File:Schwann and axon interactions.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. Analysis of the Necl proteins pr) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== | ==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== | ||
* Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. | |||
* Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. | |||
Analysis of the Necl proteins provides important new insight into molecular complexes along the internode (Maurel et al., 2007; Spiegel et al., 2007), which had not been as well defined as for the other domains. | |||
The polarity protein Par-3 colocalizes with Necl-4 in the adaxonal region of the Schwann cell (Chan et al., 2006), and it is possible that these proteins interact via PDZ and PDZ-binding motifs (red). The Necl proteins can also interact with FERM domain proteins via the FERM-binding domain (blue). Necls are also present at the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (inset). Necl-2 is not depicted but localizes to the axon–Schwann cell interface and to the incisures. | |||
==Reference== | ===Reference=== | ||
<pubmed>17724116</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2064536 PMC2064536] | [http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721.full?sid=c88c798d-80b9-4eed-916b-4907068a99d5 JCB] | <pubmed>17724116</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2064536 PMC2064536] | [http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721.full?sid=c88c798d-80b9-4eed-916b-4907068a99d5 JCB] | ||
====Copyright==== | |||
This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license, as described at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/). | |||
The figure was adapted from Voas et al. (2007). http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721/F1.large.jpg | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Glia]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Neural]] | [[Category:Glia]] [[Category:Cartoon]] [[Category:Neural]] | ||
[[Category:Schwann cell]] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:55, 9 June 2016
Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons
- Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode.
- Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode.
Analysis of the Necl proteins provides important new insight into molecular complexes along the internode (Maurel et al., 2007; Spiegel et al., 2007), which had not been as well defined as for the other domains.
The polarity protein Par-3 colocalizes with Necl-4 in the adaxonal region of the Schwann cell (Chan et al., 2006), and it is possible that these proteins interact via PDZ and PDZ-binding motifs (red). The Necl proteins can also interact with FERM domain proteins via the FERM-binding domain (blue). Necls are also present at the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (inset). Necl-2 is not depicted but localizes to the axon–Schwann cell interface and to the incisures.
Reference
<pubmed>17724116</pubmed>| PMC2064536 | JCB
Copyright
This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license, as described at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/).
The figure was adapted from Voas et al. (2007). http://jcb.rupress.org/content/178/5/721/F1.large.jpg
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Schwann and axon interactions.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Schwann_and_axon_interactions.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:41, 24 September 2010 | 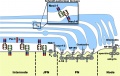 | 1,280 × 807 (196 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Model of interactions between myelinating Schwann cells and axons== Showing proteins that localize to the node, paranode, juxtaparanode, and internode. Schwann cell, blue; axon, yellow. PN, paranode; JPN, juxtaparanode. Analysis of the Necl proteins pr |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: