Endocrine - Pancreas Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(Created page with '==Introduction== thumb|Pancreas adult thumb|pancreas structure [[2009_Lecture_9|Lecture- Gastrointestinal Tract Developm…') |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
* Week 10 - glucagon (alpha) differentiate first, somatostatin (delta), insulin (beta) cells differentiate, insulin secretion begins | * Week 10 - glucagon (alpha) differentiate first, somatostatin (delta), insulin (beta) cells differentiate, insulin secretion begins | ||
* Week 15 - glucagon detectable in fetal plasma | * Week 15 - glucagon detectable in fetal plasma | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
===Reviews=== | |||
===Articles=== | |||
===Search PubMed=== | |||
Search April 2010 | |||
* Endocrine Development - All (14277) Review (4620) Free Full Text (3140) | |||
'''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=pancreas%20development pancreasl development] | |||
==Additional Images== | |||
===Adult Histology=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Terms== | |||
{{Template:Glossary}} | |||
{{Template:Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Endocrine]] [[Category:Pancreas]] | |||
Revision as of 13:06, 25 April 2010
Introduction
Lecture- Gastrointestinal Tract Development | UNSW Embryology - Pancreas Development see also GIT Notes- Pancreas
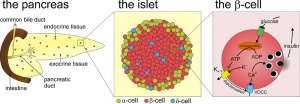
- Functions - exocrine (amylase, alpha-fetoprotein), 99% by volume; endocrine (pancreatic islets) 1% by volume
- Exocrine function - begins after birth
- Endocrine function - from 10 to 15 weeks onward hormone release
- exact roles of hormones in regulating fetal growth?
Pancreas Development
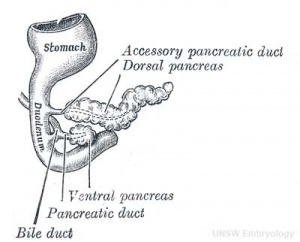
- Pancreatic buds - duodenal level endoderm, splanchnic mesoderm forms dorsal and ventral mesentery, dorsal bud (larger, first), ventral bud (smaller, later)
- Pancreas Endoderm - pancreas may be opposite of liver
- Heart cells promote/notochord prevents liver formation
- Notochord may promote pancreas formation
- Heart may block pancreas formation
- Duodenum growth/rotation - brings ventral and dorsal buds together, fusion of buds
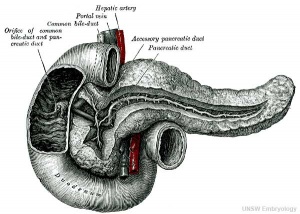
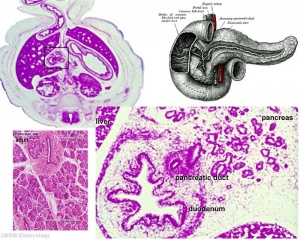
- Pancreatic duct - ventral bud duct and distal part of dorsal bud, exocrine function
- Islet cells - cords of endodermal cells form ducts, from which cells bud off to form islets
Pancreatic Islets
- Islets of Langerhans - 4 endocrine cell types
- Alpha - glucagon, mobilizes lipid
- Beta - insulin, increase glucose uptake
- Beta cells, stimulate fetal growth, continue to proliferate to postnatal, in infancy most abundant
- Delta - somatostatin, inhibits glucagon, insulin secretion
- F-cells - pancreatic polypeptide
Pancreas Timeline
- Week 7 to 20 - pancreatic hormones secretion increases, small amount maternal insulin
- Week 10 - glucagon (alpha) differentiate first, somatostatin (delta), insulin (beta) cells differentiate, insulin secretion begins
- Week 15 - glucagon detectable in fetal plasma
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search April 2010
- Endocrine Development - All (14277) Review (4620) Free Full Text (3140)
Search Pubmed: pancreasl development
Additional Images
Adult Histology
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 26) Embryology Endocrine - Pancreas Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Endocrine_-_Pancreas_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G