File:Thyroid uptake scans .jpg: Difference between revisions
(Thyroid Uptake Scans (Technetium 99) (A) Normal (B) Graves disease: diffuse increased uptake in both thyroid lobes. (C) Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG): “hot” and “cold” areas of uneven uptake. (D) Toxic adenoma: increased uptake in a singl) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Thyroid Uptake Scans | ==Thyroid Uptake Scans== | ||
(Technetium 99) | (Technetium 99) | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Graves' disease in mothers can cause thyrotoxic fetus - may have increased fetal motility and develop a range of abnormalities including: goitre, tachycardia, heart failure associated hydrops, growth retardation, craniosynostosis and accelerated bone maturation. | Graves' disease in mothers can cause thyrotoxic fetus - may have increased fetal motility and develop a range of abnormalities including: goitre, tachycardia, heart failure associated hydrops, growth retardation, craniosynostosis and accelerated bone maturation. | ||
===Reference=== | |||
<pubmed>16363909</pubmed> | |||
Image: Perros P. Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy. PLoS Med. 2005 Dec;2(12):e370. | Image: Perros P. Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy. PLoS Med. 2005 Dec;2(12):e370. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 27: | ||
http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/images/endo/10.1371_journal.pmed.0020370.g002-M.jpg | http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/images/endo/10.1371_journal.pmed.0020370.g002-M.jpg | ||
[[Category:Thyroid]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:57, 31 March 2012
Thyroid Uptake Scans
(Technetium 99)
(A) Normal
(B) Graves disease: diffuse increased uptake in both thyroid lobes.
(C) Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG): “hot” and “cold” areas of uneven uptake.
(D) Toxic adenoma: increased uptake in a single nodule with suppression of the surrounding thyroid.
(E) Thyroiditis: decreased or absent uptake.
Maternal Graves Disease - "The dose of anti-thyroid drug usually needs to be decreased during pregnancy, and often Graves disease remits completely and the medication can be withdrawn. This is probably due to the overall immunosuppressive effect of pregnancy."
Graves' disease in mothers can cause thyrotoxic fetus - may have increased fetal motility and develop a range of abnormalities including: goitre, tachycardia, heart failure associated hydrops, growth retardation, craniosynostosis and accelerated bone maturation.
Reference
<pubmed>16363909</pubmed>
Image: Perros P. Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy. PLoS Med. 2005 Dec;2(12):e370. 10.1371_journal.pmed.0020370.g002-M.jpg
http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/images/endo/10.1371_journal.pmed.0020370.g002-M.jpg
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 06:52, 6 October 2009 | 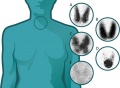 | 600 × 441 (34 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Thyroid Uptake Scans (Technetium 99) (A) Normal (B) Graves disease: diffuse increased uptake in both thyroid lobes. (C) Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG): “hot” and “cold” areas of uneven uptake. (D) Toxic adenoma: increased uptake in a singl |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 6 pages use this file: