||
* forms from mesenchymal cells. | |||
* precursor cells become rounded and form densely packed cellular masses, chondrification centres. | |||
* chondroblasts - (cartilage-forming cells) begin secreting the extracellular matrix components of cartilage. | |||
** extracellular matrix - ground substance (hyaluronan, chondroitin sulfates and keratan sulfate) and tropocollagen (polymerises into fine collagen fibres, not visible). | |||
===Growth=== | |||
* '''appositional growth''' - mesenchymal cells surrounding the cartilage in the deep part of the perichondrium (or the chondrogenic layer) differentiate into chondroblasts. Appositional growth occurs also in mature cartilage. | |||
* '''Interstitial growth''' - small groups of chondroblasts (isogenous groups) in existing cartilage, can divide and become separated from each other by a thin partition of matrix. Interstitial growth occurs mainly in immature cartilage. | |||
{{Trachea histology links}} | |||
{{Respiratory Histology}} | |||
{{Cartilage Histology}} | {{Cartilage Histology}} | ||
| Line 5: | Line 37: | ||
{{Blue Histology}} | {{Blue Histology}} | ||
[[Category:Respiratory]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 10 March 2013
Respiratory Trachea - Layers
Mucosa - formed by epithelium and underlying lamina propria.
- respiratory epithelium - (pseudostratified columnar and ciliated) ciliated cells, goblet cells, brush cells, endocrine cells, surfactant-producing cells (Clara cells), serous cells, basal cells, basement membrane.
- lamina propria - loose connective tissue, many elastic fibres
- elastic lamina - forming the border between the mucosa and submucosa is not visible in H&E stained slides.
Submucosa - connective tissue and submucosal glands
- submucosal gland - serous (dark) and mucous (light) parts have different staining appearance.
Tracheal Cartilage
- tracheal cartilage - hyaline cartilage, 16 to 20 C-shaped cartilages.
- perichondrium - surface of cartilage.
- trachealis muscle - (smooth muscle) Not visible in this section, together with connective tissue fibres, join ends of the cartilages together.
Hyaline Cartilage Development
- forms from mesenchymal cells.
- precursor cells become rounded and form densely packed cellular masses, chondrification centres.
- chondroblasts - (cartilage-forming cells) begin secreting the extracellular matrix components of cartilage.
- extracellular matrix - ground substance (hyaluronan, chondroitin sulfates and keratan sulfate) and tropocollagen (polymerises into fine collagen fibres, not visible).
Growth
- appositional growth - mesenchymal cells surrounding the cartilage in the deep part of the perichondrium (or the chondrogenic layer) differentiate into chondroblasts. Appositional growth occurs also in mature cartilage.
- Interstitial growth - small groups of chondroblasts (isogenous groups) in existing cartilage, can divide and become separated from each other by a thin partition of matrix. Interstitial growth occurs mainly in immature cartilage.
- Trachea Histology Links: Overview HE | Overview VG | Detail 1 HE Detail 2 HE | Respiratory Histology | Histology Stains | Histology
- Respiratory Histology: Bronchiole | Alveolar Duct | Alveoli | EM Alveoli septum | Alveoli Elastin | Trachea 1 | Trachea 2 | labeled lung | unlabeled lung | Respiratory Bronchiole | Lung Reticular Fibres | Nasal Inferior Concha | Nasal Respiratory Epithelium | Olfactory Region overview | Olfactory Region Epithelium | Histology Stains
- Cartilage Histology: Developing | Hyaline HE | Hyaline VG | Hyaline HE | Hyaline VG | Elastic 1 | Elastic 2 | Fibrous - articular disc | Fibrous - intervertebral disc | Articular 1 | Articular 2
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 9) Embryology Hyaline cartilage 03.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Hyaline_cartilage_03.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 23:23, 18 February 2013 | 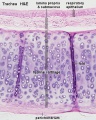 | 500 × 626 (92 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Trachea Hyaline Cartilage== {{Cartilage Histology}} {{Blue Histology}} |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 10 pages use this file:
- ANAT2241 Connective Tissue Components
- ANAT2241 Connective Tissue Types
- ANAT2241 Respiratory System
- ANAT2511 Respiratory System
- Draft 2016
- Lecture - Respiratory Development
- Respiratory System - Histology
- SH Lecture - Respiratory System Development
- SH Practical - Respiratory
- Talk:ANAT2241 Connective Tissue Types